JCSG
Java implementation of BSP based CSG (Constructive Solid Geometry). It is the only simple and free Java implementation I am aware of. This implementation uses an optimized CSG algorithm based on csg.js (see CSG and Node classes). Thanks to the author for creating the csg.js library.
In addition to CSG this library provides the following features:
- optimized
difference()andunion()operations (many thanks to Sebastian Reiter) - extrusion of concave, non-intersecting polygons (uses Poly2Tri for triangulation)
- convex hull (uses QuickHull3D)
- weighted transformations (Scale, Rotation, Translation and Mirror)
- STL import and export (STLLoader from Fiji)
- OBJ export including material information (see screenshot below)
- supports conversion of CSG's to
JavaFX 3Dnodes
To see what's possible with JCSG try JFXScad.
How to Build JCSG
Requirements
- Java >= 1.8
- Internet connection (dependencies are downloaded automatically)
- IDE: Gradle Plugin (not necessary for command line usage)
IDE
Open the JCSG Gradle project in your favourite IDE (tested with NetBeans 7.4) and build it
by calling the assemble task.
Command Line
Navigate to the Gradle project (e.g., path/to/JCSG) and enter the following command
Bash (Linux/OS X/Cygwin/other Unix-like shell)
sh gradlew assemble
Windows (CMD)
gradlew assemble
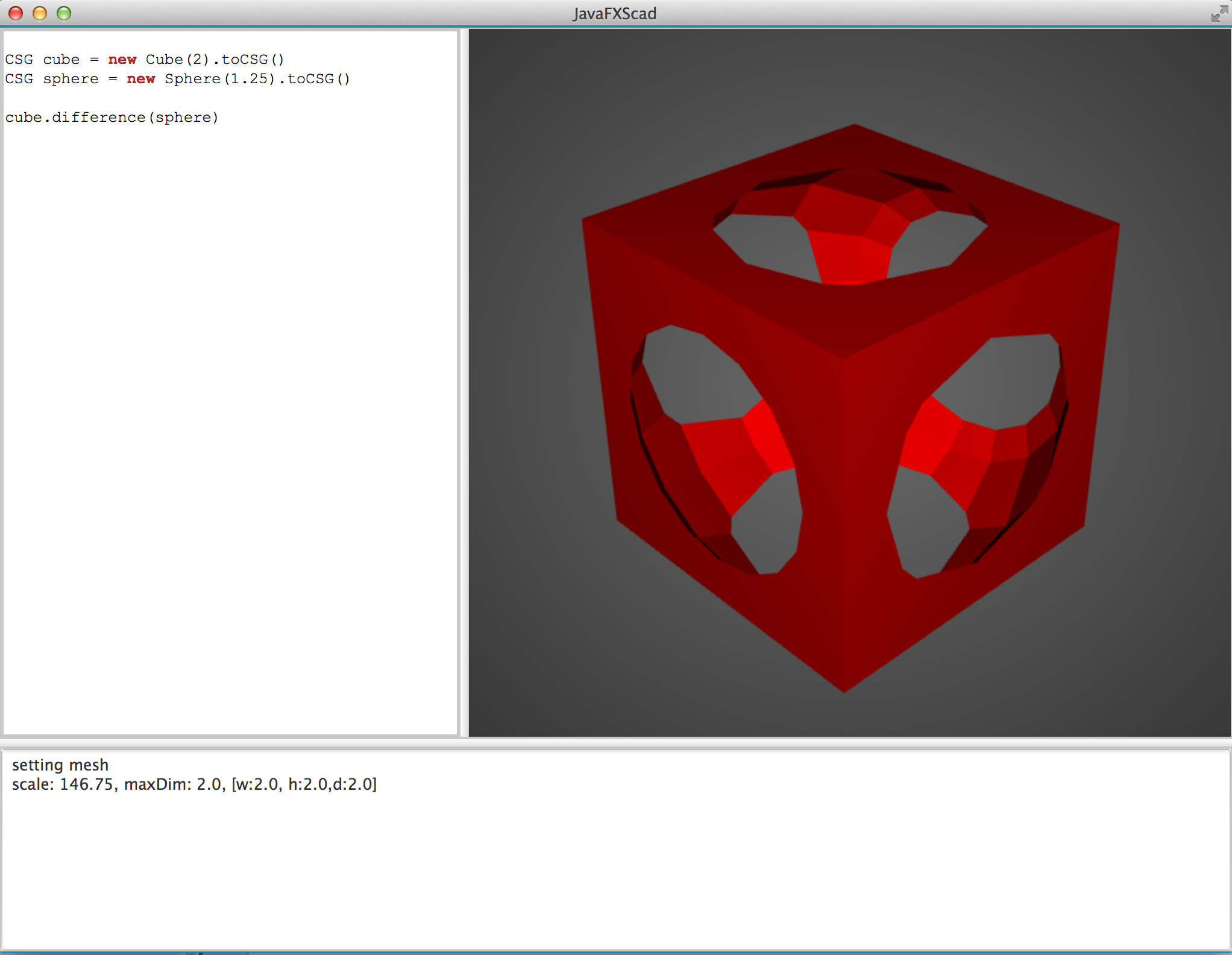
Code Sample:
// we use cube and sphere as base geometries
CSG cube = new Cube(2).toCSG();
CSG sphere = new Sphere(1.25).toCSG();
// perform union, difference and intersection
CSG cubePlusSphere = cube.union(sphere);
CSG cubeMinusSphere = cube.difference(sphere);
CSG cubeIntersectSphere = cube.intersect(sphere);
// translate geometries to prevent overlapping
CSG union = cube.
union(sphere.transformed(Transform.unity().translateX(3))).
union(cubePlusSphere.transformed(Transform.unity().translateX(6))).
union(cubeMinusSphere.transformed(Transform.unity().translateX(9))).
union(cubeIntersectSphere.transformed(Transform.unity().translateX(12)));
// save union as stl
try {
FileUtil.write(
Paths.get("sample.stl"),
union.toStlString()
);
} catch (IOException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Main.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}