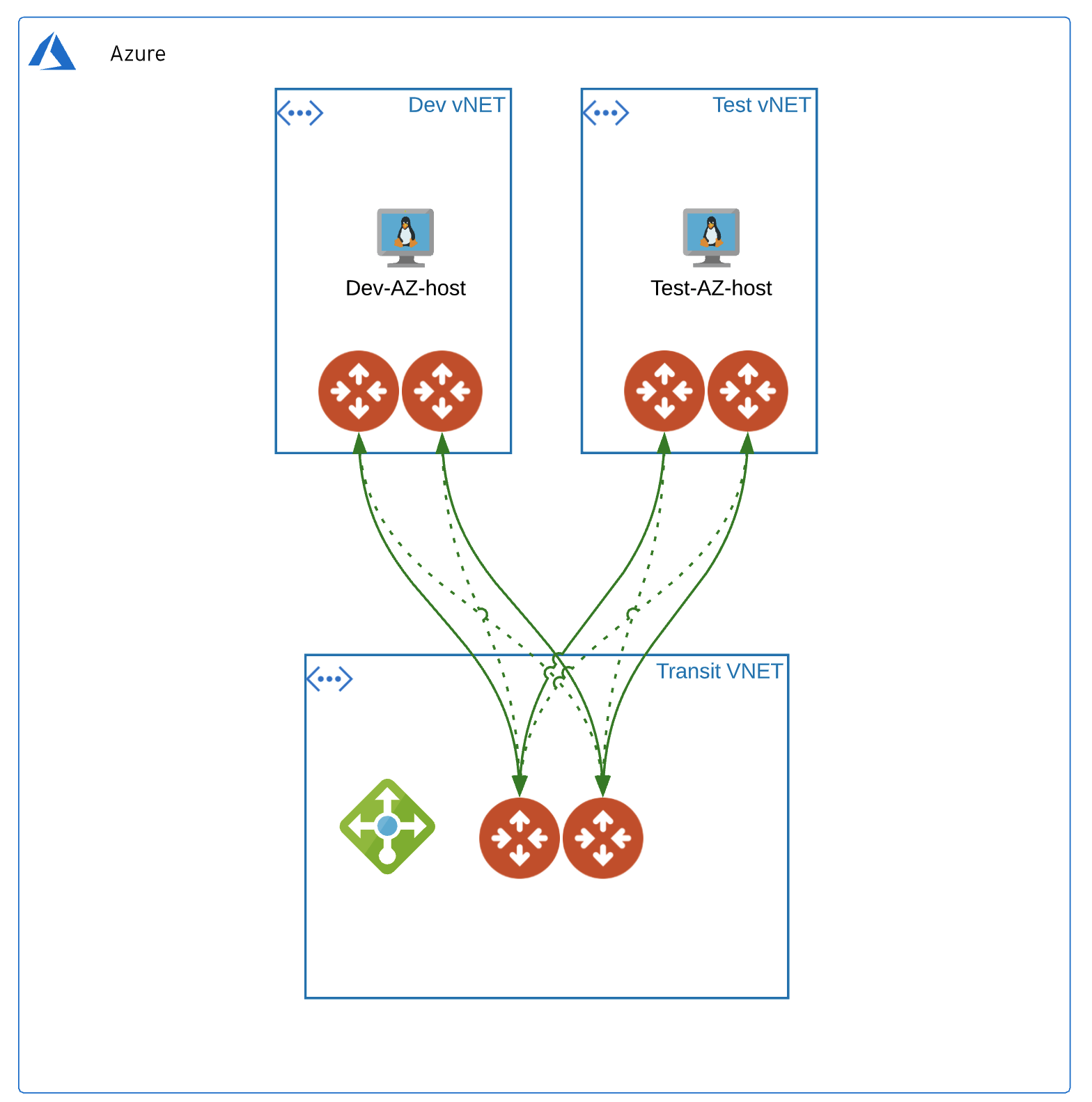
This repo builds Aviatrix Transit in Azure insane mode HPE, spokes attached each with an ubuntu test vm. The test VMs will use password authentication (randomly generated), have port 22 open and be provided public IPs. The test vm object(s) will be generated per spoke review output for public ip's.
- 1 Aviatrix Transit in Azure with N Aviatrix spokes defined in terraform.tfvars, i.e.
spokes = { "Dev" = "10.22.1.0/20" , "Test" = "10.23.3.0/20" }that will be attached to Aviatrix Transit Gateway. - 1 Azure Resource Group with Ubuntu 18.04 VM (iperf3 installed) (1 per spoke)
| Terraform version | Controller version | Terraform provider version |
|---|---|---|
| 0.13 | 6.3 | 2.18 |
| Module Name | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| terraform-aviatrix-modules/azure-transit/aviatrix | 3.0.0 | This module deploys a VNET, Aviatrix transit gateways. |
| terraform-aviatrix-modules/azure-spoke/aviatrix | 3.0.0 | This module deploys a VNET and an Aviatrix spoke gateway in Azure and attaches it to an Aviatrix Transit Gateway |
| Azure/compute/azurerm | 0.9.0 | Azure Terraform module to deploy virtual machines |
The variables are defined in terraform.tfvars.
Note: ha_enabled = false controls whether ha is built for spokes.
instance_size controls the size of all the transit spokes and gateways.
test_instance_size controls the size of the test vms.
- Software version requirements met
- Aviatrix Controller with Access Account in Azure
- Sufficient limits in place for Azure region in scope (EIPs, Compute quotas, etc.)
- terraform .13 in the user environment
terraform -vor use hashicorp/terraform docker image Instructions below. - Install the the azure cli on the workstation and authenticate with
az login
- Modify
terraform.tfvars(i.e. access account name, regions, cidrs, etc.) and save the file. terraform initterraform planterraform apply --auto-approve
You can ssh into the the test vm's created in azure like so...
ssh azureuser/test_vm_password@public_ip_address
test_vm_password,public_ip_address will be in terraform output
Replace with the private IP of one of the created test vms - check Azure console for the value. Run the client on one test vm and the server on another test vm.
iperf3 -c 10.21.3.20 -i 2 -t 30 -M 1400 -P 1 -p 5201
iperf3 -s -p 5201
docker pull hashicorp/terraform:0.13.6
docker run -i -t -v $PWD:$PWD -w $PWD \
--env TF_VAR_username=$TF_VAR_username \
--env TF_VAR_password=$TF_VAR_password \
--env TF_VAR_controller_ip=$TF_VAR_controller_ip \
hashicorp/terraform:0.13.6 init
docker run -i -t -v $PWD:$PWD -w $PWD \
--env TF_VAR_username=$TF_VAR_username \
--env TF_VAR_password=$TF_VAR_password \
--env TF_VAR_controller_ip=$TF_VAR_controller_ip \
hashicorp/terraform:0.13.6 plan
docker run -i -t -v $PWD:$PWD -w $PWD \
--env TF_VAR_username=$TF_VAR_username \
--env TF_VAR_password=$TF_VAR_password \
--env TF_VAR_controller_ip=$TF_VAR_controller_ip \
hashicorp/terraform:0.13.6 apply --auto-approve