A collection of sequencers. Most modules of this plugin are inspired by the XOR plugin which is not available in Rack v2.
Table of Contents
This type of sequencer does not have any clock inputs. The current steps are selected via voltage inputs, similar to using the step CV input from Bogaudio's ADDR sequencer. However, the plugin provides some modules which do the job of addressing based on a clock. But every other module or combinations which outputs step functions (e.g. S&H) can be used.
- The AG module provides 100 voltage addressable polyphonic gates or gate patterns.
- The number of channels can be set in the menu.
- The address input recognizes 0.1V per step.
- If the Edit button is pressed the module behaves like the address input is not connected i.e. the steps can be manually selected, otherwise a connected address input will disable manual stepping.
- A click on the copy button will make a copy of the gate values.
- After selecting a new step it can be pasted there.
Some use cases of the module:
- Meta sequencing. Turn on and off other modules.
- Drum sequencing
- Arpeggiator
- ....
- ACC is a simple accumulator.
- On every trigger event on the Clk input it updates its state by adding the value of the Step parameter
- On a trigger on the reset input the state is set to the value of the set param or set input if connected.
- The output always reflects the current the state.
If the step param is set to 0.1V ACC can be used to drive AG.
-
The Chord module provides 100 voltage addressable polyphonic semi note values in the range from C0 to C8.
-
The number of channels can be set in the menu.
-
The address input recognizes 0.1V per step.
-
If the Edit button is pressed the module behaves like the address input is not connected i.e. the steps can be manually selected, otherwise a connected address input will disable manual stepping.
-
A click on the copy button will make a copy of the note values.
-
After selecting a new step it can be pasted there.
-
Pressing the N+ button transposes one semi up.
-
Pressing the N- button transposes one semi down.
-
Pressing the O+ button transposes one octave up.
-
Pressing the O- button transposes one octave down.
-
The chord module outputs behaves like the corresponding ones in the MIDI CV module.
-
In the menu the number of polyphonic channels and the polyphony modes Rotate,Reset and Reuse for the channel assignment can be configured.
-
The Reorder action in the menu causes the chord to be ordered in the polyphonic channels from the lowest note to the highest.
-
The Auto-Reorder option causes the Reorder action on every change and the polyphony modes are ignored.
-
The Auto-Channel option causes the outputs only have as many channels as key buttons are pressed. In this case the Polyphonic Channels setting is ignored.
The ACC module can be used to drive a chord sequence.
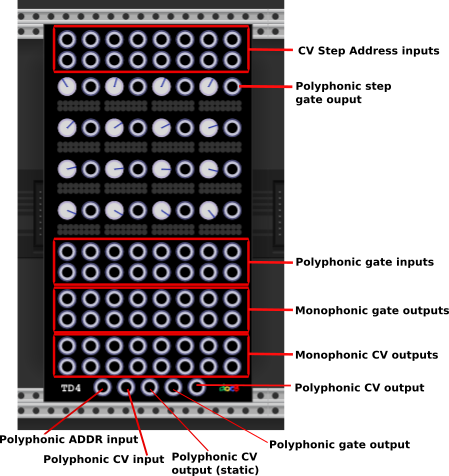
This module provides 16 Tracks of a 4x4 Grid Sequencer. It is intended to be a building block for simulating hardware sequencers like Rene or Z8000. It is inspired by the Z8K and the Renato module from the XOR plugin.
The top two input rows are the 16 CV address inputs. The 16 steps are addressed in the range of 0-10V i.e. 10/16V per step. Below there is the 4x4 Grid with 16 CV value knobs. The range of the knobs is configurable in the menu. The values can also be quantized to semi notes. The 16 lights per step show the position of each track and the polyphonic gate output besides the knob reflects the status of the lights.
Below that there are two rows of polyphonic gate inputs. With these, the steps for each track can be muted separately which is reflected by the next two rows of monophonic gate outputs, the lights and the output besides the cv knob.
The next two rows are the monophonic CV outputs for each track.
On the bottom there are some additional polyphonic inputs and outputs.
- A polyphonic address CV input which takes over the 16 address inputs
- A polyphonic CV input which takes over the CV Knob values
- A polyphonic CV output which reflects the current voltages of each knob
- A polyphonic gate output which reflects the 16 monophonic gate outputs
- A polyphonic cv output which reflects the 16 monophonic CV outputs.
Here are some modules which are suited for a clocked addressing of the TD4 but not limited to.
- A single P4 makes 4 Step Sequences inside an address space of 4-32 Steps (Size Knob). In the case of driving TD4 the size would be 16.
- The Ofs parameter controls the starting step inside the address space.
- The Perm parameter sets one of the 24 possible 4-Step permutations.
- If Y is set in the dir parameter the output is:
(step%4)*4+step/4which causes moving up or down in TD4 and other grid sequencers (see below) - It can be used to simulate the 4-Step sequencers of the Z8000, but it can do a lot more sequences.
NB: The videos have sound which could be turned on.
This example illustrates the use of four P4. The second (from right) connected P4 has an offset of 4, so it will go through the second row. The third P4 is set to Y and offset 4, so it goes through the second column. The forth P4 is set to Y and offset 12, so it goes through the forth column.
The use of AG is also shown to mute some steps via the Gate inputs.
td4_005.mp4
This example shows how to make a complex 16-step sequence with three P4 modules. Only the right most P4 is connected to the TD4. The left most is clocked x4 and controls the permutation selection and the middle P4 (also clocked x4) controls the offset - by set to direction Y it always moves the address by 4 steps.
td4_005a.mp4
The P16 module provides 100 predefined 16-Step Sequences (ok, some kind of tiny collection compared to the possible 20922789888000 permutations). But at least the direction (back or forth) and an offset can be selected per sequence. However, e.g. an S&H or Towers+SwitchN1 or like in the example above can be used to make the rest. NB: This size should be 16 for TD 4. Here an example of the first 10 sequences.
td4_005-01.mp4
PXY is a 2D walker controlled by X+,Y+,X-,Y- Trigger inputs. The start point can be controlled and the maximum length in each direction where wrapping around will occur. This size should be 16 for TD 4.
Here an example:
td4_005-02.mp4
A universal sequencer. Vaguely inspired by the o88o module from the XOR plugin.
CAUTION: This module will trick you into spending a lot of time. Consider taking a walk in nature instead.
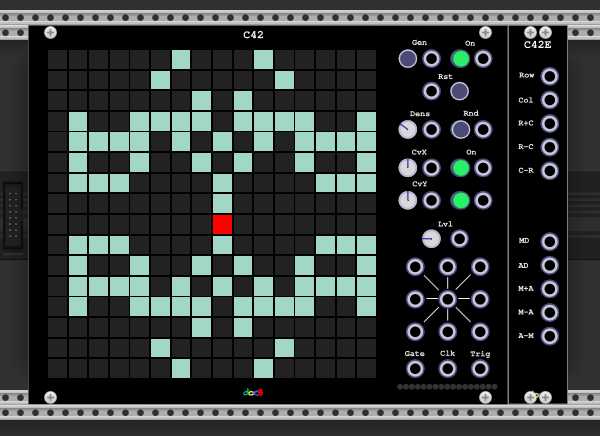
- C42 provides a grid with sizes 8x8 upto 32x32 (config in the menu).
- Each cell of the grid is either on or off.
- On the grid there can be placed up to 16 play heads.
- The play heads are placed via (polyphonic) CV addresses.
- The column of the play head is addressed via 10V/size * colum_number via CvX param
- The row of the play head is addressed via 10V/size * row_number via CvY param
- The CvX/CvY input is added to the CvX/CvY param if the right On-Button is on.
- The On Buttons can be controlled via a gate signal on the right side input.
- The resulting position is always wrapped e.g. 10.1 V will place the head on the first column or row.
- C42 outputs a trigger on the polyphonic channel of the play head
- if the play head is changed to a cell which is on
- if the cell where the play head is placed is turned on
- The gate output has 10V on the polyphonic channel of the play head while the play head is on a cell which is on, 0V otherwise.
- The clock output represents the signal on the Gen (generate) input if the gate output is high.
- There are nine polyphonic CV outputs which work as follows:
- Top-Left: Every active cell on the Top Left diagonal of the play head is counted and multiplied with the value of the level param.
- Bottom-Left, Bottom-Right, Top-Right similar.
- Col-Top: Every active cell on the column above the play head is counted and multiplied with the value of the level param
- Col-Bottom: Every active cell on the column below the play head is counted and multiplied with the value of the level param
- Row-Left: Every active cell on the row and left side of the play head is counted and multiplied with the value of the level param
- Col-Top: Every active cell on the row and right side the play head is counted and multiplied with the value of the level param
- CV Gate (centered output): If the cell of the play head is on the output is the value of the level param, 0 otherwise
There is additionally an expander C42E which provides additional outputs:
- Row (Row-Left + Row-Right)
- Col (Col-Top + Col Bottom)
- R+C (Row+Col)
- R-C (Row-Col)
- C-R (Col-Row)
- MD (Top-Left + Row Bottom)
- AD (Bottom-Left + Top-Right)
- M+A (MD+AD)
- M-A (MD-AD)
- A-M (AD-MD)
A general alternative is to combine the outputs via the Sum module (see below) and its SE Expander or any other module which processes multiple polyphonic inputs.
-
If the Gen Button is clicked or a trigger on the Gen input is received a new 2D cellular automata generation is produced
-
The following rules can be configured in the menu:
- B3/S23 Classic Conways life
- B34/S34 (34 Life)
- B234/S (Serviettes)
- B2/S (Seeds)
- B1/S1 (Gnarl)
- B36/S125 (2x2)
- B345/S5 (Long life)
-
NB: These rules all operate on a torus.
-
The reset button or a trigger on the reset input rewinds the grid to the last edit operation.
-
The Rnd button generates a random grid using the Dens (density) parameter.
Here is a demo showing classic sequencing. The melody and bass are made with one play head driven by a P16 by using the Col-Top and Col-Bottom output. The middle line where the play head is moved and which is not counted in Col-Top or Col-Bottom is used for adding some gates triggering an ADSR/filter cutoff. The level parameter is set to 1/7 (+a bit more) and the mode of Quant is "equi-likely" so that one more counted cell will move up by one position of the scale and an octave is exactly 7 counted cells.
On the second C42 one P16 and three P4 are used to make a 3-voice 32-step drum sequence.
(Due to the limited size of the video the sound quality is not so good).
output.mp4
In this example a period-16 oscillator in conways life is used. Four playheads are placed randomly via RndH. The M+A (main diagonal + anti diagonal) output of the C24E expander is used to make the CV. The trigger output triggers an ADSR/Filter cutoff.
c42_1.mp4
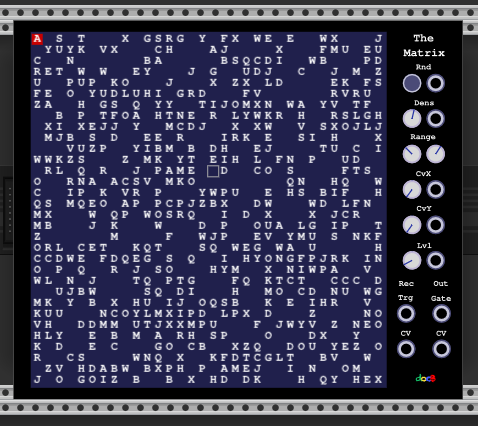
Similar to C42 TheMatrix provides a grid of size 32x32 where up to 16 play heads can be placed via the CvX/CvY params and inputs. But on each cell there can be edited an ascii char in the range from 32 (space) to 126 (~). The polyphonic CV output is built in the following way if a play head is on a cell which is no space: First an integer number is looked up from the following table:
| char | value | char | value | char | value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ! | -47 | A | -15 | a | 17 |
| " | -46 | B | -14 | b | 18 |
| # | -45 | C | -13 | c | 19 |
| $ | -44 | D | -12 | d | 20 |
| % | -43 | E | -11 | e | 21 |
| & | -42 | F | -10 | f | 22 |
| ' | -41 | G | -9 | g | 23 |
| ( | -40 | H | -8 | h | 24 |
| ) | -39 | I | -7 | i | 25 |
| * | -38 | J | -6 | j | 26 |
| + | -37 | K | -5 | k | 27 |
| , | -36 | L | -4 | l | 28 |
| - | -35 | M | -3 | m | 29 |
| . | -34 | N | -2 | n | 30 |
| / | -33 | O | -1 | o | 31 |
| 0 | -32 | P | 0 | p | 32 |
| 1 | -31 | Q | 1 | q | 33 |
| 2 | -30 | R | 2 | r | 34 |
| 3 | -29 | S | 3 | s | 35 |
| 4 | -28 | T | 4 | t | 36 |
| 5 | -27 | U | 5 | u | 37 |
| 6 | -26 | V | 6 | v | 38 |
| 7 | -25 | W | 7 | w | 39 |
| 8 | -24 | X | 8 | x | 40 |
| 9 | -23 | Y | 9 | y | 41 |
| : | -22 | Z | 10 | z | 42 |
| ; | -21 | [ | 11 | { | 43 |
| < | -20 | \ | 12 | | | 44 |
| = | -19 | ] | 13 | } | 45 |
| > | -18 | ^ | 14 | ~ | 46 |
| ? | -17 | _ | 15 | ||
| @ | -16 | ` | 16 |
Then this number is multiplied by the level parameter value and passed to the output.
So if the level parameter is set to 1/12 then we have a semi note range from C#-2 to B-3 and the letter 'A' denotes A-2.
A space will cause that the gate output is set to 0V, every other character causes the gate output set to 10V.
This seems to be a bit complicated, but there are some editing features which make life easy:
- connect a midi keyboard and the V/Oct of the MIDI CV Module to the Rec CV input and the Retrigger output to the Rec Trg input. On pressing a note on the keyboard the corresponding ascii char will be inserted so that the cell will output the same note if the level is set to 1/12.
- If the cursor is on a cell then the Keys PageUp and PageDown will increase/decrease the current character according to the ascii table.
The editor supports also selecting a rectangular region with cut/copy/paste operations. Text can also be pasted from the system clipboard.
The editor is also connected to the undo/redo system of VCVRack.
The Rnd Button or a trigger on the Rnd input will fill the grid with random characters in the range set by the Range parameters min and max. The dens parameter or input controls how many spaces are generated.
The following sequencers are reimplementations with additional/different features of some sequencers of the XOR plugin.
Uno is a reimplementation of the qu4ttro sequencer of the XOR plugin. With the default values this is a normal 8-step sequencer. However, this sequencer answers the question of what happens if a probability can be set for skipping a step.
Differences/Additions to the original:
- It does not provide 4 Tracks but a chainable expander to have an arbitrary count of tracks.
- Polyphonic inputs for the probability and CV Values are provided
- The CV Range can be adjusted in the menu
- Quantize to semis can be turned on in the menu.
- The probability for skipping a step is in the range of 0-100% and independent of the Glide and Rst.
- If the Rst is on and the step is not skipped then it resets the sequence to the first step in forward and pendulum mode and to the last step in backward mode.
- The gate output represents the clock input if the gate is on and the Glide on the step is turned off.
- If glide is On and the step is not skipped then the gate stays high
- A polyphonic step gate output is provided
- The seed input can be used to make reproducible sequences. If connected and not zero on a reset it will result in the same sequence for the same value provided.
Here an example showing the effect of the Rst button:
uno.mp4
You know, it may be better to take a walk in nature ...
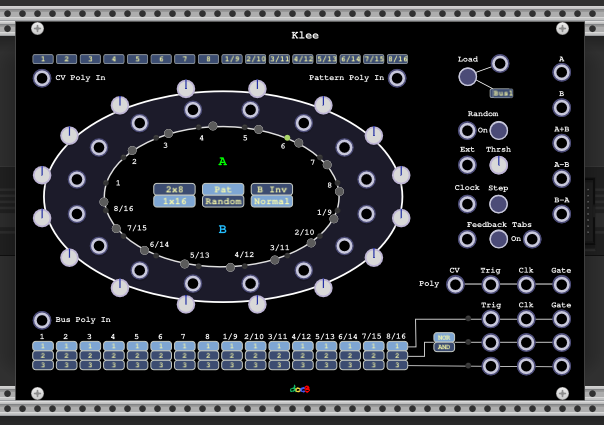
This module is a reimplementation of the Klee module of the XOR plugin with a bunch of additional features. It simulates a Klee like sequencer - please read carefully the PDF first you will find if you type 'klee sequencer pdf' in your search engine to understand what this is all about.
The additional features:
- Every CV Knob has a single input which takes over the value.
- The CV Knob range can be changed in the menu.
- The CV Values can be quantized to semi steps in the menu.
- Polyphonic inputs
- A CV input which controls all CV Knobs
- A Bus input which controls the Gate bus
- A Pattern input which controls the start pattern used when load is triggered
- Polyphonic outputs:
- A static CV output which holds all knob values
- A trigger output where a trigger is fired on a channel if the corresponding step is turned on.
- A Gate output which is high if the corresponding step is active.
- A Clock output which represents the input clock if the gate is high.
- Feedback Tabs (to make this module complex in a further dimension):
- Beside the lights there are small buttons for turning on a feedback tab for the step.
- This turns the shift register into a linear feedback shift register LFSR (see e.g. wikipedia).
- A polyphonic feedback tab input can be used to set the tabs.
- The feedback is only active if the On button on right side of the input is on.
NB: this module needs a bunch of tutorials or may be better taking a walk ....
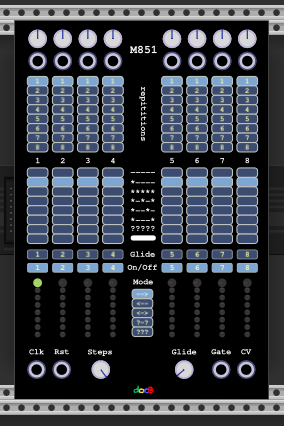
This module is a reimplementation of the M581 of the XOR plugin.
- With the default values this is a normal 8-step sequencer.
- There are additional CV inputs which take over the step CV value.
- The Knob range can be changed in the menu.
- The CV Values can be quantized to semi steps in the menu.
- The Gate output always represents the clock input (there is no gate length parameter as in the originals).
- There are five play modes: forward, backward, pendulum,random walk and random.
Things change dramatically if the repetition values are set to a higher value than one. The step then will stay for the number of repetitions. This will make the sequence longer (however the sequence length can be held constant via the rst input). Now the gate mode parameter comes into play:
- '-----' means no gate at all (works also for one repetition)
- '*----' means only a single gate at the beginning (the default)
- '*****' for every repetition there will be a gate
- '*-*-*' for repetition 1,3,5,7 there will be a gate
- '*--*-' for repetition 1,4,7 there will be a gate
- '*---*' for repetition 1,5 there will be a gate
- '?????' gates are fired randomly
- '▪▪▪▪▪' the gate will stay high for gliding to the next step
If the glide button is on, there will be a portamento with speed adjustable by the glider knob. If the step is turned off it will be skipped.
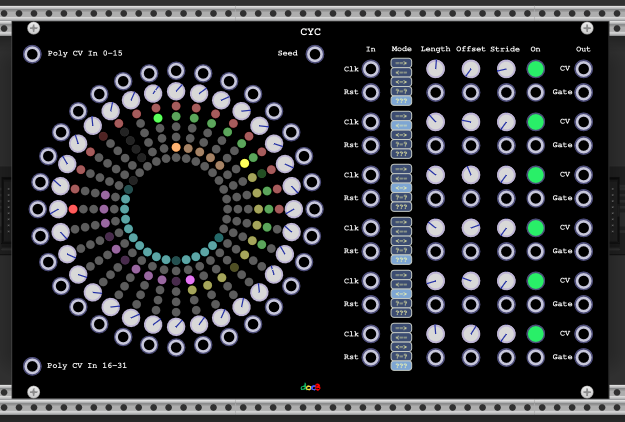
CYC is a reimplementation of the Spiral sequencer of the XOR plugin.
- CYC is a 6 track cyclic step sequencer on a common 32 knob/input value space.
- The Knob range can be changed in the menu.
- The CV Values can be quantized to semi steps in the menu.
- There are two polyphonic CV inputs for step 0-15 and 16-31
- For each track the play mode (forward, backward, pendulum,random walk and random), the offset (0-31), length (1-32) and stride (1-8) can be configured.
- For each track the steps can be muted/unmuted by clicking on the step light.
- If one of the random modes is used with the polyphonic seed input a random seed (by setting channel 1-6) can be set to obtain the same sequence (if the seed value is not zero) on every reset.
This module does the same as Sum Mk 3 from the ML Modules plugin, but it has 12 polyphonic inputs and a chainable expander which reduces the amount of cables if different sums are built from the same inputs.
CV is another discrete CV value source. The number on the selected button is multiplied by the level value and passed to the output. The original idea for this module was born after watching the video about the octave sequencer from Jakub Ciupinski. With the CV module it looks like this:
It basically behaves like the OCT module of the Fundamental plugin. It can be used without a quantizer as the level can be set to 1/12.
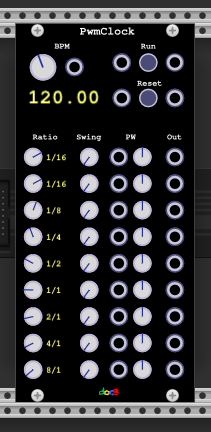
Yet another clock generator module. The purpose of this module is to have many clock generators with different ratios and adjustable pwm. You may need it when working with the sequencers described above.