Table of Contents
- Rustic
This package is based on rust-mode and provides additional features:
- flycheck integration
- cargo popup
- multiline error parsing
- translation of ANSI control sequences through xterm-color
- async org babel
- custom compilation process
- rustfmt errors in a rust compilation mode
- automatic LSP configuration with eglot or lsp-mode
- Optional rust inline documentation
- cask for testing
- requires emacs 26
- etc.
rustic only shares the rust-mode code from rust-mode.el and rust-utils.el. The other files provide functionality that is similar to some of the features of rustic, however can be considered light-weight compared to some rustic's functionality.
The shared functions and options exist as aliases in the rust-mode and rustic namespace for backwards compatability reasons(rustic has been a fork).
rustic-format-bufferoccasionally sets point to beginning of buffer, userustic-format-fileinsteadrust-syntax-propertizeandadaptive-wrap-prefix-modecan lead to severe lag when editing larger files (#107)
Simply put (use-package rustic) in your config and most stuff gets
configured automatically.
(use-package)
It's necessary to include elpa for a package dependency:
(setq package-archives '(("melpa" . "http://melpa.org/packages/")
("gnu" . "http://elpa.gnu.org/packages/")))If ‘spinner-1.7.3’ is unavailable” when trying to install rustic, you need to update GPG keys used by the ELPA package manager. Try installing gnu-elpa-keyring-update.
If you have rust-mode installed, ensure it is required before rustic
since it has to be removed from auto-mode-alist. However you only
need rust-mode if you want to use emacs-racer. There's some stuff
that isn't included in rustic.
If you have any issues with rustic, please try running emacs without
rust-mode loaded.
If you can't run rust-analyzer or cargo can't be found, your environment variables probably don't work in emacs. Try exec-path-from-shell to fix this.
straight.el clones each of your packages directly from its source. There are good additional installation instructions for moving your package management from package.el to straight.
rustfmt and most of the common cargo commands should work remotely. We are currently updating the code base. If you encounter any command that doesn't work remotely, please open an issue.
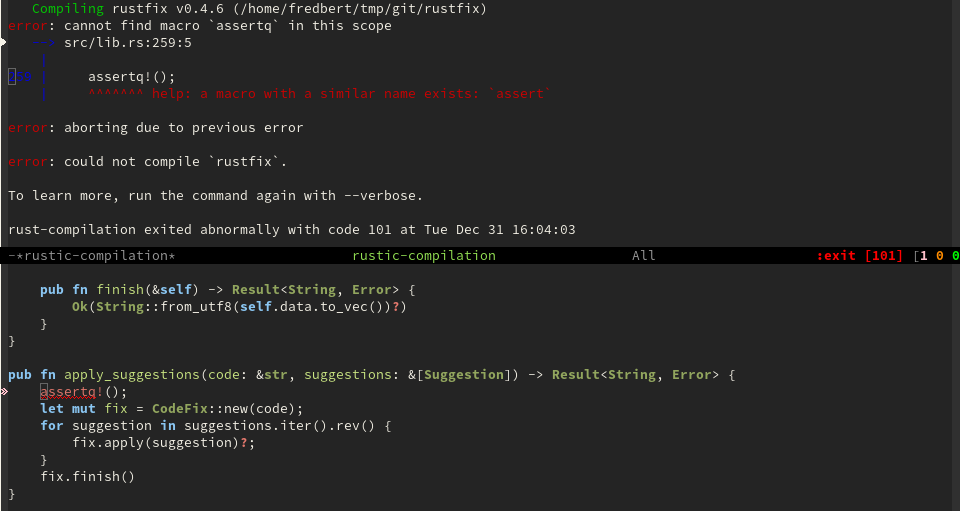
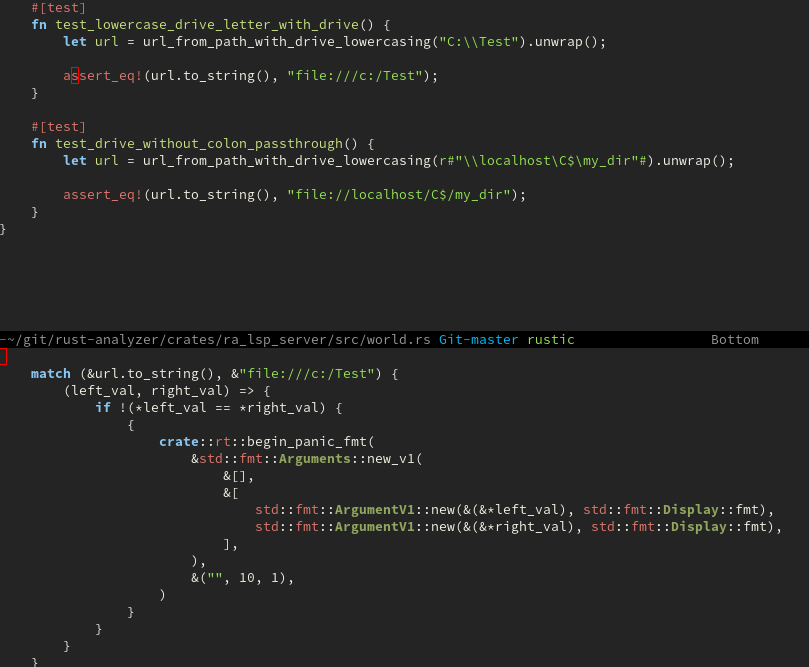
Rustic defines a derived compilation-mode. Colors can be customized
with several defcustoms. You can use next-error and
compilation-next-error as for any other compilation buffer.
However it's possible to also jump to line numbers that are displayed
at the beginning of a line. This feature is provided by a hook around
compile-goto-error(RET).
Commands:
rustic-compilecompile project usingrustic-compile-commandrustic-recompilerecompile usingcompilation-argumentsrustic-compile-send-inputsend string to process of current buffer
Customization:
rustic-compile-display-methodchoose function that displays the compilation buffer (use the functionignore, if you don't want the buffer to be displayed)rustic-compile-backtracechange backtrace verbosityrustic-compile-commanddefault command for rust compilation
Supported compile.el variables:
- compilation-arguments
- compilation-scroll-output
rustic-compile-directory-method allows you to set the directory that
is used for compilation commands. The default is the current crate
which is returned by rustic-buffer-crate(there's also
rustic-buffer-workspace).
If you want to use the project root you can use rustic-project-root
instead.
FTR #174 #179 #236
The colors that are displayed in compilation buffers come from cargo
and are translated by xterm-color. You can change these colors by
modifying rustic-ansi-faces.
rustic-compilation-mode doesn't use the default faces of
compile.el. If you want to change these colors you can use something
similar to:
(custom-set-faces
'(rustic-compilation-column ((t (:inherit compilation-column-number))))
'(rustic-compilation-line ((t (:foreground "LimeGreen")))))Additional faces:
rustic-messagerustic-compilation-errorrustic-compilation-warningrustic-compilation-info
You can format your code with:
rustic-format-bufferformat buffer with stdinrustic-format-fileformat file and revert bufferrustic-cargo-fmtrun cargo-fmt on workspacerustic-format-regionformat active region
Rustic uses the function rustic-save-some-buffers for saving buffers
before compilation. To save buffers automatically, you can change the
value of buffer-save-without-query. In case you prefer using lsp for
formatting, turn off rustic-format-on-save and set
rustic-lsp-formatto t.
Customization:
rustic-rustfmt-binpath to rustfmt executablerustic-rustfmt-argsadditional args like +nightlyrustic-rustfmt-config-alistalist of rustfmt configuration optionsrustic-format-display-methoddefault function used for displaying rustfmt buffer (use the functionignore, if you don't want the buffer to be displayed)rustic-format-on-save-methodfunction to use for on-save formattingrustic-format-trigger'on-saveformat buffer before saving'on-compilerun 'cargo fmt' before compilationnildon't format automatically
known issues:
in case you are using hideshow you might want to set rustic-format-on-save-method to rustic-format-buffer(#274)
If you want to configure the following rustfmt call
rustfmt +nightly --config hard_tabs=true --config skip_children=false main.rsyou can use
(setq rustic-rustfmt-args "+nightly")
(setq rustic-rustfmt-config-alist '((hard_tabs . t) (skip_children . nil)))If you are struggling with errors relating to the rust edition in
cargo.toml, this may in fact be a problem with rustfmt and its
default settings. To solve this, even though the error message
mentions cargo.toml, you you have to put edition = "2018" in a
rustfmt.toml. See here for more
info.
Currently only rustic-format-buffer works remotely.
rustic-rustfmt-bin needs to be an absolute path to work remotely.
Disable LSP support by setting rustic-lsp-client to nil. You have to
restart emacs when you switch lsp clients.
rust-analyzer is the default and can be changed to rls. lsp-mode
related code was moved to the lsp-mode repo. rustic-lsp-server sets
the value of lsp-rust-server.
(setq rustic-lsp-server 'rls)Change rust-analyzer path.
(setq rustic-analyzer-command '("~/.cargo/bin/rust-analyzer"))The default package is lsp-mode. But you can also use eglot.
(setq rustic-lsp-client 'eglot)LSP commands:
xref-find-definitions
xref-find-references with helm and rust-analyzer
Turn off flymake.
(add-hook 'eglot--managed-mode-hook (lambda () (flymake-mode -1)))lsp-describe-thing-at-pointdisplay documentationlsp-find-definitionmakes use of xref
You can find more information in the lsp-mode wiki.
This command can be extremely convenient when applying code actions or using auto-imports.
Run lsp-execute-code-action when lsp-ui displays code actions at the
top of the sideline.
lsp-rust-analyzer-expand-macro expand macro call at point
recursively
The results are formatted and highlighted by default, but you can use
your own function by customizing
lsp-rust-analyzer-macro-expansion-method.
rust-analyzer does work over TRAMP, but you have to register the client
manually:
(with-eval-after-load "lsp-rust"
(lsp-register-client
(make-lsp-client
:new-connection (lsp-stdio-connection
(lambda ()
`(,(or (executable-find
(cl-first lsp-rust-analyzer-server-command))
(lsp-package-path 'rust-analyzer)
"rust-analyzer")
,@(cl-rest lsp-rust-analyzer-server-args))))
:remote? t
:major-modes '(rust-mode rustic-mode)
:initialization-options 'lsp-rust-analyzer--make-init-options
:notification-handlers (ht<-alist lsp-rust-notification-handlers)
:action-handlers (ht ("rust-analyzer.runSingle" #'lsp-rust--analyzer-run-single))
:library-folders-fn (lambda (_workspace) lsp-rust-library-directories)
:after-open-fn (lambda ()
(when lsp-rust-analyzer-server-display-inlay-hints
(lsp-rust-analyzer-inlay-hints-mode)))
:ignore-messages nil
:server-id 'rust-analyzer-remote)))If you have Emacs 28, due to some compatibility issues, you might have to additionally use:
(defun start-file-process-shell-command@around (start-file-process-shell-command name buffer &rest args)
"Start a program in a subprocess. Return the process object for it. Similar to `start-process-shell-command', but calls `start-file-process'."
;; On remote hosts, the local `shell-file-name' might be useless.
(let ((command (mapconcat 'identity args " ")))
(funcall start-file-process-shell-command name buffer command)))
(advice-add 'start-file-process-shell-command :around #'start-file-process-shell-command@around)(thanks to emacs-lsp/lsp-mode#2514 (comment))
You'll have to have rust-analyzer already installed on the target machine.
cargo-edit provides commands to edit your dependencies quickly.
The rustic commands can be called with prefix C-u if you want to
modify the parameters of a command.
rustic-cargo-addAdd crate to Cargo.toml using 'cargo add'rustic-cargo-rmRemove crate from Cargo.toml using 'cargo rm'rustic-cargo-upgradeUpgrade dependencies as specified in the local manifest file using 'cargo upgrade'
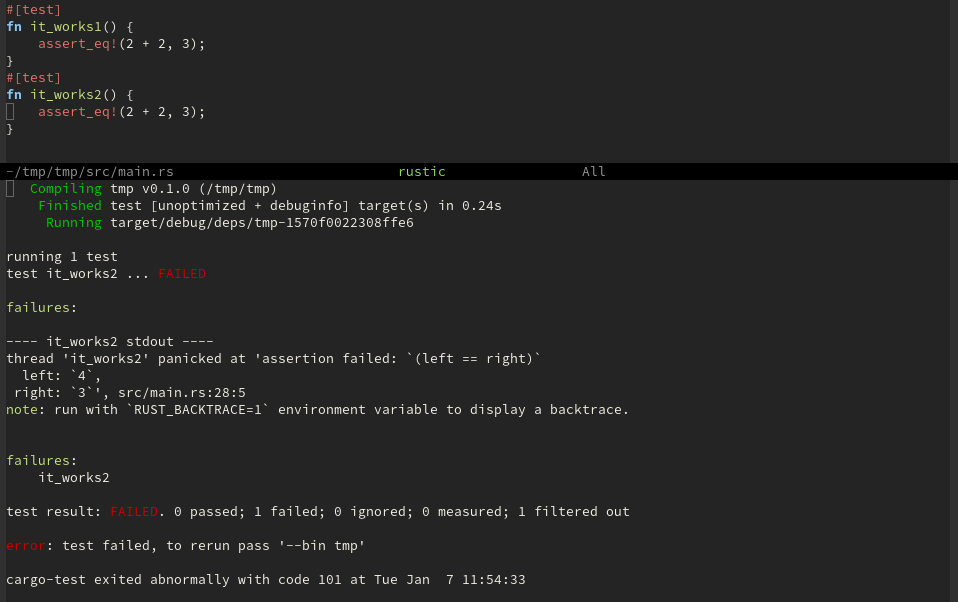
rustic-cargo-test run 'cargo test', when called with C-u store
arguments in rustic-test-arguments
rustic-cargo-test-rerun rerun 'cargo test' with arguments stored in
rustic-test-arguments
rustic-cargo-current-test run test at point, whether it's a function or a module
rustic-cargo-run run 'cargo run'. Input can be sent to the program
in one of two ways:
rustic-compile-send-input, which reads the input from the minibuffer.rustic-cargo-run-use-comint: when this variable is set to t, the input can be typed directly into the output buffer of 'cargo run' and sent off withRET, just like incomint-mode. You need polymode installed for this to work.
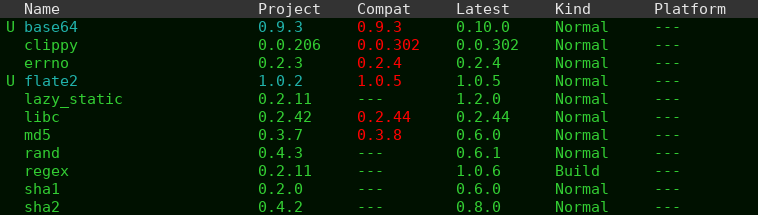
Use rustic-cargo-outdated to get a list of dependencies that are out
of date. The results are displayed in tabulated-list-mode and you
can use most commands you know from the emacs package menu. This
option requires the rust package cargo-outdated to be installed
before being used.
umark single crate for upgradeUmark all upgradable cratesmremove markxperform marked package menu actionsrrefresh crate listqquit window
rustic-cargo-initrun 'cargo init' to initialize a directoryrustic-cargo-newuse 'cargo new' to create a new packagerustic-cargo-benchrun 'cargo bench' for the current projectrustic-cargo-build-docbuild the documentation for the current projectrustic-cargo-docopen the documentation for the current project in a browser
Currently cargo does not display the correct installation command for
some toolchains when clippy isn't installed. If you have problems try
it with rustup component add --toolchain nightly clippy.
rustic-cargo-clippyto view the results in a derived compilation moderustic-cargo-clippy-fixrun 'clippy fix' usingrustic-cargo-clippy-fix-argsthe default value is "--allow-dirty"
In case you want to use clippy with flycheck but without LSP, you can activate
this checker and use the command flycheck-list-errors
(push 'rustic-clippy flycheck-checkers)Turn off flycheck.
(remove-hook 'rustic-mode-hook 'flycheck-mode)The checker automatically detects the active toolchain and applies the correct parameters You can set a default value for both stable and nightly toolchains. These are the default values.
rustic-flycheck-clippy-params-stable"--message-format=json"rustic-flycheck-clippy-params-nightly"--message-format=json -Zunstable-options"
If you are using lsp-mode with rust-analyzer, you can set
lsp-rust-analyzer-cargo-watch-command to clippy instead of
activating the checker rustic-clippy.
Blocks run asynchronously and a running babel process is indicated by
a spinner in the mode-line. It's possible to use crates in babel
blocks. Execute babel block with org-babel-execute-src-block.
Supported org babel parameters:
Write to file :results file :file ~/babel-output
Customization:
rustic-babel-format-src-blockformat block after successful buildrustic-babel-display-compilation-bufferdisplay compilation buffer of babel processrustic-babel-auto-wrap-mainwrap body into main function
You can use lsp in babel blocks with lsp-org.
rustic-babel-format-blockformat block at pointrustic-babel-visit-projectfind generated project of block at point
This block shows how to use crates with the latest version for both serde and regex.
The "*" will be added automatically for serde.
#+BEGIN_SRC rust :crates '(serde (regex . *))
extern crate regex;
extern crate serde;
use regex::Regex;
fn main() {
let re = Regex::new(r"^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}$").unwrap();
assert!(re.is_match("2014-01-01"));
}
#+END_SRC
If specific crate features are required then these can be specified
with the :features argument. Note that if it is just a single feature
then a string, instead of a list, will also be accepted:
#+BEGIN_SRC rust :crates '((tokio . 1.0)) :features '((tokio . ("rt-multi-thread" "time")))
extern crate tokio;
fn main() {
tokio::runtime::Runtime::new()
.unwrap()
.block_on(async {
tokio::time::sleep(tokio::time::Duration::from_millis(10)).await;
});
}
#+END_SRC
Similarly, to depend on local Rust crates, you can set the :paths
argument:
#+BEGIN_SRC rust :crates '((foo . 1.0)) :paths '((foo . "/home/you/code/foo"))
use foo::Foo;
fn main() {
// Your code.
}
#+END_SRC
You can also specify the :toolchain. Remember to quote the value!
#+begin_src rust :toolchain 'nightly
fn main() {
let foo: String = vec!["a", "b", "c"].into_iter().intersperse(",").collect();
println!("{}", foo);
}
#+end_src
#+RESULTS:
: a,b,c
Auto wrap whole block body in a fn main function call if none
exists.
Since this is very handy in most code snippets, so the default value
is yes. no if you don't want this feature(for example, you don't
want regex search slow things down).
You can also set a default value by:
;; By setq this default to `nil`, you'll have to explict set params to ":main yes" in each block
(setq rustic-babel-auto-wrap-main nil)#+begin_src rust :main yes
let x = vec![1, 2, 3].iter().map(|&x| x + 1).collect::<Vec<_>>();
println!("{:?}", x);
#+end_src
#+results:
: [2, 3, 4]
This parameter allows you to run code that is located in different
babel blocks by using named blocks with the :include keyword. This
feature only concats the blocks so you don't need to import the code
you want to use.
You can still use :main to wrap the code of the main block.
#+name: b1
#+begin_src rust
pub fn b1_func() -> String {
String::from("b1 function called")
}
#+end_src
#+name: b2
#+begin_src rust
pub fn b2_func() -> String {
String::from("b2 function called")
}
#+end_src
#+begin_src rust :include '("b1" "b2")
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", b1_func());
println!("{:?}", b2_func());
}
#+end_src
#+RESULTS:
: "b1 function called"
: "b2 function called"
When using this keyword blocks are treated as modules. The files are generated automatically.
#+name: mymodule
#+begin_src rust
pub fn myfunc() -> String {
String::from("mymodule function called")
}
#+end_src
#+begin_src rust :use '("mymodule")
use mymodule::myfunc;
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", myfunc());
}
#+end_src
#+RESULTS:
: "mymodule function called"
In case you want to use a different spinner type you can modify
rustic-spinner-type or turn it off completely with
rustic-display-spinner.(Available spinner
types).
It is possible to read rust documentation inside Emacs! This currently
requires LSP-mode and cargo. 
Required:
- pandoc (preferably at least version 2.11, as it will give somewhat nicer generated documentation)
- cargo
- cargo-makedocs
- fd-find
Optional:
ripgrep and helm-ag are optional but highly recommended.
If only ripgrep is installed, it will be used with the emacs grep
command. In case neither is available, the emacs grep command will
use grep, like in the good old days.
When a required cargo package is missing you will be asked if you want to install them when running rustic-doc-setup.
- Enable
rustic-doc-mode. - Run
rustic-doc-setupto download files that rustic-doc needs to convert rust documentation and also convertstd. - You can now convert package-specific documentation with
rustic-doc-convert-current-package - Search the org files with
rustic-doc-search(bound toC-#by default) if you are inRust mode,Rustic modeorOrg mode. If you hover over a symbol when you invoke the command,rustic-doc-searchwill insert a default value. - Add
universal argumentto only search for level 1 headers like struct or enum names.
You can change the defaults by modifying
rustic-doc-rg-search-commandrustic-doc-search-function
- You should re-run
rustic-doc-setuponce in a while, to update the pandoc filter. - If rustic-doc does not find the documentation for something, the
first thing to do is check the project's
target/docfolder for the corresponding.html-file. If there is no file there, there is nothing for rustic-doc to convert. If there is a file there, please create an issue!
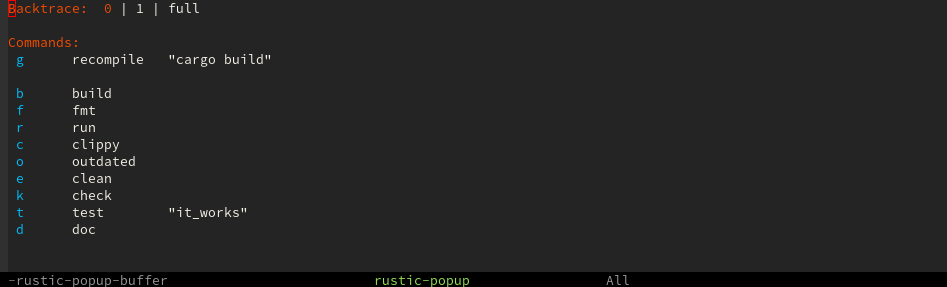
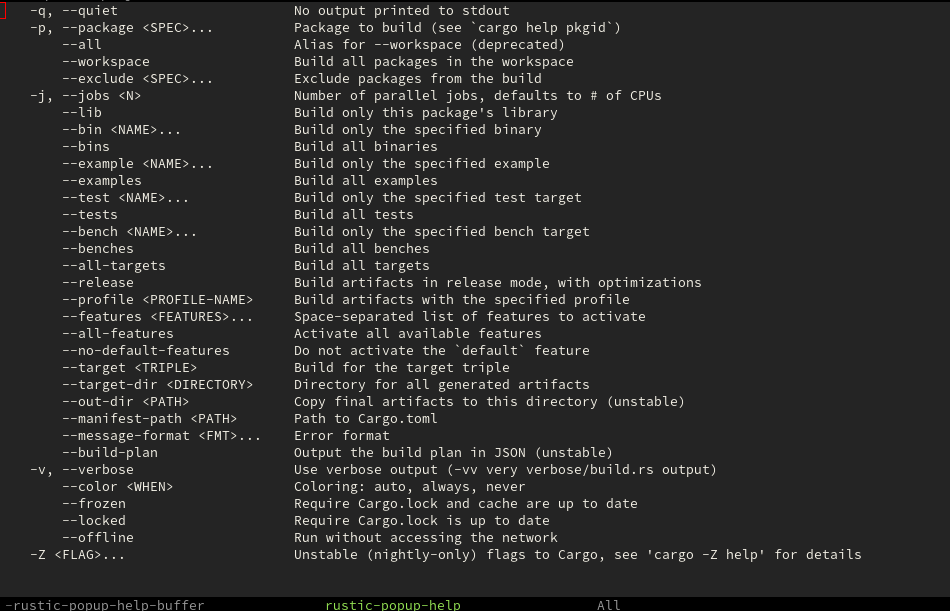
You can execute commands with rustic-popup. The list of commands can
be customized with rustic-popup-commands. The command
rustic-popup-default-action (RET or TAB) allows you to change:
RUST_BACKTRACEenvironment variablecompilation-argumentsforrecompile- arguments for
cargo test
If you want to close the popup after you ran a command you can set
rustic-kill-buffer-and-window to t.
View help buffer containing a command's flags with h:
The rustic mode derives from rust-mode using all of its functionality. However we replace default key bindings and some hooks.
There are also some additional commands:
rust-dbg-wrap-or-unwrapEither remove or add the dbg! macrorust-toggle-mutabilityToggles the mutability of the variable defined on the current linerust-promote-module-into-dirPromote the module file visited by the current buffer into its own directory
To run the tests, you will need Cask.
cask exec ert-runneralternatively you can use make test
PRs, feature requests and bug reports are very welcome. If you want to add a new feature please open an issue in advance so we can discuss the details.