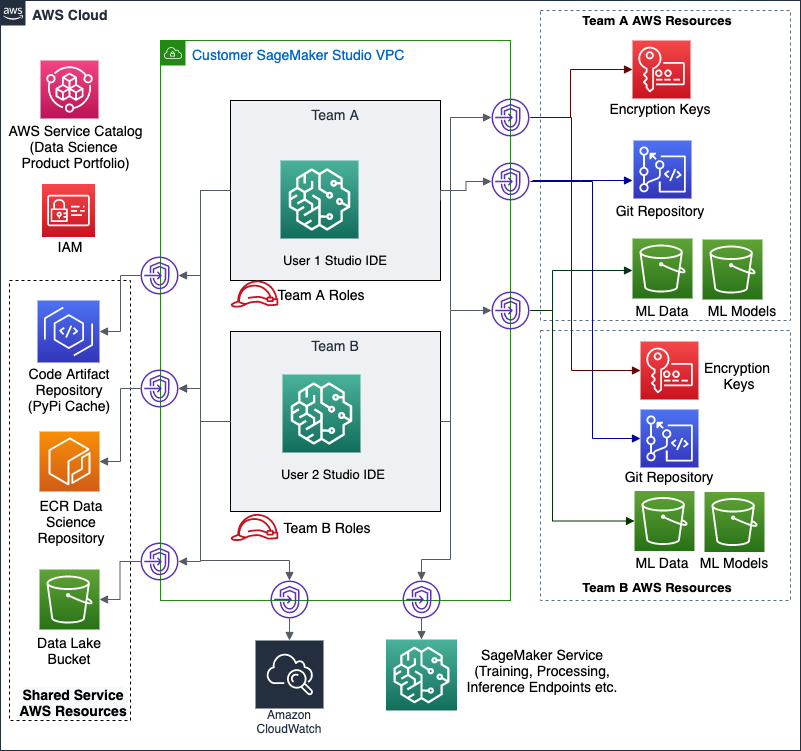
Amazon SageMaker is a powerful enabler and a key component of a data science environment, but it’s only part of what is required to build a complete and secure data science environment. For more robust security you will need other AWS services such as AWS VPC, AWS IAM, AWS KMS, Amazon CloudWatch, Amazon S3, and AWS Service Catalog just to name a few. This project aims to be an example of how to pull together these services, to use them together to create secure, self-service, data science environments.
This github repository is a companion to the Secure Data Science with Amazon SageMaker Studio Workshop. You can find detailed instructions for using the content of this github repository in the workshop.
This repository contains the following files:
├── code_artifact_login.sh # Bash shell script to obtain a new AWS CodeArtifact token to install pre-approved pip packages
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md # Guidance for participating in this open source project
├── CONTRIBUTING.md # Guidelines for contributing to this project
├── create-presigned-url.sh # Bash shell script to create pre-signed url for a user
├── install_code_artifact_pip_packages.sh # Bash shell script to install pre-approved pip packages
├── LICENSE # Details for the MIT-0 license
├── publish_cloudformation.sh # Bash shell script to package and prepare CloudFormation for deployment
├── pre-signedurl-input.json # AWS cli input json for use with create-presigned-url.sh
├── README.md # This readme
├── cloudformation
│ ├── ds_admin_detective.yaml # Deploys a detective control to manage SageMaker resources
│ ├── ds_admin_principals.yaml # Deploys the Data Science Administrator role
│ ├── ds_administration.yaml # Deploys nested stacks
│ ├── ds_env_backing_store.yaml # Deploys a team's S3 buckets and CodeCommit repository
│ ├── ds_env_principals.yaml # Creates a data science administrator and user
│ ├── ds_env_sagemaker_studio.yaml # Onboards the SageMaker Studio domain in a VPC
│ ├── ds_env_studio_user_profile_v1.yaml # Onboards a SageMaker Studio domain user profile for a team
│ ├── ds_env_studio_user_profile_v2.yaml # Onboards a SageMaker Studio domain user profile for a team with preventative control
│ ├── ds_environment.yaml # Manages nested stacks for a team
│ ├── ds_shared_code_artifact.yaml # Creates shared CodeArtifact repository for the data science environment
│ ├── ds_shared_ecr.yaml # Creates shared ECR repository for the data science environment
│ └── ds_shared_sagemaker_network.yaml # Creates a shared services VPC with private subnets and no Internet access
├── customimage
│ └── jupyter-docker-stacks-tensorflow # SageMaker custom image tensforflow 2.4.1 built with Jupyter docker stacks
│ │ ├── app-image-config-input.json # AWS cli input json for use with create-and-attach-image.sh
│ │ ├── build-publish-sm-docker-image.sh # Bash shell script to build the custom image, publish to ECR
│ │ ├── create-and-attach-image.sh # Bash shell script to build the custom image, publish to ECR and attach to a SageMaker Studio domain
│ │ ├── Dockerfile # Docker file for custom image
│ │ └── update-domain-input.json # AWS cli input json for use with create-and-attach-image.sh
│ └── tensorflow25 # SageMaker custom image tensforflow 2.5.0 built with official Tensorflow docker image
│ │ ├── app-image-config-input.json # AWS cli input json for use with create-and-attach-image.sh
│ │ ├── build-publish-sm-docker-image.sh # Bash shell script to build the custom image, publish to ECR
│ │ ├── create-and-attach-image.sh # Bash shell script to build the custom image, publish to ECR and attach to a SageMaker Studio domain
│ │ ├── Dockerfile # Docker file for custom image
│ │ └── update-domain-input.json # AWS cli input json for use with create-and-attach-image.sh
│ ├── code-artifact-login.sh # Bash shell script to obtain a new AWS CodeArtifact token inside SageMaker Studio docker image
│ ├── setup-ds-env.sh # Bash shell script to setup data science environment inside SageMaker Studio docker image
├── docs
│ └── images
│ └── hla.png # High Level Architecture diagram
└── src
├── detective_control
│ └── inspect_sagemaker_resource.py # Lambda function to detect non-VPC-attached SageMaker resources
└── project_template
├── 00_SageMaker-SysOps-Workflow.ipynb # Sample Jupyter notebbok to demonstrate security controls
├── 01_SageMaker-DataScientist-Workflow.ipynb # Sample Jupyter notebook to demonstrate secure ML lifecycle
├── 02_SageMaker-DevOps-Workflow.ipynb # Second half of a secure ML lifecycle
├── util
├── __init__.py
└── utilsspec.pyThe diagram represents high level architecture of the secure data science environment provisioned by the CloudFormation templates in this project.
Once deployed, this CloudFormation stack provides you with a Data Science Product Portfolio, powered by AWS Service Catalog. This allows users who have assumed the Data Science Administrator role to onboard SageMaker Studio domain using the SageMaker Studio Product, deploy new data science environments using the Data Science Team Environment product and onboard new users to the SageMaker Studio domain for a data science team using Data Science Studio User Profile product within the catalog. Note that the SageMaker Studio domain is onboarded only once in a region in an AWS Account.
Data Science Administrators can onboard SageMaker Studio only with network access type VPC only by specifying Studio domain name, and custom SageMaker image properties. AWS Service Catalog will then onboard SageMaker Studio to the shared service VPC:
- A private, isolated, dedicated network environment built using an Amazon VPC.
- Private connectivity to specific AWS services such as AWS CodeArtifact, AWS ECR, AWS KMS, Amazon S3, SageMaker services, AWS CodeCommit to name a few. Since SageMaker Studio is onboarded in a VPCOnly mode, it is required to use VPC Interface Endpoints to access AWS services.
Data Science Administrators can specify a team name, the environment type, and a few other criteria to launch the data science environment. AWS Service Catalog will then create a data science team environment consisting of:
- Private, dedicated Amazon S3 buckets for a team's data and intellectual property
- A team Git repository hosted by AWS CodeCommit
- Team-specific encryption keys managed by AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
- Dedicated AWS Identity & Access Management (IAM) roles for team resources
To use the data science team environment, a data science team member can assume the Data Science Administrator role or the Data Scientist User role. Once they have assumed a Data Science Administrator role users can provision AWS resources for which the role provides permissions within the data science team environment. Similarly, once a user has assumed Data Scientist user role, they can launch Amazon SageMaker Studio IDE and launch Studio notebook from the Studio IDE.
When SageMaker Studio IDE starts it starts Amazon SageMaker Studio-powered apps such as a Jupyter Server. You will use a custom SageMaker image to configure SageMaker Studio KernelGateway app environment to work within the secure data science team environment:
- When Studio UserProfile is created for a user, an IAM role is associated with the Studio UserProfile with permissions to access only team resources
- Access to a KMS-encrypted Amazon S3 bucket
- Access to a KMS encryption key for encrypting data and models stored in S3 buckets
- Studio notebook apps have no access to network resources outside of the shared service VPC
- The Studio notebook apps access AWS resources using the VPC Interface Endpoints configured for the shared service VPC
- User access to host
rootpermissions is disabled by SageMaker Studio - A convenience Python module generated with constants defined for AWS KMS key IDs, VPC Subnet IDs, and Security Group IDs is placed in a custom SageMaker docker image to setup data science for all SageMaker images (prebuilt or custom)
- An AWS Account.
- An AWS user with Admin role (with
AdministratorAccesspolicy attached). - AWS CLI is installed on your developer machine.
- Docker CLI is installed on your developer machine.
- Git CLI is installed on your developer machine.
- Access to Docker Hub.
- Unix like environment - Linux or MacOS.
We recommend that you use AWS Cloud9 as it will get you going fastest with all the tools preinstalled. Cloud9 is a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) that lets you write, run, and debug your code with just a browser. It includes a code editor, debugger, and terminal. Cloud9 comes prepackaged with essential tools for development and includes AWS CLI, docker, git and much more. Cloud9 runs on an Amazon EC2 instance with Amazon Linux 2 by default.
This project builds custom SageMaker Studio images and requires access to docker hub in order to build custom docker images.
Assuming you are signed into the AWS console with Admin role, follow instructions to setup Cloud9
as an Individual User by accepting all defaults. Launch Cloud9 IDE by clicking on Open IDE
after your Cloud9 environment is ready. If you have used any IDE before then Cloud9 should feel very familiar. You can take
a quick tour of the Cloud9 if needed to get
familiar with the UI. In particular how to launch a bash shell terminal which is straight forward, use top menu
Window -> New Terminal. Most of the tasks will be executed in a bash shell by Cloud Platform Engineering team.
Following setups are needed before you can deploy the Shared Service infrastructure:
- Increase disk space for the Cloud 9 environment to 30 GB using instructions for resizing Cloud9 EBS volume. You should restart the Cloud9
environment after increasing disk size by executing
sudo rebooton bash terminal of the IDE. - Install jq for JSON processing on command line and bash-completion:
sudo yum -y install jq bash-completion
- Set up AWS_DEFAULT_REGION and AWS_ACCOUNT_ID environment variables for your bash shell environment:
echo "export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=`curl -s http://169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document|jq -r .region`" >> ~/.bash_profile echo "export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=`curl -s http://169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document|jq -r .accountId`" >> ~/.bash_profile . ~/.bash_profile
- Clone this repo in Cloud9 IDE:
cd ~/environment # Internal only git clone https://gitlab.aws.dev/aws-ai-machine-learning-tfc/secure-data-science-with-sagemaker-studio.git # Actual public repo git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/secure-data-science-with-sagemaker-studio.git
With Cloud9 environment setup complete, you can deploy the Shared Service data science infrastructure.
Upload CloudFormation templates to S3 bucket in your account: Use Cloud9 bash shell to execute the steps below:
cd ~/environment/secure-data-science-with-sagemaker-studio- Check that AWS_DEFAULT_REGION, AWS_ACCOUNT_ID environment variables are set in your Cloud9 bash shell, these environment
variables were configured above:
echo $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION, this should print your AWS region where Cloud9 is running.echo $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID, this should print your AWS account number.- If any of the variable are not set, follow the instructions provided earlier.
- Upload cloudformation templates to S3 bucket in the target region by running
./package_cloudformation.shscript:- Review Script: You can review the script by double-clicking on
package_cloudformation.shfile to open in Cloud9 IDE. - Upload CloudFormation templates to S3 bucket: run
./package_cloudformation.shin bash terminal tab.- When complete all the cloud formation templates needed to create infrastructure for the workshop is in an S3 bucket printed by the script. Make note of this S3 bucket name. You can use Amazon S3 console to see the contents of this bucket.
- When the script is done, it will print a command to run create-stack using
ds_administration.yamltemplate.
- Review Script: You can review the script by double-clicking on
Deploy Shared Service infrastructure for data science teams:
As Cloud Platform Engineering team member with AWS Administration role, you will now deploy the Shared Service infrastructure.
- Deploy Shared Service infrastructure by creating the CloudFormation stack using AWS CLI, this command will use
ds_administration.yamlCloudFormation template. Run the command printed from previous step, it will look like this:aws cloudformation create-stack \ --template-url https://s3.${REGION}.amazonaws.com/${CFN_BUCKET_NAME}/${PROJECT_NAME}/ds_administration.yaml \ --region ${REGION} --stack-name secure-ds-shared-service \ --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \ --parameters ParameterKey=QuickstartMode,ParameterValue=true
After approximately 5-7 minutes the stack will have deployed a Shared Services VPC with private subnets and no Internet access, a Amazon Elastic Container Registry repository, a AWS CodeArtifact repository to be leveraged across all data science environments. ECR repository is a shared resource to host pre-approved SageMaker container images. Similarly, CodeArtifact repository is for hosting pre-approved Python packages within your network. This step also installs AWS Service Catalog products for Data Science administrator and Data Science users along with required IAM Roles.
There are three additional steps required as AWS admin before proceeding to Step 2:
Use Cloud9 bash shell to execute the steps below.
-
Build and publish a custom SageMaker docker image to Elastic Container repository:
cd ~/environment/secure-data-science-with-sagemaker-studio.- Change directory to custom images:
cd customimage/jupyter-docker-stacks-tensorflow. - Run the script from bash terminal tab:
./build-publish-sm-docker-image.shfrom thecustomimage/jupyter-docker-stacks-tensorflowdirectory. - Verify that custom SageMaker docker image was uploaded to ECR: Visit ECR console in AWS Management Console, once there:
- Click on
Repositorieslink in left navigation panel underAmazon ECRsection. - Click on
ds-shared-container-imagesin the list of Repositories in the Private tab of main window. This repository was created by Cloud Formation template earlier. This is the data science shared ECR repository for hosting custom SageMaker docker images. - Notice the custom SageMaker docker image named
ds-custom-tensorflow241underImagesthat you built and pushed in previous step.
- Click on
-
Install PIP packages from public PyPI repository to CodeArtifact repository:
cd ~/environment/secure-data-science-with-sagemaker-studio.- Obtain CodeArtifact token: Now run the script from bash terminal tab:
./code_artifact_login.sh. You should see a message stating successfully configured pip to use AWS CodeArtifact repository and login expires in 12 hours. - Install Python packages: With pip configured, run the script to install approved Python packages from bash terminal tab:
./install_code_artifact_pip_packages.sh. This script demonstrates installation of approved Python packages by data science administrators. Examine the Python packages installed by the script. - Verify that Python packages were installed: Visit Code Artifact console in AWS Management Console, once there:
- Click on
Repositorieslink in left navigation bar - Click on
ds-shared-repoin the list of Repositories in the main window. - Notice the Python packages under
Packagessection.
- Click on
-
Upload Dataset for use in Python notebooks to the S3 data lake bucket: For the notebooks in the labs, you will use the public Credit Card default dataset from UCI Machine Learning repository and referenced in:
Yeh, I. C., & Lien, C. H. (2009). The comparisons of data mining techniques for the predictive accuracy of probability of default of credit card clients. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2), 2473-2480.
- Download the
Credit Card default dataset:curl -o credit_card_default_data.xls https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00350/default%20of%20credit%20card%20clients.xls
- Upload the dataset to S3 data lake bucket:
- Obtain the S3 data lake bucket name
export S3_DATA_LAKE=`aws s3 ls | grep ds-data-lake- | awk '{print $3}'`
- Upload the data using the following command:
aws s3 cp credit_card_default_data.xls s3://${S3_DATA_LAKE}/secure-sagemaker-demo/credit-card-default/credit_card_default_data.xls
- Obtain the S3 data lake bucket name
- Download the
With dataset uploaded to S3 data lake bucket, you can start using the Python notebooks and follow instructions in the notebook.
To access the service catalog portfolio click the Outputs tab of the CloudFormation stack and use the AssumeDataScienceAdminRole link to become a Data Science administrator,
capable of onboarding Amazon SageMaker Studio domain to the AWS account configured to use a Shared Service VPC,
creating data science team environments and adding new SageMaker Studio user profiles for the data science teams.
Once you've assumed the role you can visit the AWS Service Catalog console
to onboard SageMaker Studio, deploy a data science environment and onboard users to SageMaker Studio domain.
You keep parameters tab from ds_administration stack deployed in step 1 above in CloudFormation console open as you will need value that you provided earlier.
Onboard SageMaker Studio domain: This is a one time activity. Click the context menu icon next to the SageMaker Studio Product product
and click Launch product. After you provide a name for the product launch, provide values as below for following parameters, click Launch:
- StudioDomainName:
ds-studio-domain(this is default) - SharedServiceStackSetName:
DSSharedServices(this is default) - CustomImageEcrUri:
ECR URI for the custom SageMaker docker image published in Step 1e.g. ACCOUNT_NUMBER.dkr.ecr.REGION.amazonaws.com/sm-studio-workshop:ds-custom-tensorflow-2.4.1. - CustomImageName:
ds-custom-tensorflow241 - CustomImageDescription:
Custom TensorFlow v2.4.1 Image - AppImageConfigName:
ds-tensorflow241-image-config - KernelSpecsName:
python3 - KernelSpecsDisplayName:
Python 3 (TensorFlow 2.4.1)
This will launch a CloudFormation stack to provision the data science environment.
This will require about 10 minutes to execute.
Create a Data Science team Environment: Visit Service Catalog console and click the context menu icon next to the Data Science team Environment product
and click Launch product. After you provide a name for the product launch, and provide a team name, click Launch and
you will have created your first data science team environment. This will launch a CloudFormation stack to provision the
data science environment. This will require about 5-7 minutes to execute.
Onboard a user profile to SageMaker Studio domain for the Data Science Team Environment: Visit Service Catalog console and click
the context menu icon next to the Data Science User Profile product and click Launch product. After you provide a name for the product launch,
provide values for following parameters, click Launch:
- StudioUserProfileName:
userprofile name, this will be the data science user. - SharedServiceStackSetName:
DSSharedServices(this is default). - TeamName:
team name, from previous step, the data science environment i.e. team you want to on-board a new user to. - EnvType:
dev(this is default), the data science environment for the team you want to on-board a new user to.
This will launch a CloudFormation stack to provision a new SageMaker user profile to data science environment.
This will require about 1-2 minutes to execute.
When the data science team environment has completed its deployment you will have 2 links available from the Service Catalog
console to assume user roles in the data science environment. Click on the AssumeDataScientistUserRole. Goto SageMaker console, click on
Amazon SageMaker Studio on the left navigation bar, this will open SageMaker Studio Control Panel. Click Open Studio next to user name
created in previous step to launch the SageMaker Studio IDE. First launch will take about 10 minutes as SageMaker service prepares the environment for
newly create user profile.
From the Jupyter notebook instance, using the sample notebooks, you can develop features, train, host, and monitor a machine learning model in a secure manner. If you assume your original AWS role you can also, from the AWS console, explore the various features deployed by the CloudFormation stacks.
This source code demonstrates a self-service model for enabling data science teams to create data science environments that employ a number of recommended security practices. Some of the more notable features are listed below. The controls, mechanisms, and services deployed by this source code is intended to provide operations and security teams with the assurance that their best practice is being employed while also enabling data science teams to self service, move quickly, and stay focused on the data science task at hand.
The SageMaker Studio domain is onboarded in VPC Only mode to use a Shared Services VPC, with VPC Only mode Studio sends all traffic over your specified VPC. Every data science environment is now configured to host Amazon SageMaker and other components of the data science environment in Shared Services VPC. The VPC provides a familiar set of network-level controls to allow you to govern ingress and egress of data. These templates create a VPC with no Internet Gateway (IGW), therefore all subnets are private, without Internet connectivity. Network connectivity with AWS services or your own shared services is provided using VPC endpoints and PrivateLink. Security Groups are used to control traffic between different resources, allowing you to group like resources together and manage their ingress and egress traffic.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is used to create least-privilege, preventive controls for many aspects of the data science enviroments.
These preventive controls, in the form of IAM policies, are used to control access to a team's data in Amazon S3, control who
can access SageMaker resources like SageMaker Studio Notebook apps (jupyter server, kernel gateway etc.), and are also applied as
VPC endpoint policies to put explicit controls around the API endpoints created in a data science environment.
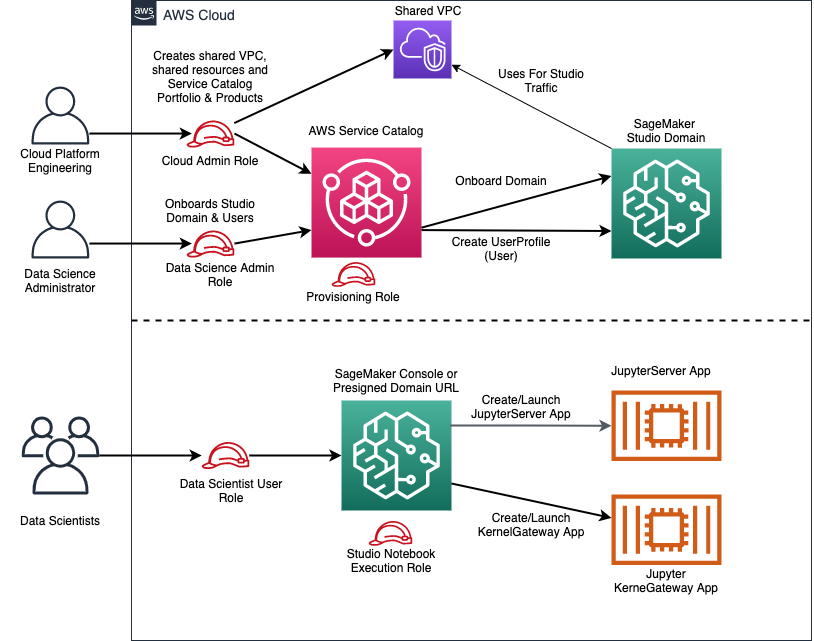
There are several IAM roles deployed by this source code to manage permissions and ensure separation of concerns at scale. The diagram below shows these roles and their intent:
-
Cloud Administrator role (AWS Administrator)
This IAM role (IAM
Adminrole withAdministratorAccessIAM policy) is for Cloud Platform Engineering team with full administrator access to AWS cloud.This role is responsible for creating shared sevices VPC, shared ECR repository, shared CodeArtifact repository, provisioning AWS Service Catalog portfolio and products to enable self-service administration by Data Science Administrator for onboarding SageMaker Studio domain, creating data science team environments and onboarding users to SageMaker Studio domain for a team. Cloud Administrator also creates a number IAM roles to enable self-service and delagated administration by Data Science administrators.
-
Data Science Administrator role
This role is for the Data Science administrators who are delegated the data science administration responsibilities and support multiple data science teams.
Responsibilities: onboarding SageMaker Studio domain, creating data science team environments and onboard SageMaker Studio User Profiles (i.e. users) to a specific data science team, all using the AWS Service Catalog. The Data Science Administer can add pre-approved pip packages to Code Artifact repository, build and publish SageMaker custom images to ECR repository, attach SageMaker images and versions to SageMaker Studio domain. Granting permissions to administer team-specific resources.
Examine Data Science Administrator Principals template to review IAM role and associated policy document.
-
AWS Service Catalog Launch role
The AWS Service Catalog Launch role is the role that AWS Service Catalog assumes when an end user launches a product. This allows end users to provision products and create AWS resources without giving end users (and their role) higher level permissions, thus making it possible to implement the least privileges model of security. A good example of this is AWS IAM role creation which is a highly privileged permission. You use Service Catalog launch role associated with a product to give end users ability to create role that they need without giving them permission to create an IAM role.
Examine Data Science Administrator Principals template to review IAM role and associated policy document.
-
Data Science Team Administrator role
This role is for use by the data science team, where one of the team members is given this role as delegated data science administrator for the team, allowing them to self-service and support the team's admin needs.
Examine Data Science Team Environment Principals template to review IAM roles and associated policy document.
-
Data Scientist User role
This role is for the end users - the data scientist, ML developers and engineers, who are members of a data science team.
This role grants Console access, permissions to launch SageMaker Studio IDE and Studio Jupyter notebook, permissions to create a Jupyter notebook and share Jupyter notebooks.
Note that this role is separate from SageMaker Notebook execution role attached to a SageMaker Studio UserProfile.
Examine Data Science Team Environment Principals template to review IAM roles and associated policy document.
-
SageMaker Studio UserProfile Execution role
This role is used by SageMaker Studio UserProfile which is created for each user. It grants the Studio Apps such as NotebookServer or KernelGateway access to SageMaker services and AWS resources. This role gives permissions to data scientist to perform data processing, training, deploy inference endpoint, use bias detection services, access S3 buckets, S3 data lakes and so on.
This role can be re-used for training jobs, batch transformations, and other Amazon SageMaker resources to support auditbility.
Examine Data Science Environment User Profile v1 template and Data Science Environment User Profile v2 templateto review IAM roles and associated policy document.
The IAM policies created by this source code use many IAM conditions to grant powerful permissions but only under certain conditions.
It is worth highlighting that the SageMaker service provides several SageMaker IAM roles that you should learn more about as you will need them in order to manage permissions and ensure separation of concerns at scale. Some of these roles are:
-
Training / Transform job execution role
Used by Training Jobs or Batch Transform jobs to access AWS resources like Amazon S3
-
Endpoint creation role
Used by your CI/CD pipeline to create hosted ML model endpoints
-
Endpoint hosting role
Used by a hosted ML model to access AWS resources such as Amazon S3
-
Endpoint invocation role
Used by an application to call a hosted ML model endpoint
It is assumed that a data science environment contains highly sensitive data to train ML models, and that there is also sensitive
intellectual property in the form of algorithms, libraries, and trained models. There are many ways to protect data such as
the preventive controls described above, defined as IAM policies.
In addition this source code encrypts data at rest using managed encryption keys.
Many AWS services, including Amazon S3, and Amazon SageMaker, are integrated with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to make it very easy to encrypt your data at rest. This source code takes advantage of these integrations to ensure that your data is encrypted in Amazon S3 and on Amazon SageMaker resources, end to end. SageMaker Studio domain is configured to use AWS Key Management Service (KMS). The Studio EFS volume is encrypted using a KMS key created specifically for use by SageMaker Studio domain. This encryption is also applied to your intellectual property as it is being developed in the many places it may be stored such as Amazon S3, EFS volumes, ECR respository or AWS CodeCommit git repository.
Using cloud services in a safe and responsible manner is good, but being able to demonstrate to others that you are operating in a governed manner is even better. Developers and security officers alike will need to see activity logs for models being trained and persons interacting with the systems. Amazon CloudWatch Logs and CloudTrail are there to help, receiving logs from many different parts of your data science environment to include:
- Amazon S3
- Amazon SageMaker Studio Notebooks
- Amazon SageMaker Training Jobs
- Amazon SageMaker Hosted Models
- VPC Flow Logs
There is a multitude of material and resources available to you to advise you on how to best support your business using AWS services. The following is a non-exhaustive list in no particular order:
- Amazon SageMaker documentation regarding security
- AWS Well-Architected Framework: Machine Learning Lens
- Building secure machine learning environments with Amazon SageMaker
- Setting up secure, well-governed machine learning environments on AWS
- Configuring Amazon SageMaker Studio for teams and groups with complete resource isolation
- Securing Amazon SageMaker Studio connectivity using a private VPC
- Building secure Amazon SageMaker access URLs with AWS Service Catalog
- Private package installation in Amazon SageMaker running in internet-free mode
- Bringing your own custom container image to Amazon SageMaker Studio notebooks
- Secure and Compliant Machine Learning Workflows with Amazon SageMaker (video)
- An Overview of Amazon SageMaker Security (video)
- Building Secure Machine Learning Environments using Amazon SageMaker (video)
- AWS Cloud Security
This source code is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file for details.