A tutorial on setting up Dokku on your local machine via Vagrant and on AWS EC2. Thanks to this article for teaching me how to do this.
-
Clone the Dokku repo to your local machine
git clone git@github.com:dokku/dokku.git -
Install Vagrant (I suggest installing via brew cask)
brew cask install vagrant -
Install VirtualBox in order to set up Vagrant
brew cask install virtualbox -
(Optional) I would also install Vagrant Manager to manage your Vagrant machines
brew cask install vagrant-manager
For this tutorial, I'm going to use an Express app as an example. You can clone the example app repo here.
The folder name should be express-example and we will use this name as our project name for the tutorial.
-
Create the Vagrant virtual machine by changing directory to your local Dokku repo
cd /path/to/local/dokku -
Create a Vagrant virtual machine with Dokku!
vagrant up -
You want to set the local IP (default is 10.0.0.2) of your Vagrant machine in your
/etc/hostsfile and pick a hostname. For this tutorial, we will use the hostnamedokku.me
10.0.0.2 dokku.me
-
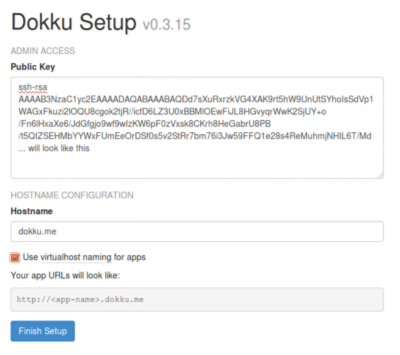
Access dokku.me on your browser.
-
Paste your ssh public key, found at
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. This ssh public key should be the same key you used to clone the example app. -
Set
Hostnametodokku.me -
Check
Use virtualhost naming for appsThis will allow you to access<project-name>.dokku.me -
Edit your
/etc/hostsfile and add another host
10.0.0.2 express-example.dokku.me
-
Add the new Dokku instance as a git remote to our example app so we can start pushing changes locally to Dokku on our local Vagrant virtual machine.
git remote add local dokku@dokku.me:express-example -
Make a change to your view in the Express example app and push your changes
git push local master
Now we're going to set up Dokku on our AWS EC2 server so we can push our changes remotely to our server.
-
Launch a new instance for EC2.
-
From the Quick Start page, select the Ubuntu Server machine image.

-
Select any instance type. For this tutorial, you probably want to select the
t2.microtype, since it is eligible for free tier users. -
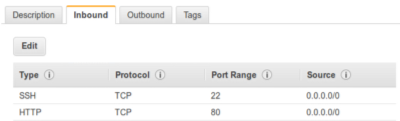
Configure your security group by adding types:
-
Launch your new instance and download the
.pemfile for ssh access. -
Once you have launched your instance, get it's public IP and add it to your
/etc/hostsfile. We will use the hostnamedokku.aws.me
<instance's public IP> dokku.aws.me
-
SSH into your EC2 instance
ssh -i /path/to/file.pem ubuntu@dokku.aws.me -
Install Dokku via
wget
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/progrium/dokku/v0.4.5/bootstrap.sh
sudo DOKKU_TAG=v0.4.5 bash -
Once Dokku is installed, access dokku.aws.me on your browser.

-
Paste the same ssh public key as before, from
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub -
Set
Hostnametodokku.aws.me -
Check
Use virtualhost naming for apps -
Add another hostname to your
/etc/hostsfile.
<instance's public IP> express-example.dokku.aws.me
-
Add the EC2 instance as a git remote to our example app so we can start pushing changes remotely to Dokku on our EC2 Ubuntu server.
git remote add aws dokku@dokku.aws.me:express-example -
Make a change to your view in the Express example app and push your changes
git push aws master
You can now see your changes on http://express-example.dokku.aws.me! By having Dokku set up on our local machine via Vagrant and on EC2, we now have two environments to push and deploy our app.
I'm still learning how to use Dokku so if there are any errors, please let me know!