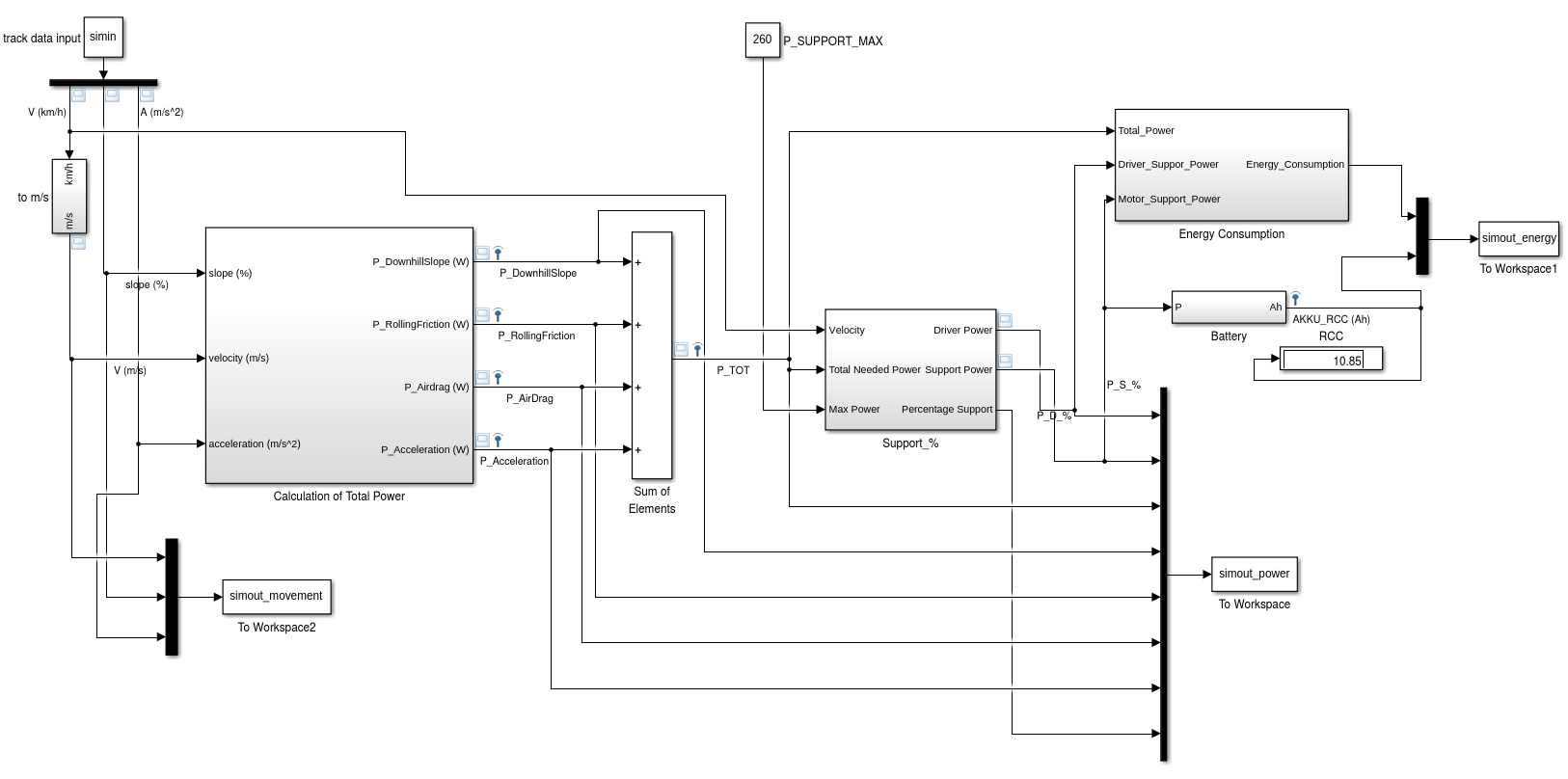
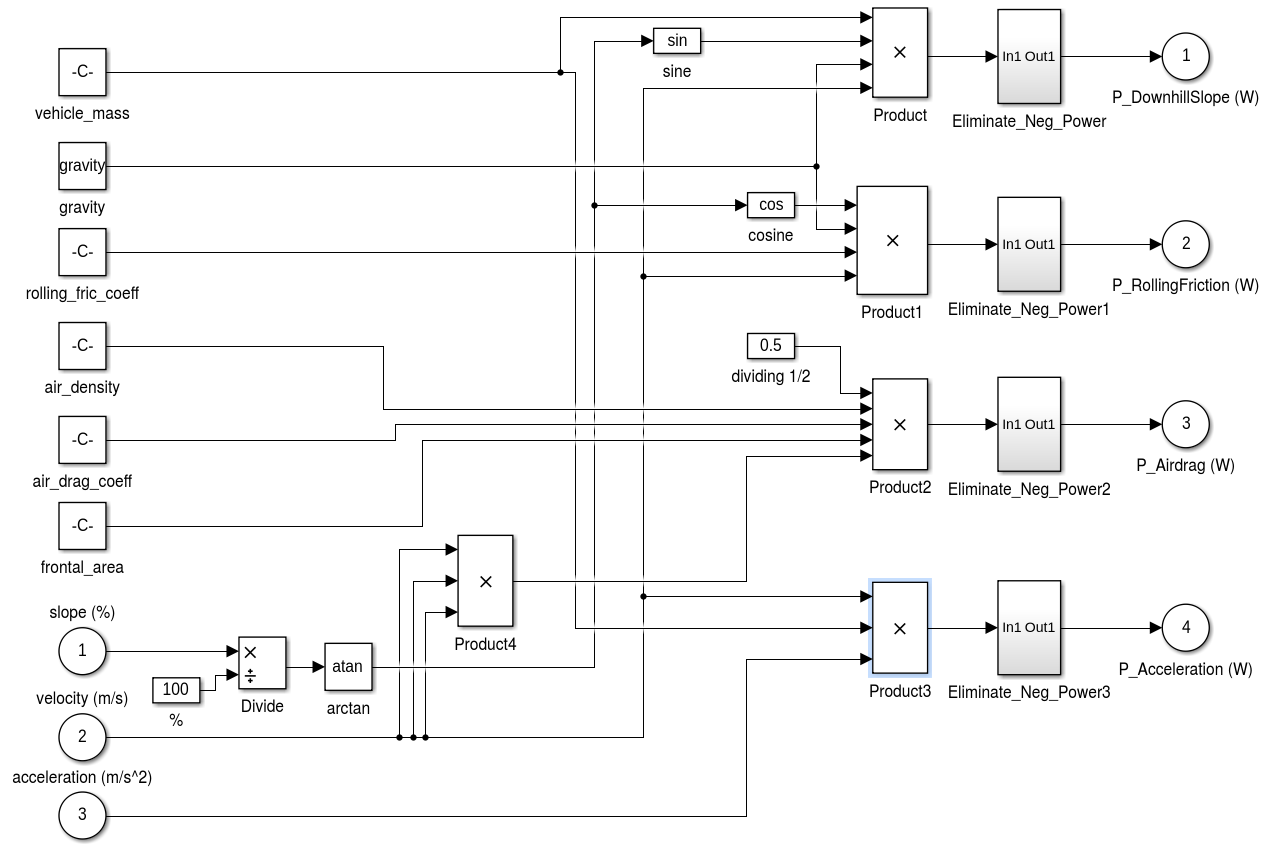
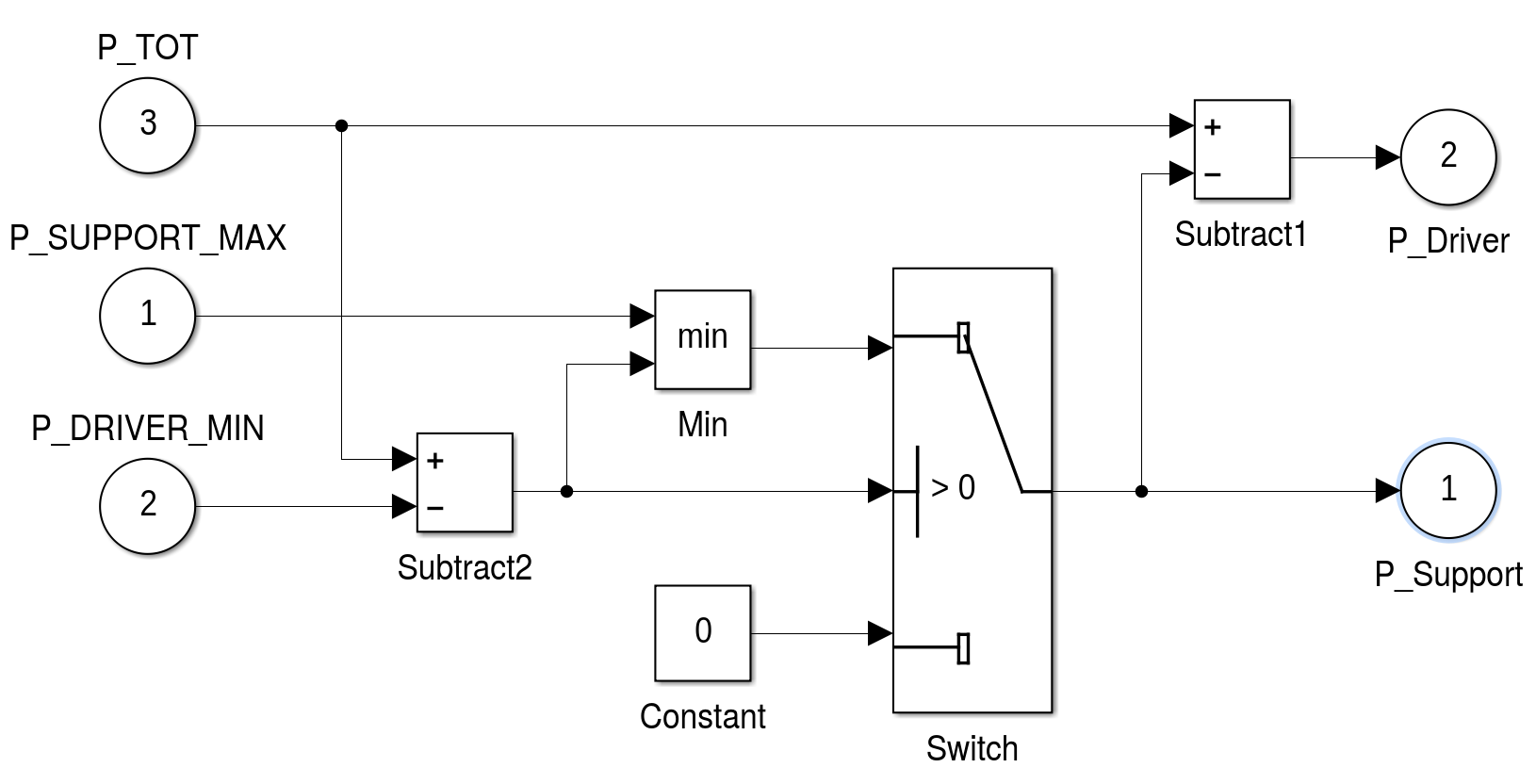
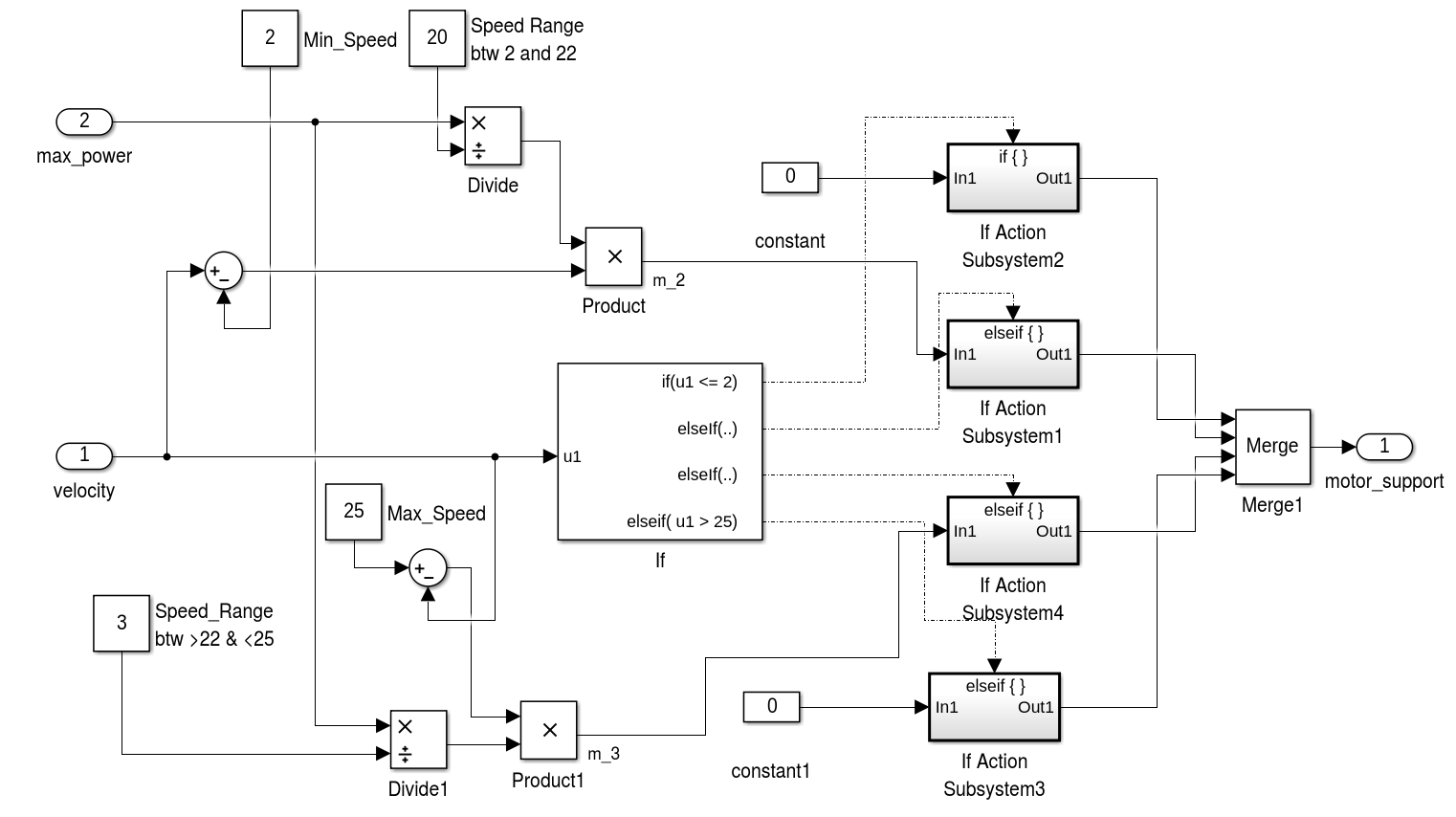
Reader can refer to the report for technical details.
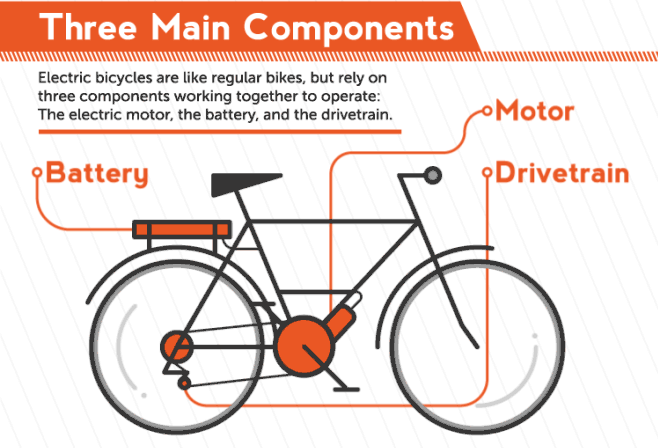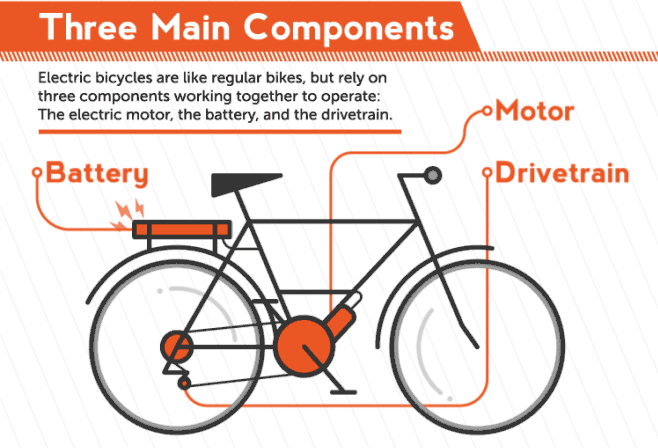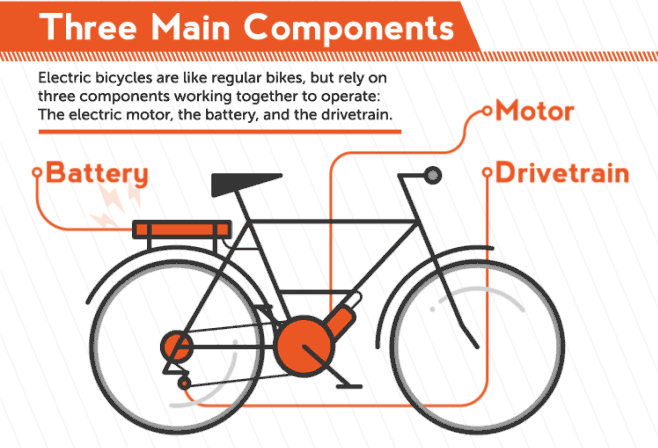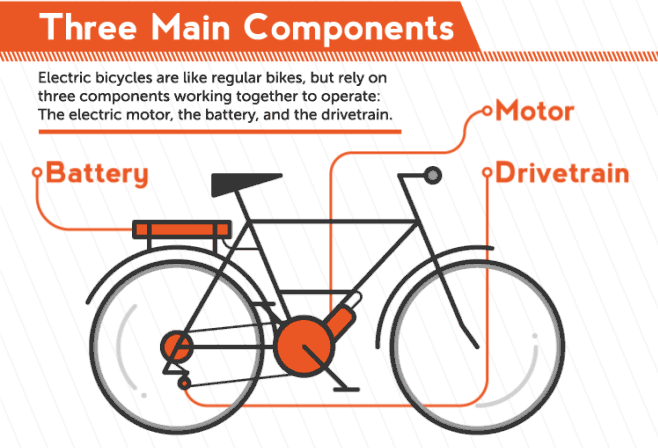
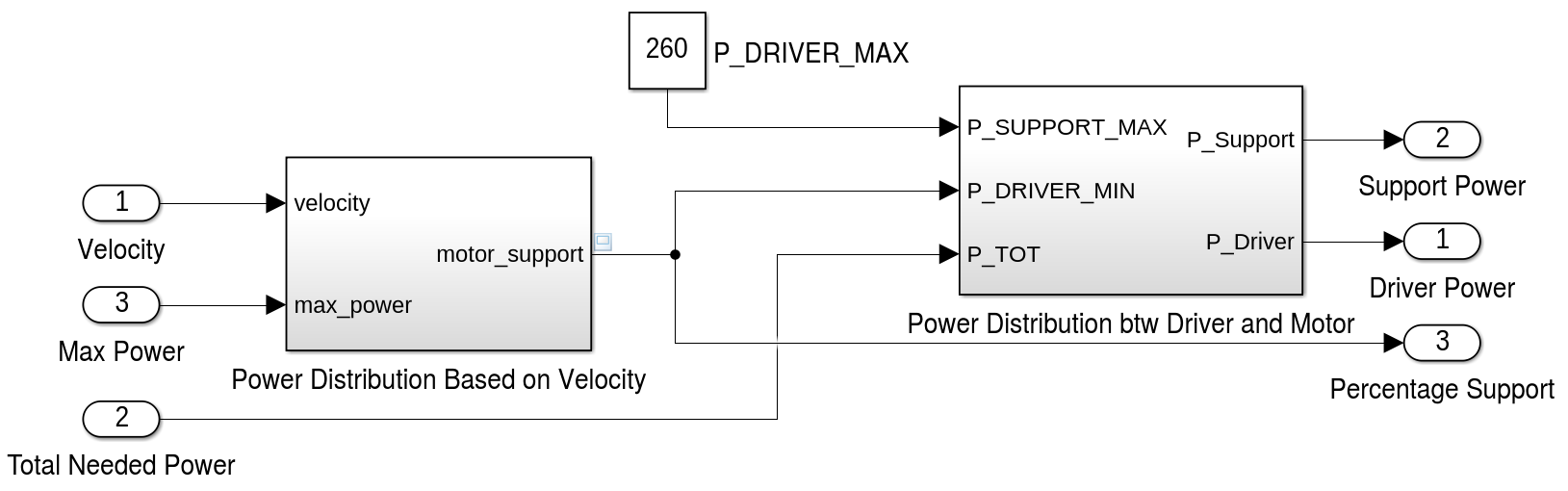
E-bike is a general term that refers to different kinds of bicycles that can be powered either by an electric motor, the drivers own muscle-power or a combination of both. This kind of e-bike can be considered as a hybrid electric vehicle and is motor and human powered. By statutory rule it is only allowed to assist the driver while he is actively pedaling and only up to a velocity of 25 km/h. Above this velocity the full power has to be provided by the driver alone and the motor has to be automatically shut off.
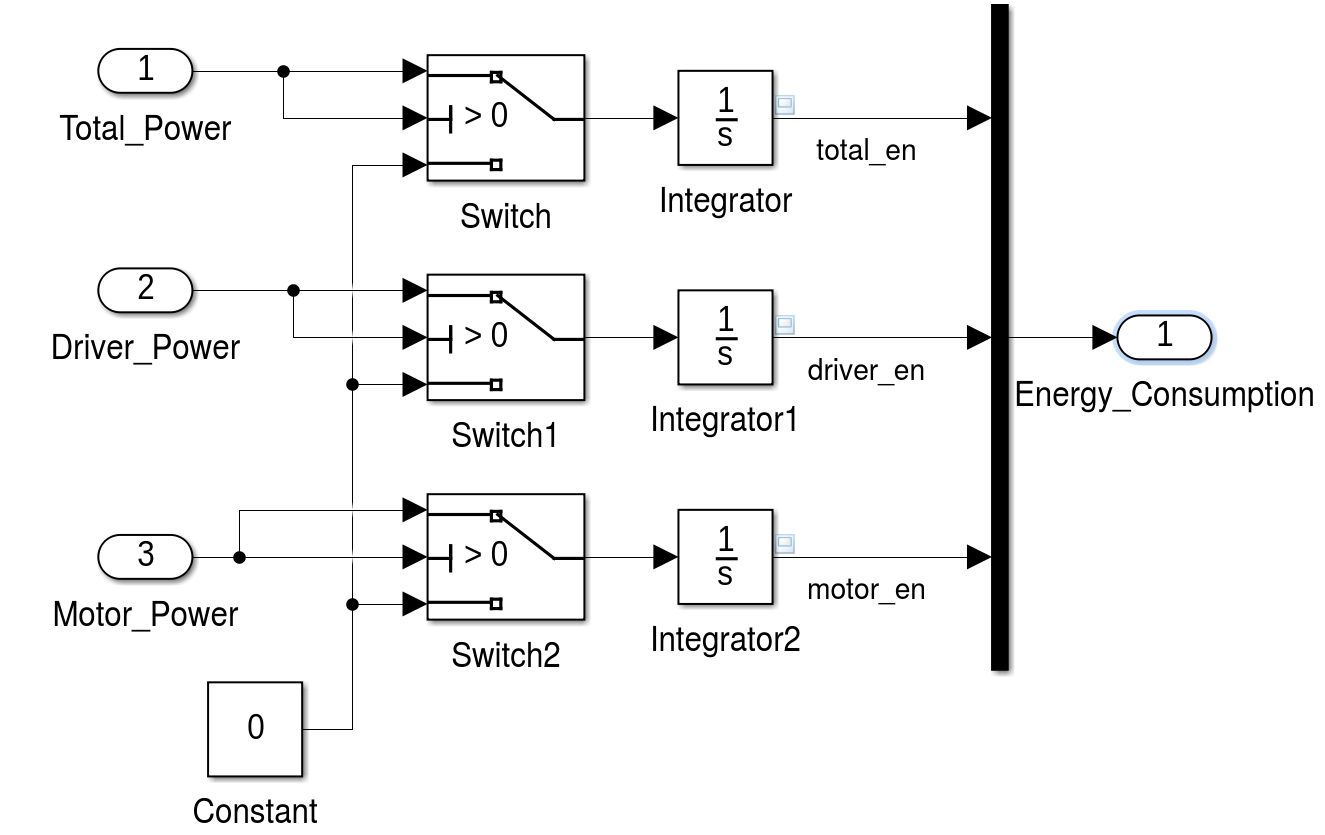
The simulation has to use a method to distribute the power between driver and bike to consider those legal requirements. For this the template model uses a fixed minimal driver power. If the power over a segment is below this parameter value, the driver has to provide all the power. Should p i exceed the minimal driver power, then the motor will support up to its maximum power. Other methods of balancing the power between driver and bike are left as an exercise. Finally, to draw a conclusion after the simulation, the total energy used by the motor has to be compared to the current capacity of the bikes battery. If the computed total energy is larger than the capacity of the bikes battery, the track can not be driven with the motor support distribution used by the simulation. The simulation template includes a simple virtual battery subsystem that continually drains energy from a initial battery capacity.