- About
- Try the network mapper
- Installation instructions
- How does the network mapper work?
- Exporting a network map
- Learn more
- Contributing
- Slack
mapper.mp4
The Otterize network mapper is a zero-config tool that aims to be lightweight and doesn't require you to adapt anything in your cluster. Its goal is to give you insights about traffic in your cluster without a complete overhaul or the need to adapt anything to it.
You can use the Otterize CLI to list the traffic by client, visualize the traffic, export the results as JSON or YAML, or reset the traffic the mapper remembers.
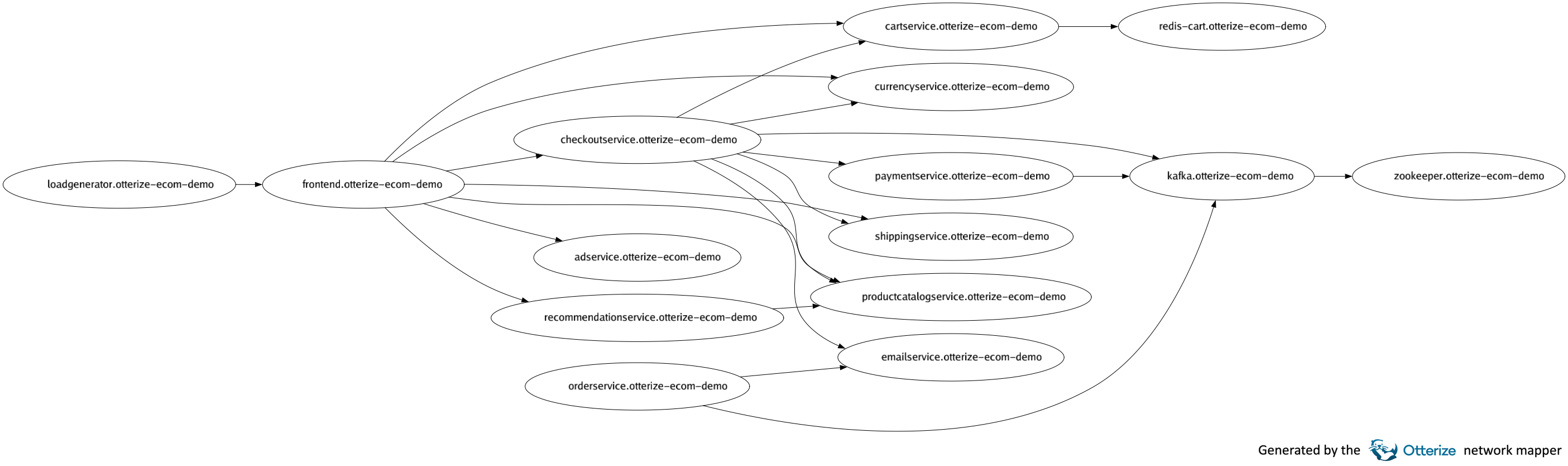
Example output after running otterize network-mapper visualize on the Google Cloud microservices demo:
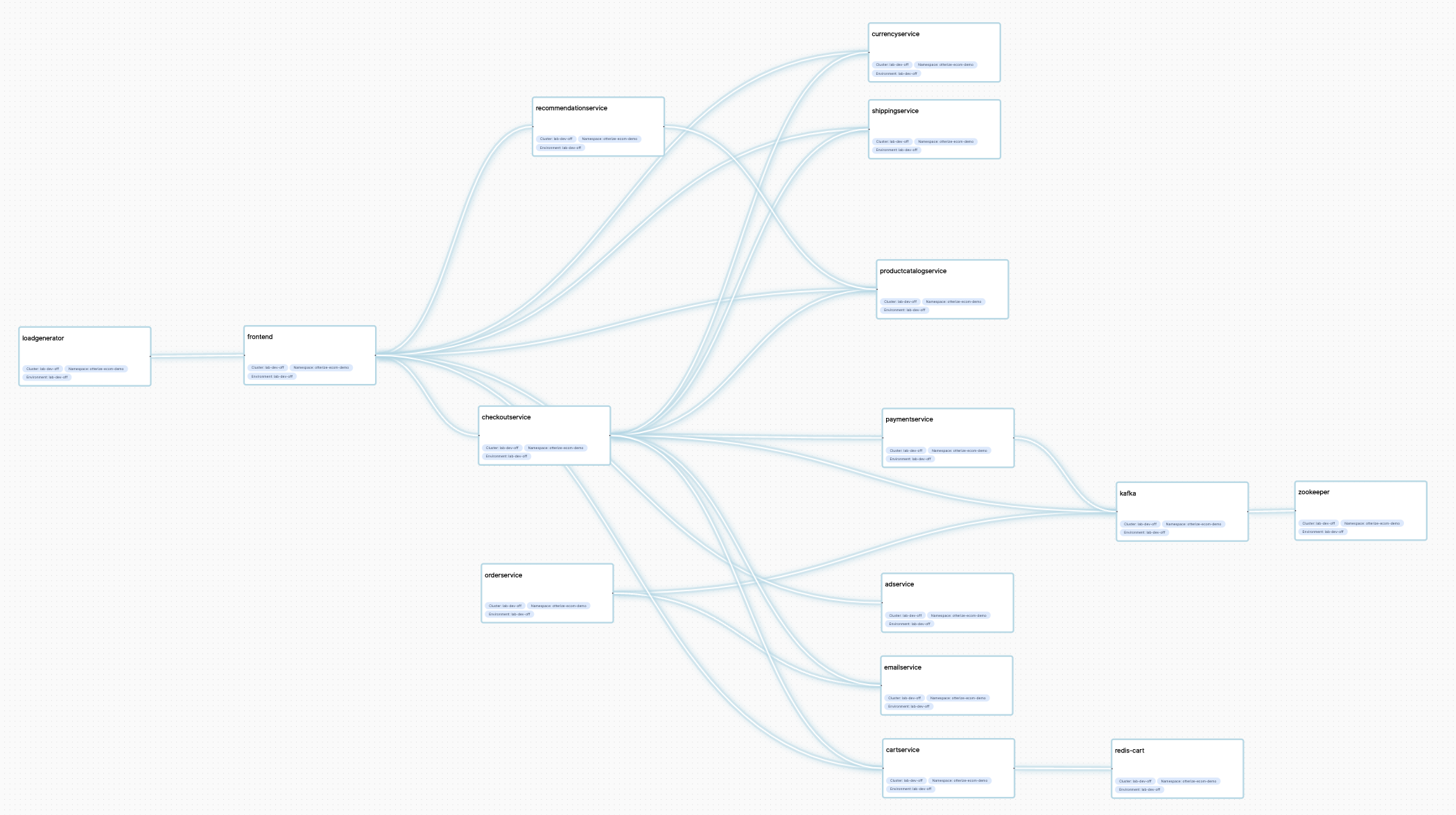
The same microservices demo in the Otterize Cloud access graph, as it appears when you choose to connect the network mapper to Otterize Cloud:
Example output after running otterize network-mapper list on the Google Cloud microservices demo:
cartservice in namespace otterize-ecom-demo calls:
- redis-cart
checkoutservice in namespace otterize-ecom-demo calls:
- cartservice
- currencyservice
- emailservice
- paymentservice
- productcatalogservice
- shippingservice
frontend in namespace otterize-ecom-demo calls:
- adservice
- cartservice
- checkoutservice
- currencyservice
- productcatalogservice
- recommendationservice
- shippingservice
loadgenerator in namespace otterize-ecom-demo calls:
- frontend
recommendationservice in namespace otterize-ecom-demo calls:
- productcatalogserviceTry the quick tutorial guide to get a hands-on experience in 5 minutes.
helm repo add otterize https://helm.otterize.com
helm repo update
helm install network-mapper otterize/network-mapper -n otterize-system --create-namespace --waitMac
brew install otterize/otterize/otterize-cliLinux 64-bit
wget https://get.otterize.com/otterize-cli/v0.1.20/otterize_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
tar xf otterize_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
sudo cp otterize /usr/local/binWindows
scoop bucket add otterize-cli https://github.com/otterize/scoop-otterize-cli
scoop update
scoop install otterize-cliFor more platforms, see the installation guide.
The Otterize network mapper creates a map of in-cluster traffic by capturing DNS traffic and inspecting active connections then resolving the IP addresses participating in connections to their pods, and crawling up the ownership of the pod until it reaches the root object. The network mapper continues building the network map as long as it's deployed.
- Mapper: the mapper is deployed once, and resolves service names using the Kubernetes API with traffic information reported by the sniffers.
- Sniffer: the sniffer is deployed to each node, and is responsible for capturing node-local DNS traffic and inspecting open connections.
- Kafka watcher (experimental): deployed once to your cluster, and is responsible for capturing kafka server logs and reporting them through the network mapper.
Service names are resolved in one of two ways:
- If an
otterize/service-namelabel is present, that name is used. - If not, a recursive look-up is performed for the Kubernetes resource owner for a pod until the root is reached.
For example, if you have a
Deploymentnamedclient, which then creates and owns aReplicaSet, which then creates and owns aPod, then the service name for that pod isclient- same as the name of theDeployment. The goal is to generate a mapping that speaks in the same language that dev teams use.
The network mapper continuously builds a map of pod to pod communication in the cluster. The map can be exported at any time in either JSON or YAML formats with the Otterize CLI.
The YAML export is formatted as ClientIntents Kubernetes resource files. Client intents files can be consumed by the Otterize intents operator to configure pod-to-pod access with network policies, or Kafka client access with Kafka ACLs and mTLS.
Explore our documentation site to learn how to:
- Map pod-to-pod communication.
- Automate network policies.
- And more...
- Feel free to fork and open a pull request! Include tests and document your code in Godoc style
- In your pull request, please refer to an existing issue or open a new one.
- See our Contributor License Agreement.
To join the conversation, ask questions, and engage with other users, join the Otterize Slack!


