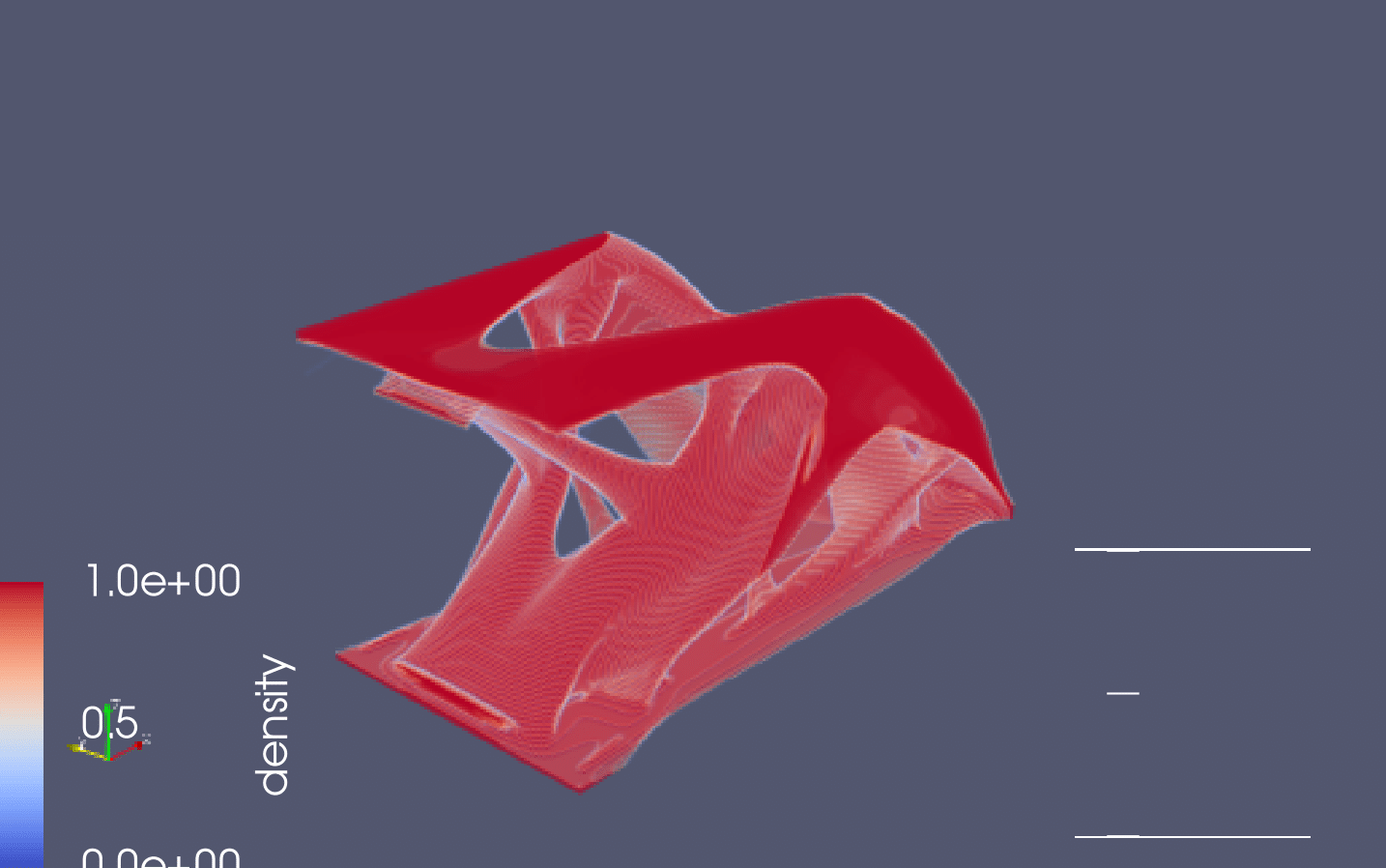
This repository contains an implementation of a topology optimisation solver for linear elastic compliance minimisation in three dimensions. The implementation is based on OpenMP target offloading to one GPU.
The result after 20 design iterations can be seen in the folloowing figure.
Even though OpenMP offloading to GPUs is supported by a wide range of compilers such as LLVM/Clang, ROCm, ICPC, NVC, and GCC, the compilers do not support the same subset of the OpenMP specification. We used NVIDIA's NVC compiler from the NVIDIA HPC SDK. The OpenMP directives may need to be adjusted if you choose to use another compiler.
We used the following versions of the cholmod library and the nvc compiler.
| Pachage | Version | Installation |
|---|---|---|
SuiteSparse/CHOLMOD |
5.1.2 | See Github release notes |
nvhpc |
22.5 | NVIDIA HPC SDK |
CUDA |
11.1 | CUDA Toolkit 11.1.0 |
To load the dependencies, you may adjust the module names in setup_gbar_env.sh. To load the modules and update LD_LIBRARY_PATH, run the following command.
$ source setup_gbar_env.shAfter loading the modules and updating the dynamic link loader path, you may simply compile the project with
$ makeNote that the project has been tuned for an NVIDIA Tesla A100 GPU which has compute capability -gpu=cc80. For an NVIDIA Tesla V100, the compute capability must be adjusted to -gpu=cc70.
To run 20 iterations of the code on a grid of 128 times 64 times 64 voxels and save the result you may use the following commands:
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=12
$ export OMP_TARGET_OFFLOAD=MANDATORY
$ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
$ ./top3d -x 16 -y 8 -z 8 -l 4 -w 1In the above example, we specify that we wish to use four levels in the multi-grid preconditioner with -l 4. Therefore we must divide the domain size by 2^l-1 to find the size of the coarsest grid which the application takes as input.
The following table includes a list of all the available options.
| Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| -x | The number of elements in the x-dimension on the coarsest grid. | 12 |
| -y | The number of elements in the y-dimension on the coarsest grid. | 6 |
| -z | The number of elements in the z-dimension on the coarsest grid. | 6 |
| -f | Volume fraction | 0.20 |
| -r | Filter radius in elements | 1.5 |
| -i | Number of design iterations | 20 |
| -v | Verbose mode. Select 0 to disable. Set to 1 to enable. Set to 2 to get detailed information. | 0 |
| -l | Number of layers in multigrid. | 4 |
| -w | Write result to .vtu file by setting -w 1. |
0 |
This code has been developed by Erik Albert Träff and Anton Rydahl under the supervision of Niels Aage, Ole Signmund, and Sven Karlsson.