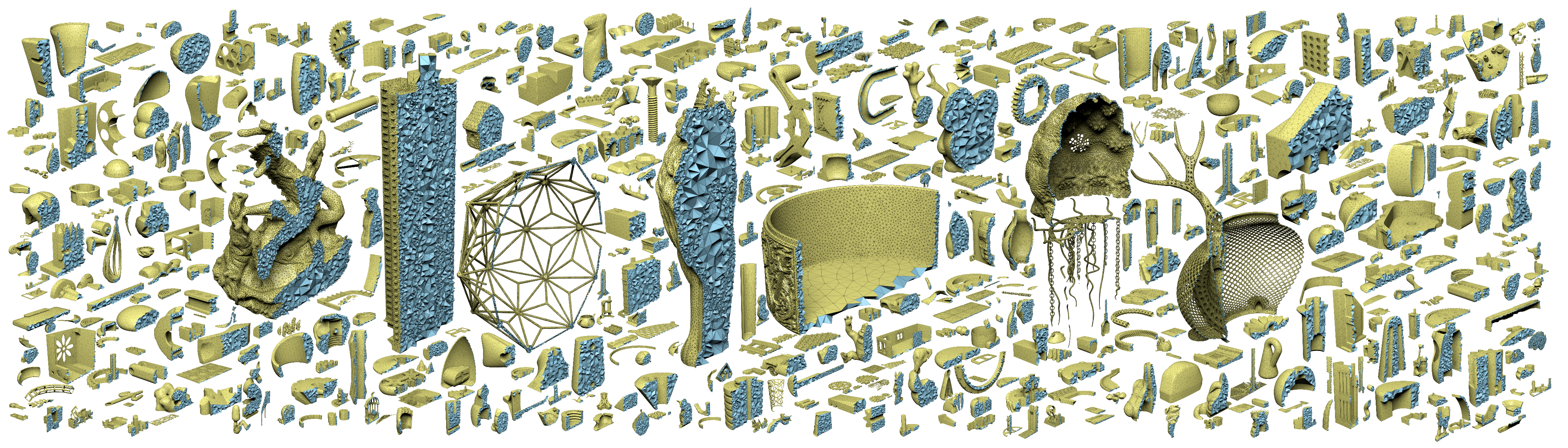 Yixin Hu, Qingnan Zhou, Xifeng Gao, Alec Jacobson, Denis Zorin, Daniele Panozzo.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2018). paper
Yixin Hu, Qingnan Zhou, Xifeng Gao, Alec Jacobson, Denis Zorin, Daniele Panozzo.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2018). paper
Here is pre-generated tetmeshes and the extracted surface meshes for research-purpose usage.
-
Input: Thingi10k
-
Output: 10k tetmeshes, 10k surface meshes
Our code was originally developed on MacOS and has been tested on Lunix and Windows.
- Clone the repository into your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/Yixin-Hu/TetWild --recursive- Compile the code using cmake (default in release mode):
You need to install CGAL before compiling the code.
cd TetWild
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make💡 If you find Could not find Matlab or Could not find Mosek in the output of cmake, it does not matter since they are not used.
The inputs of our software are triangle surface meshes in .off/.obj/.stl/.ply format.
We support .mesh/.msh format output. The default output format is .msh with minimum dihedral angle recorded as element scalar field, which can be visualized by software Gmsh. You can use PyMesh::MshLoader and PyMesh::MshSaver in pymesh/ for read and write .msh meshes.
Our software is quite easy to use. Basically, users only need to provide a surface triangle mesh as input and our mesher would output a tetrahedral mesh by using default settings. If you want to customize your own tetmeshes, we also provide some options.
- Envelope of size epsilon
Using smaller envelope preserves features better but also takes longer time. The default value of epsilon is b/1000, where b is the length of diaginal of bounding box.
- Ideal edge length
Using smaller ideal edge length gives a denser mesh but also takes longer time. The default ideal edge length is b/20
- Filtering energy
Our mesher stops optmizing the mesh when maximum energy is smaller than filtering energy. Thus, larger filtering energy means less optimization and sooner stopping. If you do not care about quality, then give a larger filtering energy would let you get the result earlier. The energy we used here is conformal AMIPS whose range is from 3 to +inf. The default filtering energy is 10.
💡 We suggest not to set filtering energy smaller than 8 for complex input.
- Maximum number of optimzation passes
Our mesher stops optmizing the mesh when the maximum number of passes is reached. The default number is 80.
- Targeted number of vertices
We allow users to input the targeted number of vertices and the mesher would try its best to match that number with 5% error. When the targeted number of vertices is unrealistically small, then the output tetmesh may not have number of vertices matched.
💡 If you want a tetmesh with low resolution, please use larger envelop and larger ideal edge length.
- Sizing field
Users can provide a background tetmesh in .msh format with vertex scalar field values stored. The scalar field values is used for controling edge length. The scalars inside an element of the background mesh are linearly interpolated.
💡 Here is an example including input surface mesh, background mesh and output tetmeshes with/without sizing control.
- Smoothing open regions
Our method can fill gaps and holes but the tetmesh faces on those parts could be bumpy. We provide users an option to do Lapacian smoothing on those faces to get a smoother surface.
Our software only supports usage in commnad line. Here is an overview of all command line switches.
Usage:
./TetWild [options]
Options:
--input <INPUT> Input surface mesh INPUT in .off/.obj/.stl/.ply format. (string, required)
--postfix <POSTFIX> Postfix for output files. (string, optinal, default: '_')
--output <OUTPUT> Output tetmesh OUTPUT in .mesh/.msh format. (string, optional, default: INPUT+POSTFIX+'.msh')
--ideal-edge-length <L> ideal_edge_length = diag_of_bbox / L. (double, optional, default: 20)
--epsilon <EPS> epsilon = diag_of_bbox / EPS. (double, optional, default: 1000)
--stage <STAGE> Run pipeline in stage STAGE. (integer, optional, default: 1)
--filter-energy <ENERGY> Stop mesh improvement when the maximum energy is smaller than ENERGY. (double, optional, default: 10)
--max-pass <PASS> Do PASS mesh improvement passes in maximum. (integer, optional, default: 80)
--is-quiet <Q> Mute log info and only output tetmesh if Q = 1. Otherwise, Q = 0. (integer, optional, default: 0)
--targeted-num-v <TV> Output tetmesh that contains TV vertices. (integer, optinal, tolerance: 5%)
--bg-mesh <BGMESH> Background tetmesh BGMESH in .msh format for applying sizing field. (string, optional)
--is-laplacian <ISLAP> Do Laplacian smoothing for the surface of output on the holes of input, if ISLAP = 1. Otherwise, ISLAP = 0. (integer, optinal, default: 0)
We provide a wrapper for TetWild in tetwild.h, allowing users do the tetrahedaliztion without read/write data from/to files. One can use it in the following way:
-
Include the header file
tetwild.h. -
Set parameters through a struct variable
tetwild::parameters. The following table provides the correspondence between parameters and command line switches.Switch Parameter --input N/A --postfix N/A --output N/A --ideal-edge-length parameters.i_ideal_edge_length--epsilon parameters.i_epsilon--stage parameters.stage--filter-energy parameters.filter_energy--max-pass parameters.max_pass--is-quiet parameters.is_quiet--targeted-num-v parameters.targeted_num_v--bg-mesh parameters.bg_mesh--is-laplacian parameters.is_laplacian -
Call function
tetwild::tetrahedralization(v_in, f_in, v_out, t_out)by providing the input verticesv_in, input triangle facesf_in, output verticesv_out, and output tetrahedrat_outin the following data type:Variable Type v_inconst std::vector<std::array<double, 3>>&f_inconst std::vector<std::array<int, 3>>&v_outstd::vector<std::array<double, 3>>&t_outstd::vector<std::array<int, 4>>&
TetWild is MPL2 licensed. But it contains CGAL code under GPL license. We're currently working on replacing these pieces of code.
We used several useful libraries in our implement, testing, and rendering listed as follows. We would like to especially thank their authors for their great work and publishing the code.