Truc Nguyen (UFID: 9482-7764)
- GCC >= 7.4.0
$ make$ ./risingCity </path/to/input/file></path/to/input/file>: path to the input text file
This project is implemented as a discrete-event simulator. There are two kinds of event:
- Read the next command from the input file
- Choose the building to work on
Each event is associated with a timestamp. At any point in time, the simulator will choose the event that has the smallest timestamp and update its global timestamp with that of the chosen event. The event loop of the simulator is implemented using the following pseudo-code:
global_timestamp = 0;
while (there is some event)
{
if (the timestamp of event 1 <= the timestamp of event 2)
{
// This is the event for reading the next command
Update the executed_time of the current building
global_timestamp = timestamp of event 1; // update the global time
Read and execute the current command
Update the timestamp of event 1 with the timestamp of the next command in the input file
}
else
{
// This is the event for choosing the next building
Update the executed_time of the current building
global_timestamp = timestamp of event 2; // update the global time
if (the current building is finished)
remove the building
else
Reinsert it to the heap
Choose the next building to work on based on the min heap
The timestamp of event 2 = global_timestamp + min(totalTime - executedTime, 5)
}
}As recommended by the TA, when choosing the building to work on, it will perform the ExtractMin operation on the min heap (i.e., remove the root of the heap and return that root). Note that it won't do anything to the red-black tree. After the 5-day period, the building will be inserted back to the min heap.
When the program encounters an Insert command, it will perform insertion on both the min heap and the red black tree.
For example:
0: Insert(50, 100)
2: Insert(51, 100)
3: Insert(52, 100)
4: Insert(53, 100)
At 0, the building 50 is inserted to the data structures, then chosen and extracted from the min heap. At 2, 3, and 4, the building 51, 52, and 53 is inserted to the data structure,respectively. The 50 will be inserted back to the heap at 5, and a new building will be chosen to build.
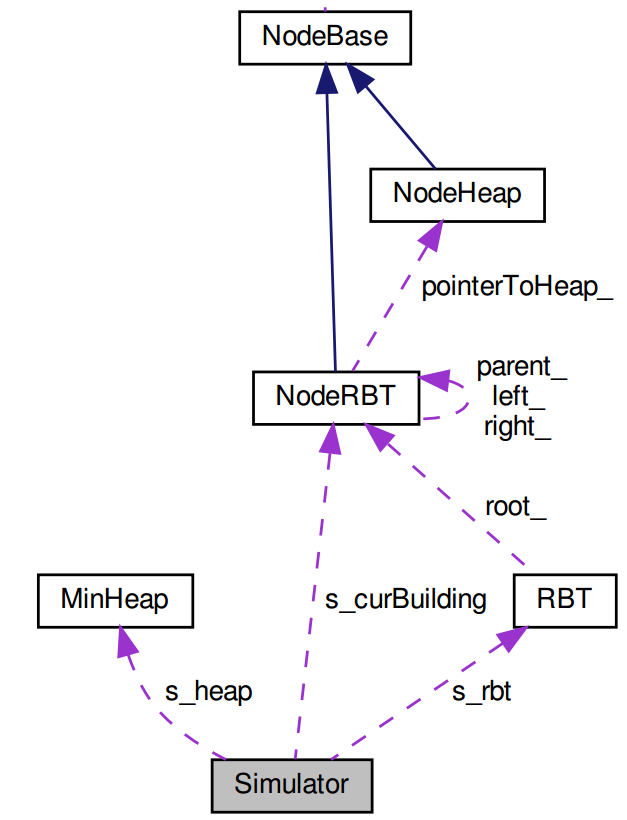
The architectural overview of the implementation is illustrated via the following class diagram
There are 6 main classes in this program:
Simulator: this class implements the discrete-event simulator with the event loop. This is a static class and represents the main workflow of the program. The building that is currently being worked on is denoted ass_curBuildingand it is of typeNodeRBTNodeBase: this is the base class (pure virtual) for representing a node/building. This class stores the building record(buildingNums, executedTime, totalTime)and implements some basic and virtual operations.NodeHeap: this class is derived fromNodeBaseand represents a node in the min heap. It implements some of the necessary methods for the heap structure.NodeRBT: this class is derived fromNodeBaseand represents a node in the red-black tree. It stores some additional attributes like color, parent, left child, and right child. It also stores a pointer to the corresponding node. Some of the necessary methods for the red-black tree are also implemented.MinHeap: this class implements the min heap structure usingNodeHeapas its node. The heap is implemented as array-based.RBT: this class implements the red-black tree usingNodeRBTas its node. All the operations are implemented in the same manner as the class lectures.