中文 | English
In this program, you can learn about the following
- A quick overview about the classification as well as the characteristics of large language model watermarking techniques
- A quick hands-on TuningScope tutorial to play around with large model watermarking
- Details about large model watermarking, including three different modes of watermarking methods
- Watermark injection and validation performance data, including extra elapsed time and extra video memory usage
- Deployment tutorial, using ChatGLM and GPT-3.5-turbo as examples.
- Methods for building APIs, we provide examples for OpenAI style APIs
- Review of open-source WMs work
- Overview of watermarking techniques for specific domains (e.g. code generation)
- Use of protocols
- ...
If you encounter a problem, please prioritize querying [FAQ] (./question/FAQ.md). If it is still not resolved, feel free to submit an issue (but it is recommended to use English or provide a translation, it provides help to more users). Feel free to submit Pull Requests if you want to help us improve!
If you want to discuss and chat with us, join our WeChat group and Discord (see the beginning of the document for the entrance)!
In this section, we will introduce the three mainstream watermarking methods currently used by the community, including the representative papers corresponding to each method, as well as the analysis of advantages and disadvantages. For more guidelines or analysis of the papers (as well as the roadmap for future implementations), please refer to technology roadmap
At present, we categorize all technical articles included and expected to be realized into (1) Published at conferences. (2) Preprints. (3) Blogs(or product prototypes). (4) Others.
| Watermarking Method Name | Implementation Difficulty | Flexibility | Robustness | Semantic Preservation | Watermarking Bit Limits | Time Cost | Computational Resource Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based | ★ | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | No | Low | Low |
| Inference-time | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★ | No | Middle | High |
| NN-based | ★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★★ | Yes | high | Middle |
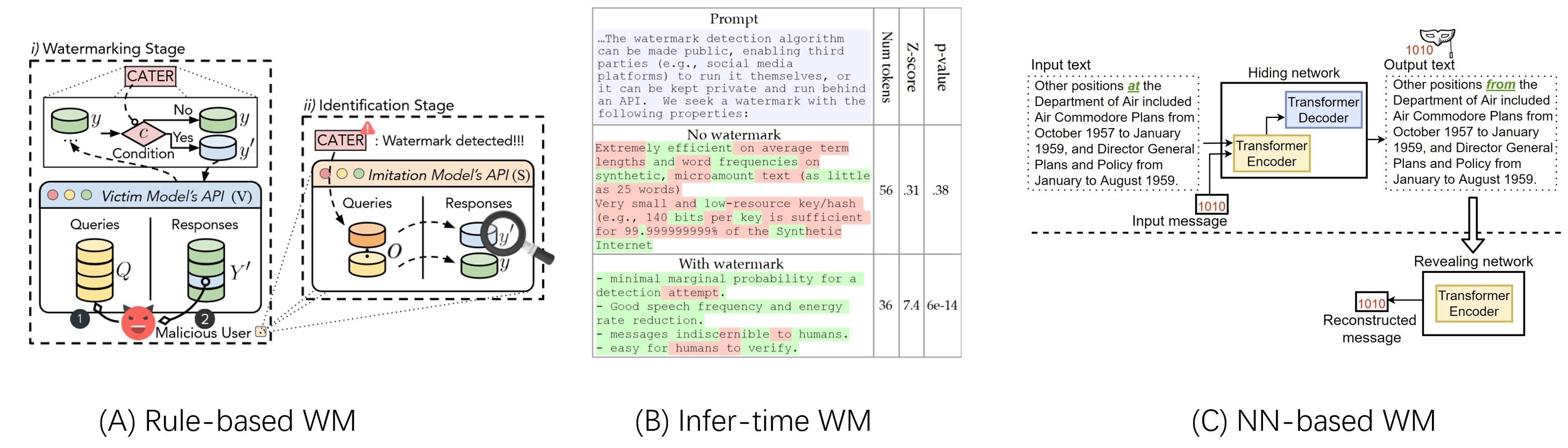
Below are specific technology overview diagrams, three images are copyrighted to the original paper authors
This section focuses on the work of Xuanli He of Monash University [1,2] as a sample of the series of work which has been published in AAAI, NIPS, Impletation
Rule-based watermarking is a text watermarking technique that involves replacing synonyms or transforming syntactic structures in a paragraph to insert watermarks. The manually designed features make the inserted signatures statistically removable through word distribution or syntactical analysis. This method has been used extensively in text watermarking due to its simplicity and ease of implementation. The rule-based approach ensures that the inserted watermark is statistically robust against attacks, making it difficult for attackers to remove the watermark without significantly altering the text's meaning. This technique is particularly useful in situations where the generated text is expected to undergo multiple transformations, such as in the case of machine translation or text summarization. The rule-based watermarking method has several advantages. It is easy to implement and can be applied to any text generation model. Additionally, the inserted watermark is statistically robust, making it difficult to remove without significantly altering the text's meaning. However, this method has some limitations. The inserted watermark is not semantically coherent with the generated text, making it easy to detect. Furthermore, the watermark signature length is limited to the number of synonyms or syntactic structures that can be replaced in the text, hindering its practical usage.
[1] He, Xuanli, et al. "Protecting intellectual property of language generation apis with lexical watermark." Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vol. 36. No. 10. 2022. AAAI 2022
[2] He, Xuanli, et al. "Cater: Intellectual property protection on text generation apis via conditional watermarks." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022): 5431-5445. NIPS 2023
This section focuses on a sample of the work of John Kirchenbauer of the University of Maryland [3], which has been published in ICML 2023, Impletation.
The inference-time watermarking technique is another text watermarking technique that centers on restricting the generated text at the LLM decoding phase. It divides the vocabulary into green/red lists and restricting the LLM decoding to predict the next tokens from the green list. This technique ensures that the inserted watermarks are statistically robust against attacks, making it difficult for attackers to remove the watermark without significantly altering the text's meaning. However, the decoding strategy drastically distorts the semantic similarity between the watermarked and original LLM outputs. Inference-time watermarking has several advantages. The inserted watermark is statistically robust, making it difficult to remove without significantly altering the text's meaning. Additionally, this technique can be applied to any text generation model. However, the decoding strategy significantly distorts the semantic similarity between the watermarked and original LLM outputs, making it easy to detect.
[3] Kirchenbauer, John, et al. "A watermark for large language models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10226 (2023). ICML 2023
This section focuses on a sample of the work of Sahar Abdelnabi of the CISPA Institute [4], which was published in S&P 21, Impletation.
NN-based watermarking is a text watermarking technique that leverages an end-to-end learning technique to integrate the binary watermarking signatures into the LLM-generated texts while maintaining semantic coherence. This method ensures that the inserted watermark is statistically robust against attacks while maintaining semantic coherence with the generated text. However, the maximum encodable signature length per token segment is limited compared with the rule-based and inference-time frameworks, hindering the practical usage of this approach.
NN-based watermarking has several advantages. The inserted watermark is statistically robust, making it difficult to remove without significantly altering the text's meaning. Additionally, this method maintains semantic coherence with the generated text, making it difficult to detect. However, the maximum encodable signature length per token segment is limited, hindering its practical usage. Despite this limitation, neural-based watermarking is a promising solution to tackle issues of asserting ownership of generated output and tracing the source of content.
[4] Abdelnabi, Sahar, and Mario Fritz. "Adversarial watermarking transformer: Towards tracing text provenance with data hiding." 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. S&P 21
In this section, we will introduce the current ** officially published in the top international computer conferences ** watermarking methods for different than dialog text, including the corresponding representative papers of each method and the advantages and disadvantages of the analysis, for more guidelines or analysis of the papers (and the roadmap for future implementation), please refer to Additional Technology Roadmap
| Papers | Research Organizations | Targets | Technology Roadmap | Semantic Preservation | Time Cost | Computational Resource Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSLGuard[1] | CISPA | Encoders | Retrain | - | Medium | High |
| CodeWatermark[2] | HKUST | Code | Rule-based | ★★★★ | low | low |
[1] Cong, Tianshuo, Xinlei He, and Yang Zhang. "SSLGuard: A watermarking scheme for self-supervised learning pre-trained encoders." CCS 2022
[2] Zongjie Li, et al. "Protecting Intellectual Property of Large Language Model-Based Code Generation APIs via Watermarks." CCS 2023
- Python 3.10 or higher
- PyTorch 2.0.1 or higher, recommended version 2.1 or higher
- CUDA 12.2 or higher is recommended (GPU users need to consider this option, otherwise some watermark methods may not be executed or executed too slowly)
We provide a simple example to demonstrate how to use TuningWM with 🤖 TuningScope and 🤗 Transformers.
Before starting, make sure you have configured your environment and installed the relevant code packages. Most importantly, make sure you meet the above requirements and install the relevant dependency libraries.
If you find our work helpful, please cite this repo or give a star!
Researchers can use the TuningScope framework for research activities. Unless otherwise specified (such as referencing third-party content), the content related to different technical analyses in the repository is owned by the project team. If you need to use it, please fill out the Analysis Content Usage Application Form.
We also allow commercial use, please refer to the LICENSE for specific details. If you need to use it for commercial purposes, please fill out the Commercial Application Form.
If you want to leave a message for our development and product teams, please leave the issue.