This is a simple repostory that was made to teach myself (and anyone else) how to easily create a mdBook Github Page Workflow utilizing custom domains.
- Live Site: https://example.hotbox.zip
Note
This example is a manual walkthrough of setting up the Github Pages mdBook Workflow WITHOUT having to setup/use mdbook locally on your own system.
- Steps 2 through 4 are normally done automatically by running
mdbook init. - Using a custom domain name is NOT a requirement for setting up a successful Github Page, but I included it in this repository for the sake of completion and vebosity. To skip custom domain configuration:
- Remove the
[output.html]section frombook.tomlin step 4. - Skip steps 8 and 9 entirely.
- Remove the
- The root
.mdfile should beSUMMARY.md.- Formatting documentation can be found here.
- Example
SUMMARY.md:
# Summary
# Primary Section
- [mdBook Github Page Creation](Primary%20Directory/mdBook_GithubPages_Creation.md)
# Secondary Section
- [Obsidian Markdown Comparison](Secondary%20Directory/Obsidian_Markdown_Comparison.md)
# Tertiary Section
- [Export-Obsidian.ps1](Tertiary%20Directory/Export-Obsidian.md)- Your custom domain name should be included.
- Simply remove the
[output.html]section to avoid custom domain configuration.- If no domain name is specified, Github Pages will opt for:
https://<username>.github.io/<repository>
- If no domain name is specified, Github Pages will opt for:
- Example
book.toml:
[book]
authors = ["Tyler McCann (@tylerdotrar)"]
language = "en"
multilingual = false
src = "src"
title = "Example mdBook Site"
[build]
build-dir = "public"
[output.html]
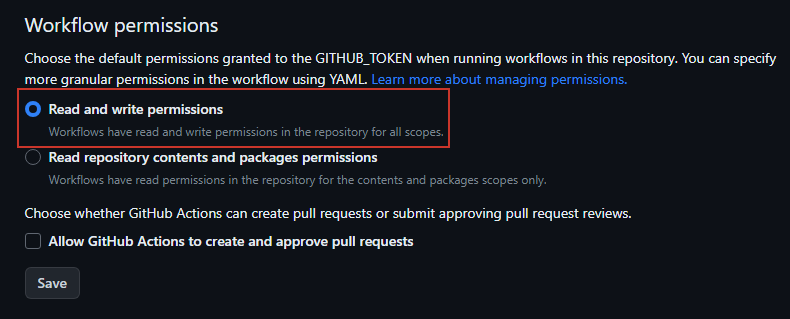
cname="example.hotbox.zip"Repository --> Settings --> Actions --> General --> Workflow Permissions
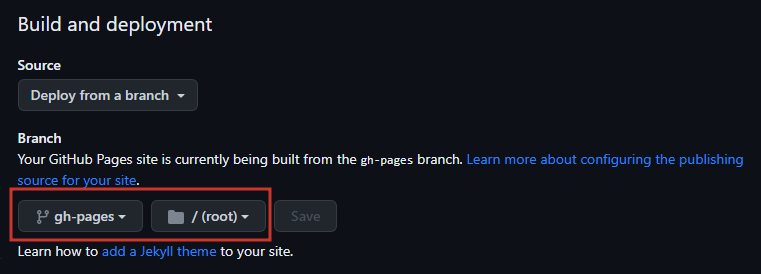
Repository --> Actions --> Pages --> View All --> mdBook --> Configure- The default deployment yelled at me, so I opted for a simpler, custom
mdbook.yml.- You should be able to copy and paste this example file verbatim.
- Example
mdbook.yml:
name: Deploy mdBook Github Pages
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-20.04
concurrency:
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup mdBook
uses: peaceiris/actions-mdbook@v1
with:
mdbook-version: '0.4.21'
# mdbook-version: 'latest'
- run: mdbook build
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
if: ${{ github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' }}
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
publish_dir: ./public- The 'gh-pages' branch will be created by the
mdbook.ymlworkflow (assuming no errors occur). - Once it is created, you can set that branch as your deployment branch.
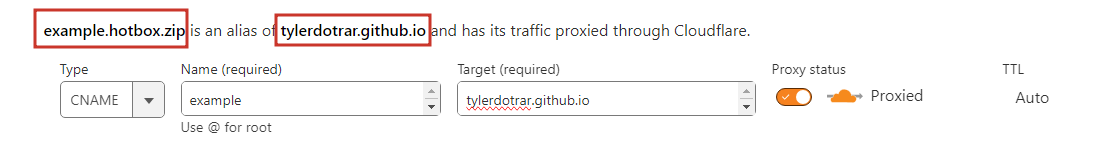
- Documentation on configuring subdomains with Github Pages can be found here.
- This step will vary for everyone, so below is my experience with Cloudflare.
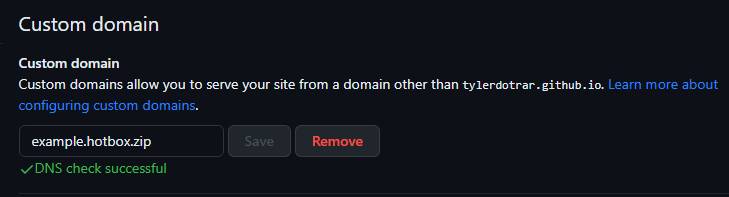
Repository --> Settings --> Pages --> Custom Domain- Once your CNAME finishes propegating, your mdBook should now be accessible.