A Spell Checker for Code!
cspell is a command line tool and library for spell checking code.
- Spell Checks Code -- Able to spell check code by parsing it into words before checking against the dictionaries.
- Supports CamelCase, snake_case, and compoundwords naming styles.
- Self contained -- does not depend upon OS libraries like Hunspell or aspell. Nor does it depend upon online services.
- Fast -- checks 1000's of lines of code in seconds.
- Programming Language Specific Dictionaries -- Has dedicated support for:
- JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, PHP, C#, C++, LaTex, Go, HTML, CSS, etc.
- Customizable -- supports custom dictionaries and word lists.
- Continuous Integration Support -- Can easily be added as a linter to Travis-CI.
cspell was initially built as the spell checking service for the spell checker extension for Visual Studio Code.
npm install -g cspellExample: recursively spell check all javascript files in src
cspell "src/**/*.js"cspell --helpcspell check <filename>It will produce something like this:
To get color in less, use --color and less -r
cspell check <filename> --color | less -rcspell needs Node 8 and above.
The concept is simple, split camelCase and snake_case words before checking them against a list of known words.
camelCase->camel caseHTMLInput->html inputsrcCode->src codesnake_case_words->snake case wordscamel2snake->camel snake-- (the 2 is ignored)function parseJson(text: string)->function parse json text string
- Escape characters like
\n,\tare removed if the word does not match:\narrow->narrow- becausenarrowis a word\ncode->code- becausencodeis not a word.\network->network- but it might be hiding a spelling error, if\nwas an escape character.
- This spellchecker is case insensitive. It will not catch errors like
englishwhich should beEnglish. - The spellchecker uses dictionaries stored locally. It does not send anything outside your machine.
- The words in the dictionaries can and do contain errors.
- There are missing words.
- Only words longer than 3 characters are checked. "jsj" is ok, while "jsja" is not.
- All symbols and punctuation are ignored.
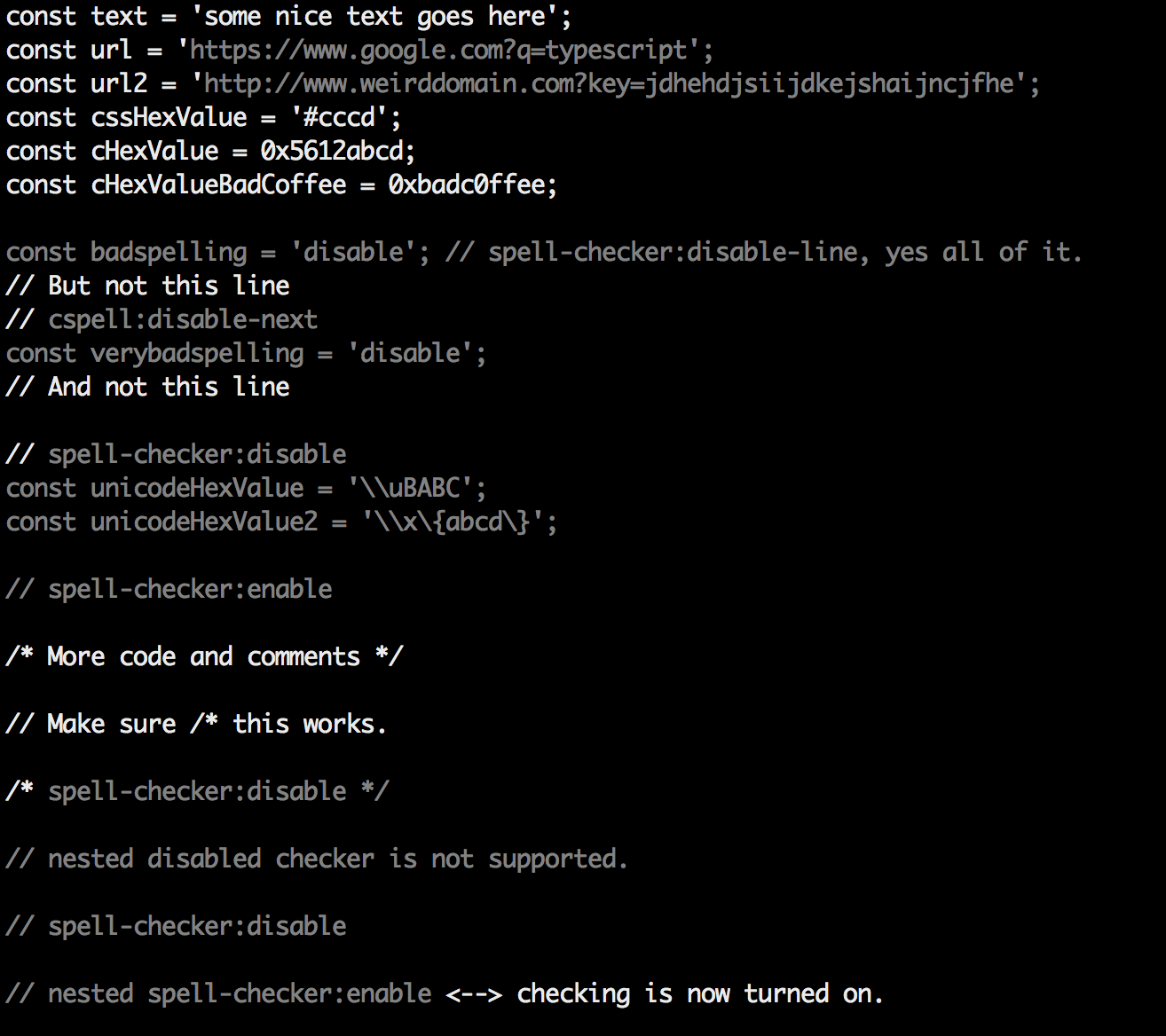
It is possible to add spell check settings into your source code. This is to help with file specific issues that may not be applicable to the entire project.
All settings are prefixed with cSpell: or spell-checker:.
disable-- turn off the spell checker for a section of code.enable-- turn the spell checker back on after it has been turned off.ignore-- specify a list of words to be ignored.words-- specify a list of words to be considered correct and will appear in the suggestions list.ignoreRegExp-- Any text matching the regular expression will NOT be checked for spelling.includeRegExp-- Only text matching the collection of includeRegExp will be checked.enableCompoundWords/disableCompoundWords-- Allow / disallow words like: "stringlength".
It is possible to disable / enable the spell checker by adding comments to your code.
/* cSpell:disable *//* spell-checker: disable *//* spellchecker: disable */// cspell:disable-line-- disables checking for the current line./* cspell:disable-next-line */-- disables checking till the end of the next line.
/* cSpell:enable *//* spell-checker: enable *//* spellchecker: enable */
// cSpell:disable
const wackyWord = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm'];
/* cSpell:enable */
const words = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm']; // cspell:disable-line disables this entire line
// To disable the next line, use cspell:disable-next-line
const moreWords = ['ieeees', 'beees', 'treeees'];
// Nesting disable / enable is not Supported
// spell-checker:disable
// It is now disabled.
var liep = 1;
/* cspell:disable */
// It is still disabled
// cSpell:enable
// It is now enabled
const str = "goededag"; // <- will be flagged as an error.
// spell-checker:enable <- doesn't do anything
// cSPELL:DISABLE <-- also works.
// if there isn't an enable, spelling is disabled till the end of the file.
const str = "goedemorgen"; // <- will NOT be flagged as an error.Ignore allows you the specify a list of words you want to ignore within the document.
// cSpell:ignore zaallano, wooorrdd
// cSpell:ignore zzooommmmmmmm
const wackyWord = ['zaallano', 'wooorrdd', 'zzooommmmmmmm'];Note: words defined with ignore will be ignored for the entire file.
The words list allows you to add words that will be considered correct and will be used as suggestions.
// cSpell:words woorxs sweeetbeat
const companyName = 'woorxs sweeetbeat';Note: words defined with words will be used for the entire file.
In some programing language it is common to glue words together.
// cSpell:enableCompoundWords
char * errormessage; // Is ok with cSpell:enableCompoundWords
int errornumber; // Is also ok.Note: Compound word checking cannot be turned on / off in the same file. The last setting in the file determines the value for the entire file.
By default, the entire document is checked for spelling.
cSpell:disable/cSpell:enable above allows you to block off sections of the document.
ignoreRegExp and includeRegExp give you the ability to ignore or include patterns of text.
By default the flags gim are added if no flags are given.
The spell checker works in the following way:
- Find all text matching
includeRegExp - Remove any text matching
excludeRegExp - Check the remaining text.
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp 0x[0-9a-f]+ -- will ignore c style hex numbers
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp /0x[0-9A-F]+/g -- will ignore upper case c style hex numbers.
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp g{5} h{5} -- will only match ggggg, but not hhhhh or 'ggggg hhhhh'
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp g{5}|h{5} -- will match both ggggg and hhhhh
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp /g{5} h{5}/ -- will match 'ggggg hhhhh'
/* cSpell:ignoreRegExp /n{5}/ -- will NOT work as expected because of the ending comment -> */
/*
cSpell:ignoreRegExp /q{5}/ -- will match qqqqq just fine but NOT QQQQQ
*/
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp /[^\s]{40,}/ -- will ignore long strings with no spaces.
// cSpell:ignoreRegExp Email -- this will ignore email like patterns -- see Predefined RegExp expressions
var encodedImage = 'HR+cPzr7XGAOJNurPL0G8I2kU0UhKcqFssoKvFTR7z0T3VJfK37vS025uKroHfJ9nA6WWbHZ/ASn...';
var email1 = 'emailaddress@myfancynewcompany.com';
var email2 = '<emailaddress@myfancynewcompany.com>';Note: ignoreRegExp and includeRegExp are applied to the entire file. They do not start and stop.
In general you should not need to use includeRegExp. But if you are mixing languages then it could come in helpful.
# cSpell:includeRegExp #.*
# cSpell:includeRegExp ("""|''')[^\1]*\1
# only comments and block strings will be checked for spelling.
def sum_it(self, seq):
"""This is checked for spelling"""
variabele = 0
alinea = 'this is not checked'
for num in seq:
# The local state of 'value' will be retained between iterations
variabele += num
yield variabeleUrls1 -- Matches urlsHexDigits-- Matches hex digits:/^x?[0-1a-f]+$/iHexValues-- Matches common hex format like #aaa, 0xfeef, \u0134Base641 -- matches base64 blocks of text longer than 40 characters.Email-- matches most email addresses.
Everything1 -- By default we match an entire document and remove the excludes.string-- This matches common string formats like '...', "...", and `...`CStyleComment-- These are C Style comments /* */ and //PhpHereDoc-- This matches PHPHereDoc strings.
1. These patterns are part of the default include/exclude list for every file.
cspell's behavior can be controlled through a config file. By default it looks for any of the following files:
cspell.json.cspell.jsoncSpell.json
Or you can specify a path to a config file with the --config <path> argument on the command line.
// cSpell Settings
{
// Version of the setting file. Always 0.1
"version": "0.1",
// language - current active spelling language
"language": "en",
// words - list of words to be always considered correct
"words": [
"mkdirp",
"tsmerge",
"githubusercontent",
"streetsidesoftware",
"vsmarketplacebadge",
"visualstudio"
],
// flagWords - list of words to be always considered incorrect
// This is useful for offensive words and common spelling errors.
// For example "hte" should be "the"
"flagWords": [
"hte"
]
}-
version- currently always 0.1 -
language- this specifies the language local to use in choosing the general dictionary. For example:"language": "en-GB"tells cspell to use British English instead of US English. -
words- a list of words to be considered correct. -
flagWords- a list of words to be allways considered incorrect -
ignoreWords- a list of words to be ignored (even if they are in the flagWords). -
ignorePaths- a list of globs to specify which files are to be ignored.Example
"ignorePaths": ["node_modules/**"]
will cause cspell to ignore anything in the
node_modulesdirectory. -
maxNumberOfProblems- defaults to 100 per file. -
minWordLength- defaults to 4 - the minimum length of a word before it is checked. -
allowCompoundWords- defaults to false; set to true to allow compound words by default. -
dictionaries- list of the names of the dictionaries to use. See Dictionaries below. -
dictionaryDefinitions- this list defines any custom dictionaries to use. This is how you can include other langauges like Spanish.Example
"language": "en", // Dictionaries "spanish", "ruby", and "corp-term" will always be checked. // Including "spanish" in the list of dictionaries means both Spanish and English // words will be considered correct. "dictionaries": ["spanish", "ruby", "corp-terms", "fonts"], // Define each dictionary. Relative paths are relative to the config file. "dictionaryDefinitions": [ { "name": "spanish", "path": "./spanish-words.txt"}, { "name": "ruby", "path": "./ruby.txt"}, { "name": "company-terms", "path": "./corp-terms.txt"} ],
-
ignoreRegExpList- list of patterns to be ignored -
includeRegExpList- (Advanced) limits the text checked to be only that matching the expressions in the list. -
patterns- this allows you to define named patterns to be used withignoreRegExpListandincludeRegExpList. -
languageSettings- this allow for per programming language configuration settings. See LanguageSettings
The spell checker includes a set of default dictionaries.
- en_US - Derived from Hunspell US English words.
- en-gb - Derived from Hunspell GB English words.
- companies - List of well known companies
- softwareTerms - Software Terms and concepts like "coroutine", "debounce", "tree", etc.
- misc - Terms that do not belong in the other dictionaries.
- typescript - keywords for Typescript and Javascript
- node - terms related to using nodejs.
- php - php keywords and library methods
- go - go keywords and library methods
- python - python keywords
- powershell - powershell keywords
- html - html related keywords
- css - css, less, and scss related keywords
- cpp - C++ related keywords
- csharp - C# related keywords
- latex - LaTex related words
- fonts - long list of fonts - to assist with css
- filetypes - list of file typescript
- npm - list of top 500+ package names on npm.
- name - The reference name of the dictionary, used with program language settings
- description - Optional description
- path - Path to the file, can be relative or absolute. Relative path is relative to the
current
cspell.jsonfile. - repMap - Optional replacement map use to replace character prior to searching the dictionary.
Example:
// Use Compounds
// Replace various tick marks with a single ' "repMap": [["'|`|’", "'"]]
- useCompounds - allow compound words
// Define each dictionary. Relative paths are relative to the config file.
"dictionaryDefinitions": [
{ "name": "spanish", "path": "./spanish-words.txt"},
{ "name": "ruby", "path": "./ruby.txt"},
{ "name": "company-terms", "path": "./corp-terms.txt"}
],It is possible to prevent a dictionary from being loaded. This is useful if you want to use your own dictionary or just off an existing dictionary.
"dictionaries": ["!cpp"],The Language Settings allow configuration to be based upon the programming langauge and/or the local.
There are two selector fields local and languageId.
languageIddefines which programming languages to match against. A value of"python,javascript"will match against python and javascript files. To match against ALL programming languages, use"*".localdefines which spoken langauges to match against. A value of"en-GB,nl"will match against British English or Dutch. A value of"*"will match all spoken languages.- Most configuration values allowed in a
cspell.jsonfile can be define or redefine within thelanguageSettings.
"languageSettings": [
{
// VSCode languageId. i.e. typescript, java, go, cpp, javascript, markdown, latex
// * will match against any file type.
"languageId": "c,cpp",
// Language local. i.e. en-US, de-AT, or ru. * will match all locals.
// Multiple locals can be specified like: "en, en-US" to match both English and English US.
"local": "*",
// To exclude patterns, add them to "ignoreRegExpList"
"ignoreRegExpList": [
"/#include.*/"
],
// List of dictionaries to enable by name in `dictionaryDefinitions`
"dictionaries": ["cpp"],
// Dictionary definitions can also be supplied here. They are only used iff "languageId" and "local" match.
"dictionaryDefinitions": []
}
]Overrides are useful for forcing configuration on a per file basis.
Example:
"overrides": [
// Force `*.hrr` and `*.crr` files to be treated as `cpp` files:
{
"filename": "**/{*.hrr,*.crr}",
"languageId": "cpp"
},
// Force `*.txt` to use the Dutch dictionary (Dutch dictionary needs to be installed separately):
{
"language": "nl",
"filename": "**/dutch/**/*.txt"
}
]