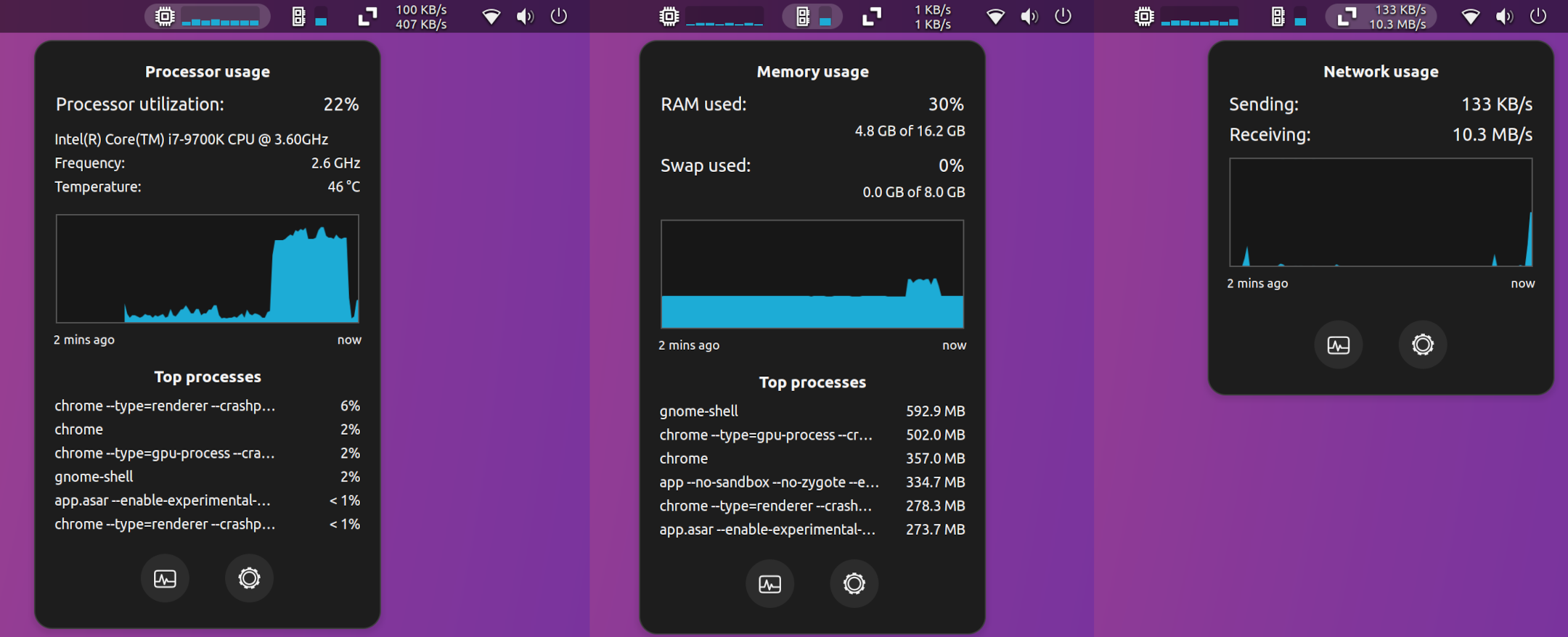
TopHat aims to be an elegant system resource monitor for the GNOME shell. It displays CPU, memory, disk, and network activity in the GNOME top bar.
See RELEASES.md for the list of fixes and new functionality included in each release.
Install TopHat from the GNOME Shell extensions page.
Most Debian-based systems (including Ubuntu and Pop!_OS) will also need
'gir1.2-gtop-2.0' to be installed. Usually this means running the command
sudo apt install gir1.2-gtop-2.0 followed by a system restart.
- GNOME 45 or newer (older releases of TopHat are available for GNOME 3.32 - 44 in the legacy branch at https://github.com/fflewddur/tophat/tree/legacy)
- The gtop system monitoring library (e.g., 'libgtop' on Debian-based systems, likely already installed as part of GNOME)
- GIRepository (gir) bindings for the gtop system monitoring library (e.g., 'gir1.2-gtop-2.0' on Debian-based systems)
The latest release of TopHat has been tested on the following systems:
- Arch Linux
- Fedora 39
- Ubuntu 23.10 (first install gir1.2-gtop-2.0 package)
Even if your system is not in this list, as long as it meets the requirements mentioned above, you should be able to run TopHat. If not, please file a bug report on the issue tracker.
If you prefer not to use https://extensions.gnome.org to install and update
GNOME Shell extensions, you can manually install TopHat by following these
steps. You may need to install the unzip and gnome-extensions-app
utilities first.
- Download the latest TopHat release from https://github.com/fflewddur/tophat/releases.
- Ensure your local extension directory exists by running the command
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/gnome-shell/extensions/tophat@fflewddur.github.io. - Extract the TopHat ZIP file into your local extension directory with the
command
unzip [path-to-tophat.zip] -d ~/.local/share/gnome-shell/extensions/tophat@fflewddur.github.io - Log out of your computer and log back in (or restart your system).
- Enable TopHat in the
gnome-extensions-app.
Contributions to improve TopHat are welcome! To avoid duplicate work, check the issue tracker first. If an issue doesn't already exist for your idea, please create one.
To keep the code format consistent, please use eslint before submitting a
PR. You can install eslint by running the command npm install eslint from
the TopHat repo directory. To run the linter, use the command
./node_modules/eslint/bin/eslint.js . --ext .js; alternatively, the ESLint
plugin for VS Code will automatically run the linter for you.
To view logs for GNOME Shell: journalctl -f /usr/bin/gnome-shell
To view logs for extension preferences: journalctl -f /usr/bin/gjs
To simulate heavy system load, use the stress-ng tool, e.g. stress-ng --timeout 10s --cpu 8 or stress-ng --vm-bytes 80% --vm-populate -t 30 -vm 4.
To test the development version:
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/gnome-shell/extensions/
ln -s [path to tophat repository]/tophat@fflewddur.github.io ~/.local/share/gnome-shell/extensions/tophat@fflewddur.github.io
TopHat is distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License, version 3 or later. See the license file for details.
TopHat was designed and written by Todd Kulesza, with much inspiration from the GNOME system-monitor extension and iStat Menus.
The images in the 'icons' directory are derived works from thenounproject.com and used under the Creative Commons Attribution license. The authors of each original work are:
icons/cpu.svg: jai
icons/disk.svg: guntur cahya
icons/logo.svg: Sergey Krivoy
icons/mem.svg: Loudoun Design
Co.
icons/net.svg: Pixel Bazaar
All icons were edited to make them more legible at small sizes.