These data constitute an effort to update the NOAA Atlas 14 for Alaska using more recent historical observed climate information and adding in the effects of a changing climate. The goal is to produce a similar set of data as is displayed and served currently through the NOAA Atlas 14 Precipitation Frequency Web Interface, using the WRF Dynamically Downscaled Data for Alaska produced by researchers affiliated with the Alaska Climate Adaptation Science Center (AK-CASC). This work is funded by the Alaska Department of Transportation (AKDOT) to add climate futures data to existing workflows designing culverts and other engineering features of road construction.
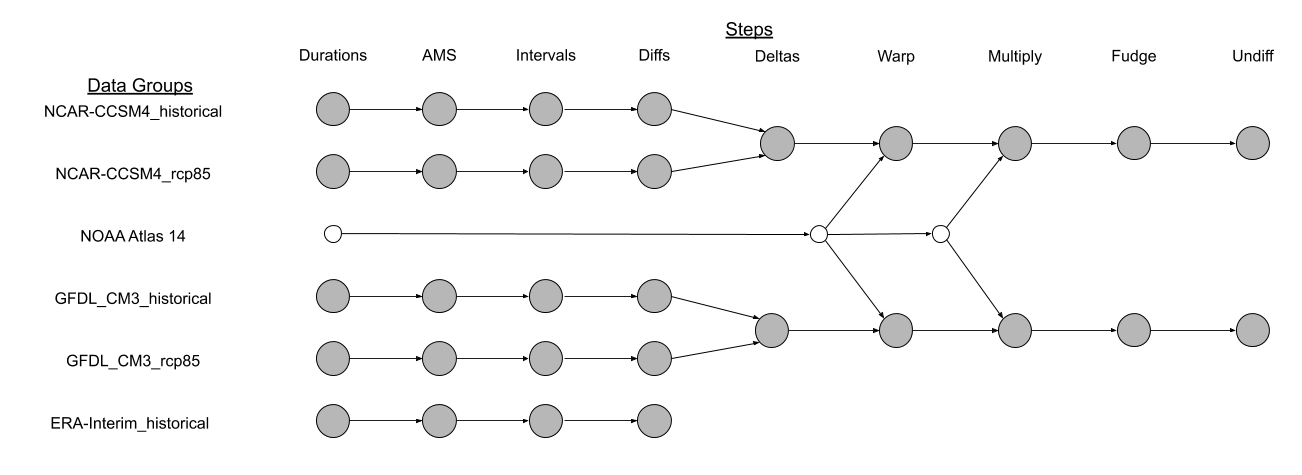
The data transformation in this project follows a pipeline with the following steps:
- Starting point: WRF hourly pcpt data (can be obtained here), along with the NOAA Atlas 14 data. (See the scripts in here for help obtaining and pre-processing the NOAA Atlas 14 data).
- Durations: Calculate duration series for various time periods.
- AMS: Calculate Annual Maximum Series for all duration series.
- Intervals: Calculate return intervals based off AMS.
- Diff: Rewrite confidence bounds as differences from the median
- Deltas: Calculate the difference, as a ratio, between the historical WRF data and the multiple decades of projected data.
- Warp: Reinterpolate this grid of deltas to match the grid of the NOAA Atlas 14 data.
- Multiply: Multiply the NOAA Atlas 14 data by the deltas to get the final precipitation estimates.
- Fudge: Fudge values for consistency
- Undiff: Re-apply the diffs created in the Diff step and add header information to data
- Fudge CI Fudge confidence interval values for consistency
The WRF data includes 5 different models/data groups (listed below). The pipeline is repeated for every group:
- NCAR-CCSM4_historical
- NCAR-CCSM4_rcp85
- ERA-Interim_historical
- GFDL-CM3_historical
- GFDL-CM3_rcp85
The diagram below outlines the relationship between the different data groups and their involvement in each step of the pipeline:
The python scripts in the pipeline directory are used to execute different steps of the pipeline and the run-pipeline script is used to execute all or part of the entire pipeline.
If you're running on SNAP's ATLAS server, then some of this has probably already been done for you.
- Install Dependencies: Call
pip install -r requirements.txtto install all of the necessary python packages (it is recommended that you do this inside a new virtual environment or conda environment). You may also need to install various libraries such as HDF5 and NetCDF to get the packages to install. - Set up Data Directory: Decide on the directory where you want to store all the data.
- In that directory, create another directory called
pcptand download all of hourly pcpt WRF data into it. (The data can be found on S3 here). - Create another directory (in the main data directory) called
NOAAwhich will store all the NOAA Atlas 14 data.
- In that directory, create another directory called
Simply calling ./run-pipeline will execute the entire pipeline for all data sets with default options configured for running on SNAP's ATLAS server. However, the run-pipeline script is very powerful and through various command-line options, it can be customized to run just subsets of the pipeline, in different directories, with or without SLURM and more. Call ./run-pipeline --help for more information.
Running the pipeline on ATLAS with SLURM:
You can call run-pipeline using the 'sbatch' command to run it with SLURM. Since this will copy the script to a temporary directory before running it, you will have to manually specify the script directory. You will also likely want to override the python executable to use whichever virtual environment you're in at the time. The command below will work to run the entire pipeline
on SLURM.
sbatch ./run-pipeline -e $(which python3) --script-dir $(pwd)/pipeline/ -p 64
Running the pipeline on your own:
Running the pipeline by yourself is generally simpler, but you will have to override the default data directory.
./run-pipeline -d path/to/your/data/directory
- documents: Scraps of project documentation.
- other_scripts: Other data processing scripts that were used at one point or another.