Segmentation tools based on the graph cut algorithm. You can see video to get an idea. There are two algorithms implemented. Classic 3D Graph-Cut with regular grid and Multiscale Graph-Cut for segmentation of compact objects.
please cite:
@INPROCEEDINGS{jirik2013,
author = {Jirik, M. and Lukes, V. and Svobodova, M. and Zelezny, M.},
title = {Image Segmentation in Medical Imaging via Graph-Cuts.},
year = {2013},
journal = {11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis: New Information Technologies (PRIA-11-2013). Samara, Conference Proceedings },
url = {http://www.kky.zcu.cz/en/publications/JirikMmjirik_2013_ImageSegmentationin},
}
- Miroslav Jirik
- Vladimir Lukes
See third party licenses
https://github.com/mjirik/imcut
https://github.com/amueller/gco_python
New BSD License, see the LICENSE file.
conda install -c mjirik -c conda-forge imcut pygco
Sometimes (on Linux) you will need to install pygco with pip
conda install pip
pip install pygco
pip install pygco imcut
See INSTALL.md file for more information
conda install -c mjirik -c conda-forge seededitorqt
The intensity of the seed is used to train the intensity model based on the Gaussian mixture. The location of the voxel is used to set a hard constraint in the graph.
- 0 - we have no information about this voxel
- 1 - for sure, the voxel on the same location in the image data is the segmented object
- 2 - for sure, the voxel on the same location in the image data is the background
There are two more types used when the voxel is object or background but you dont want to use it for intensity model training because its intensity is not good representation.
- 3 the voxel is the object but we do not want to use it for intensity training
- 4 the voxel is the background but we do not want to use it for intensity training
The output segmentation:
- 0 - trained from
seeds==1(object) - 1 - trained from
seeds==2(background)
The only difference between object and background is in the postprocessing with the connected object filter.
It can be turned off by setting "return_only_object_with_seeds":True in segparams.
import imcut.pycut
import numpy as np
im = np.random.random([5, 5, 1])
im[:3, :3] += 1.
seeds = np.zeros([5, 5, 1], dtype=np.uint8)
seeds[:3,0] = 1 # foreground
seeds[:3,4] = 2 # background
gc = imcut.pycut.ImageGraphCut(im)
gc.set_seeds(seeds)
gc.run()
print(gc.segmentation.squeeze())[[0 0 0 1 1]
[0 0 0 1 1]
[0 0 0 1 1]
[1 1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1 1]]
Create output.mat file:
python imcut/dcmreaddata.py -i directoryWithDicomFiles --degrad 4
See data:
python imcut/seed_editor_qt.py -f output.mat
Make graph_cut:
python imcut/pycut.py -i output.mat
import numpy as np
import imcut.pycut as pspc
data = np.random.rand(30, 30, 30)
data[10:20, 5:15, 3:13] += 1
data = data * 30
data = data.astype(np.int16)
igc = pspc.ImageGraphCut(data, voxelsize=[1, 1, 1])
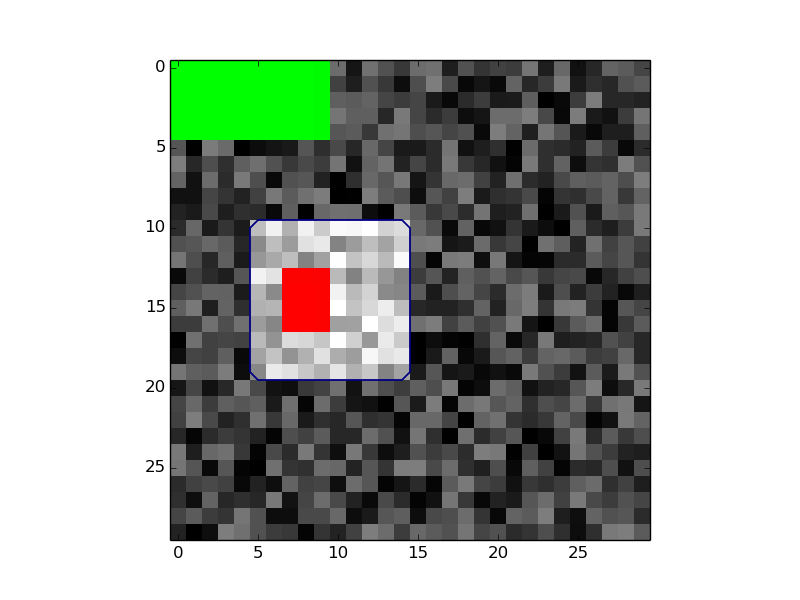
seeds = igc.interactivity()import numpy as np
import imcut.pycut as pspc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create data
data = np.random.rand(30, 30, 30)
data[10:20, 5:15, 3:13] += 1
data = data * 30
data = data.astype(np.int16)
# Make seeds
seeds = np.zeros([30,30,30])
seeds[13:17, 7:10, 5:11] = 1
seeds[0:5:, 0:10, 0:11] = 2
# Run
igc = pspc.ImageGraphCut(data, voxelsize=[1, 1, 1])
igc.set_seeds(seeds)
igc.run()
# Show results
colormap = plt.cm.get_cmap('brg')
colormap._init()
colormap._lut[:1:,3]=0
plt.imshow(data[:, :, 10], cmap='gray')
plt.contour(igc.segmentation[:, :,10], levels=[0.5])
plt.imshow(igc.seeds[:, :, 10], cmap=colormap, interpolation='none')
plt.show()
- Pretrain the model to make things faster
- Use additional information about pixels
- Use custom feature vector
- See the likelihood in image and use different density functions
- Use custom density functions
pairwise_alpha control the complexity of the object shape. Higher pairwise_alpha => more compact shape.
segparams = {
'method': 'graphcut',
"pairwise_alpha": 20,
'modelparams': {
'cvtype': 'full',
"params": {"covariance_type": "full", "n_components": 1},
},
"return_only_object_with_seeds": True,
}segparams = {
# 'method':'graphcut',
'method': 'graphcut',
'use_boundary_penalties': False,
'boundary_dilatation_distance': 2,
'boundary_penalties_weight': 1,
'modelparams': {
'type': 'gmmsame',
'fv_type': "fv_extern",
'fv_extern': fv_function,
'adaptation': 'original_data',
},
'mdl_stored_file': False,
}mdl_stored_file: if this is set, load model from file, you can see more in function test_external_fv_with_save in pycut_test.py