this repo provides code examples for various forecasting use-cases using Vertex Forecast (deep learning AutoML), BigQuery ML's ARIMA+ model, and Vertex Tabular Workflows (pipeline orchestration)
02-vf-sdk-example/- needs updated SDK version03-bqml-sdk-examples/- up-to-date04-pipeline-examples/- needs updated versions for SDK and pipeline components05-tabular-workflows/- current focus: consolidating examples; using BQ public dataset
see the
knowledge-sharefolder for discussion on select topics
(1) Create Vertex Workbench instance; clone repo
from an instance terminal window: git clone https://github.com/tottenjordan/vertex-forecas-repo.git
pip install -U google-cloud-storage --user
pip install kfp==1.8.19 --user
pip install google_cloud_pipeline_components==1.0.41 --user
pip install--U google-cloud-aiplatform==1.23.0 --user
pip install gcsfs==2023.1.0 --user- 02-vf-sdk-examples/ - Vertex Forecast via SDK
- 03-bqml-sdk-examples/ - BQML ARIMA+ and regression; submit SQL through BigQuery python client
- 04-pipeline-examples/ - (WIP) Orchestrate Vertex Forecast with Vertex Managed Pipelines
- 05-tabular-workflows/ - Train and eval Vertex Forecast models via Vertex AI Tabular Workflows (creates pipelines)
- Creates one “global” model for many time series
- Learns patterns across time series
Better model complex scenarios
- Cold start / new items
- Short product life cycles
- Burstiness, sparsity
- Unstructured data such as text descriptions
- Feature driven time series
Handle a large number of drivers across three distinct types of demand influencing factors:
- Features that are not time-dependent (e.g., rich metadata such as product attributes, location attributes, etc.)
- Factors only know up to prediction time (e.g., historical values for inventory, weather, etc.)
- Factors known in the future (e.g., planned promotions/events, holidays)
For more on this concept, see intuiton-behind-past-only-covariates in the knowledge-share folder
Model types
- Time series Dense Encoder (TiDE)
- Temporal Fusion Transformer (TFT)
- AutoML (L2L)
- Seq2Seq+
*Model architecture spotlight: TiDE
- A new (2023) Google Research model for time series forecasting using multi-layer perceptron architecture.
- Compared to state of art transformer models TiDE has a simpler architecture and same or better accuracy.
- main benefit == efficiency:
- Massive training throughput improvement: 10x to 30x (especially on longer horizons)
- Massive prediction throughput improvement: 3x to 10x
Find more details and the whitepaper in the research blog post: Recent advances in deep long-horizon forecasting
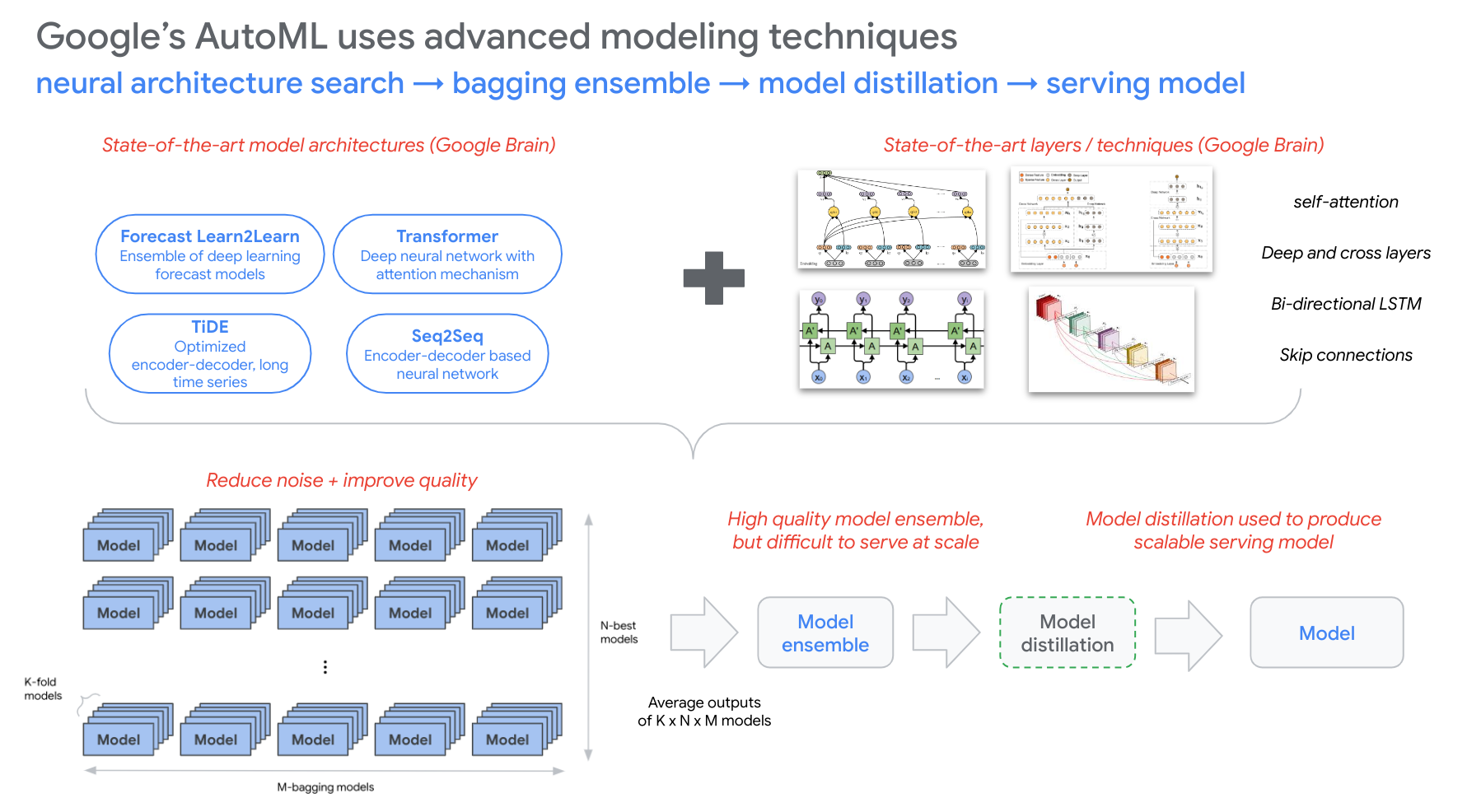
AutoML forecasting process
- Neural architecture search (NAS) begins with multiple model types
- With these model types and state-of-the-art layers/techniques (e.g.,
self-attention,Deep and cross layers,Bi-directional LSTM,Skip connections, etc.), VF builds several model architectures of various complexity to compete against each other - Candidate models are evaluated over multiple trials, where higher performing candidates are promoted to subsequent trials, and less performant candidates are retired
- The highest performing models are trained in a k-fold cross validation, ultimately so that a diverse set of models are produced for the ensembling
Optimization Objectives (docs)
| Objective | API | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | minimize-rmse |
Minimize root-mean-squared error (RMSE). Captures more extreme values accurately and is less biased when aggregating predictions.Default value. |
| MAE | minimize-mae |
Minimize mean-absolute error (MAE). Views extreme values as outliers with less impact on model. |
| RMSLE | minimize-rmsle |
Minimize root-mean-squared log error (RMSLE). Penalizes error on relative size rather than absolute value. Useful when both predicted and actual values can be large. |
| RMSPE | minimize-rmspe |
Minimize root-mean-squared percentage error (RMSPE). Captures a large range of values accurately. Similar to RMSE, but relative to target magnitude. Useful when the range of values is large. |
| WAPE | minimize-wape-mae |
Minimize the combination of weighted absolute percentage error (WAPE) and mean-absolute-error (MAE). Useful when the actual values are low. |
| QUANTILE | minimize-quantile-loss |
Minimize the scaled pinball loss of the defined quantiles to quantify uncertainty in estimates. Quantile predictions quantify the uncertainty of predictions. They measure the likelihood of a prediction being within a range. |