Treat a Google Sheet like a database table.
For simple projects, you often don't have the time (or the patience) to build a full admin backend for your app. A Google Sheets document makes an ideal backend for these situations because:
- You don't have to build an admin UI
- It's easy and intuitive to view and even edit the data (it's just a spreadsheet)
- You can easily layer on all kinds of extra analytics capabilities like pivot tables, charts, and graphs.
This simple library allows you to read and write data to individual sheets within a Google Sheets document as if they were tables and rows in a database.
- Search for rows using familiar predicate syntax, similar to the JavaScript
Array.find()API - Easily find rows identified by one or more keys
- Count all of the data rows in the table
- Insert, update, and delete individual rows
- Concurrent access to a given spreadsheet is prevented (using a mutex)
npm install google-sheets-tableimport { GoogleSheetsTable } from "google-sheets-table";
const {
GOOGLE_AUTH_CLIENT_EMAIL: client_email,
GOOGLE_AUTH_PRIVATE_KEY: private_key,
GOOGLE_SPREADSHEET_ID: spreadsheetId,
} = process.env;
const table = new GoogleSheetsTable({
// using a Google service account
credentials: {
client_email,
private_key,
},
spreadsheetId,
sheetName: "products",
// enforce that 'id' and 'sku' columns are unique
columnConstraints: { uniques: ["id", "sku"] },
});The credentials object is a Google JWTInput interface which supports the use of Google service accounts. To create a service account and give it the necessary access to your document, do the following:
-
If you don't already have one, create a new project in the Google Cloud Console
-
In the project, enable the Google Sheets API
-
Create a service account in IAM Credentials
-
Download the JSON key and extract the
client_emailandprivate_keyproperties -
Export them in your environment as shown above
-
Share access to your document, giving the service account (identified by its email address) either
Vieweraccess (if your app only needs read-only access) orEditoraccess (if it needs full read/write)
The sheetName property identifies which sheet in the Google Sheets document will be used as the table.
The columnConstraints property specifies column constraints that will be enforced when new rows are inserted or existing rows are updated.
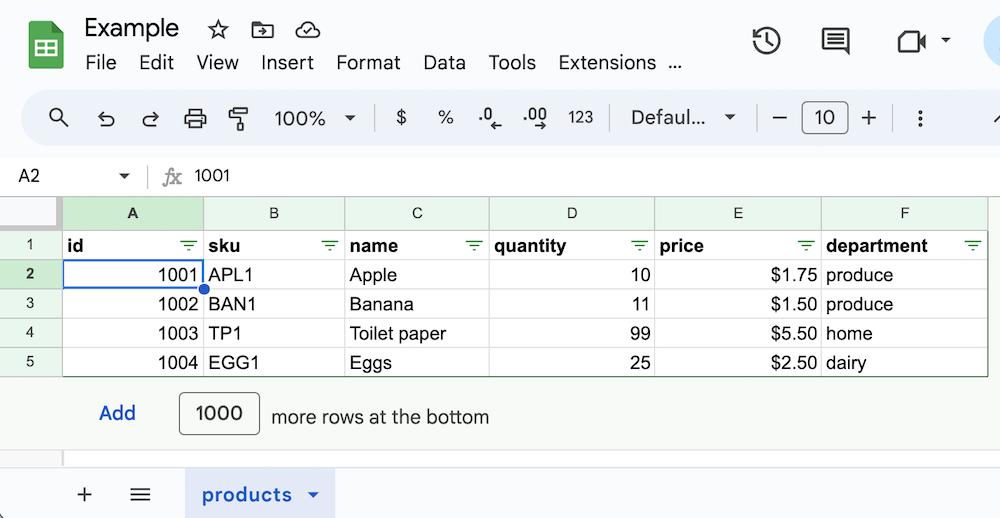
So imagine you have the following Google Sheets document that contains this products sheet:
Finding a single row:
const { row } = await table.findRow((r) => r.id === 1001);
console.log(row);
// => { _rowNumber: 2, id: 1001, sku: 'APL1', name: 'Apple', quantity: 10, price: 1.75, department: "produce" }The
_rowNumberproperty is a metadata field identifying the sheet row number
Get all rows:
const { rows: allRows } = await table.findRows();
console.log(allRows);
// => [
// { _rowNumber: 2, id: 1001, sku: 'APL1', name: 'Apple', quantity: 10, price: 1.75, department: "produce" },
// { _rowNumber: 3, id: 1002, sku: 'BAN1', name: 'Banana', quantity: 11, price: 1.50, department: "produce" },
// { _rowNumber: 4, id: 1003, sku: 'TP1', name: 'Toilet paper', quantity: 99, price: 5.50, department: "home" },
// { _rowNumber: 5, id: 1004, sku: 'EGG1', name: 'Banana', quantity: 25, price: 2.50, department: "dairy" },
// ]Finding specific rows:
const { rows } = await table.findRows((r) => r.quantity < 50);
console.log(rows);
// => [
// { _rowNumber: 2, id: 1001, sku: 'APL1', name: 'Apple', quantity: 10, price: 1.75, department: 'produce' },
// { _rowNumber: 3, id: 1002, sku: 'BAN1', name: 'Banana', quantity: 11, price: 1.5, department: 'produce' },
// { _rowNumber: 5, id: 1004, sku: 'EGG1', name: 'Eggs', quantity: 25, price: 2.5, department: 'dairy' }
// ]Finding rows and sorting them:
const { rows: sortedRows } = await table.findRows(
(r) => r.quantity < 50,
[{ asc: "department" }, { desc: "name" }],
);
console.log(sortedRows);
// => [
// { _rowNumber: 5, id: 1004, sku: 'EGG1', name: 'Eggs', quantity: 25, price: 2.5, department: 'dairy' },
// { _rowNumber: 3, id: 1002, sku: 'BAN1', name: 'Banana', quantity: 11, price: 1.5, department: 'produce' },
// { _rowNumber: 2, id: 1001, sku: 'APL1', name: 'Apple', quantity: 10, price: 1.75, department: 'produce' }
// ]Finding rows by one or more keys:
const { rowsByKey } = await table.findKeyRows((r) => r.sku, ["APL1", "EGG1"]);
console.log(rowsByKey);
// => {
// APL1: { _rowNumber: 2, id: 1001, sku: 'APL1', name: 'Apple', quantity: 10, price: 1.75, department: "produce" } },
// EGG1: { _rowNumber: 5, id: 1002, sku: 'BAN1', name: 'Banana', quantity: 11, price: 1.50, department: "produce" } }
// }Counting rows:
const count = await table.countRows();
console.log(count);
// => 4Inserting a new row:
const { insertedRow } = await table.insertRow({
id: 1005,
sku: "BUT1",
name: "Buttr", // notice the typo
quantity: 15,
price: 3.5,
department: "dairy",
});
console.log(insertedRow);
// => { _rowNumber: 6, id: 1005, sku: 'BUT1', name: 'Buttr', quantity: 15, price: 3.5, department: "dairy" }Updating an existing row:
const { updatedRow } = await table.updateRow((r) => r.sku === "BUT1", {
name: "Butter",
});
console.log(updatedRow);
// => { _rowNumber: 6, id: 1005, sku: 'BUT1', name: 'Butter', quantity: 15, price: 3.5, department: "dairy" }Deleting an existing row:
await table.deleteRow((r) => r.sku === "BUT1");
// NOTE: throws if row not foundSee the example.js for the full example.
Check it out 👉 API
- Improve performance with larger tables by not having to download the entire table for each operation
- Add support for batch operations
- Support concurrency locking across processes