Service Discovery & Load Balancing service implementation using UDP broadcasting and TCP
Developed by Umutcan Sevdi, İsmet Güngör, Metin Usta and Emre Arslanoğlu.
Table of Contents
Service providing systems generally start as small-sized projects. However, over time they need methods to scale their systems to keep up with the incoming demand. Sometimes these scaling mechanisms are improved throughout the lifecycle of the application.
Systems require additional tools and structures for the future to keep providing services. One of these mechanisms is called Service Discovery. When the registry handling and the discovery are done by an additional server, it is called server-side service discovery.
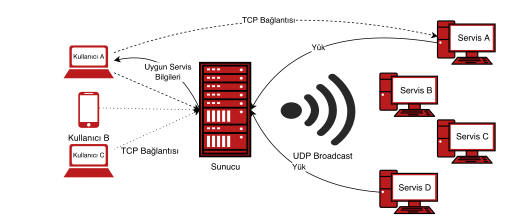
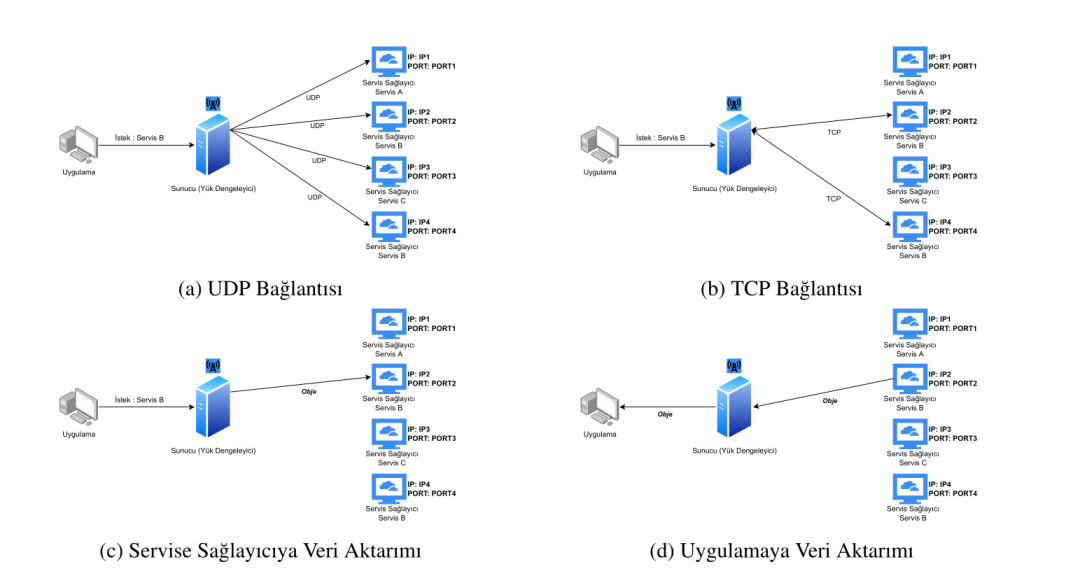
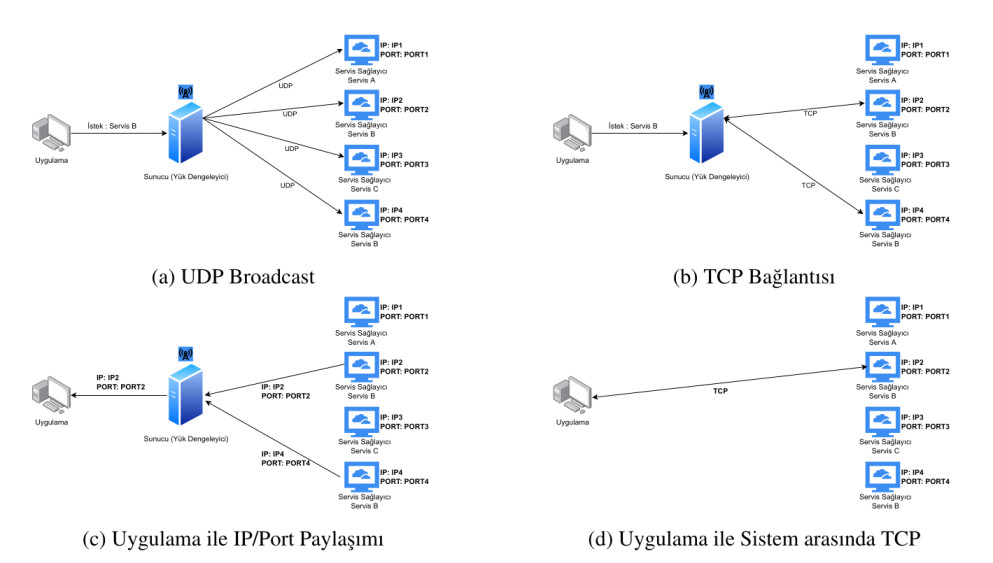
Within the scope of our project, we will implement a server that combines the Service Registry and the Load Balancer. However, instead of storing service provider addresses in a database-like system, we will use UDP broadcasting to discover them.
The server and the client communicate through TCP. But the communication between server and service applications are done through UDP.
The client requests a service using TCP to the server. When the server receives the request sends a UDP broadcast message to all services. If the application services type matches the client's request, they respond to this message with their IP address, port number and a number corresponding to their busyness, using TCP.
The server waits until the timeout and saves all responses during that time. After the timeout, the server analyzes all responses and selects the best service. Then sends its IP and port values to the client.
After that, the service application and client communicate directly through TCP.
The project includes three applications:
- Client is the application that represents the end-user. It sends the type of service application the user would like to interact with to the server and connects to the best available server. Then client application sends TCP requests to the application servers.
- Server is the load balancer and the service discoverer. Upon receiving a TCP request from clients, searches given query using UDP broadcast and registers incoming requests. Selects the best available server and returns its address to the client.
- Service is the service application. It represents backend applications in which clients interact. Upon receiving a UDP broadcast from the server, the service's UDP module responds to it with its load. Then it executes application programs for the clients.
service-discovery/
├── client
│ └── src
│ ├── data
│ │ └── Address.java
│ └── Main.java
├── server
│ └── src
│ ├── ApplicationServer.java
│ ├── data
│ │ ├── Address.java
│ │ └── ServerResponse.java
│ ├── exception
│ │ ├── NoResponseException.java
│ │ └── TimeoutException.java
│ ├── Main.java
│ └── UDPServer.java
└── service
└── src
├── data
│ ├── Address.java
│ └── UDPRequest.java
├── exception
│ └── InvalidRequestException.java
├── executor
│ ├── DateTime.java
│ ├── DNSLookup.java
│ ├── Encryptor.java
│ ├── EvaluateExpression.java
│ └── Executor.java
├── GenericExecutionServer.java
├── Main.java
└── UDPResponseServer.java
In this section, we examined our system's performance.
It is hard to determine the efficiency of such a system with arithmetic calculations. Using UDP broadcasting to determine services may look like it's creating an overhead. However, it also provides speed since it doesn't spend time on database transactions and data synchronizations.
It will also make adding new servers or removing existing ones easier. Adding new services will have little or no effect on the server's architecture.
When the system was initially designed, the server was also responsible for the data transfer between the client and the service. Although this creates anonymity over service applications, it was also causing an increase in the response time.
In our system, the server is responsible for both server discovery and load balancing. So adding data transfer would cause heavyweight. To reduce its load, we changed the way our system works. When the load balancer detects the services, it returns its address information to the client. Then client directly connects to those services. This way server can perform data transfers more efficiently.
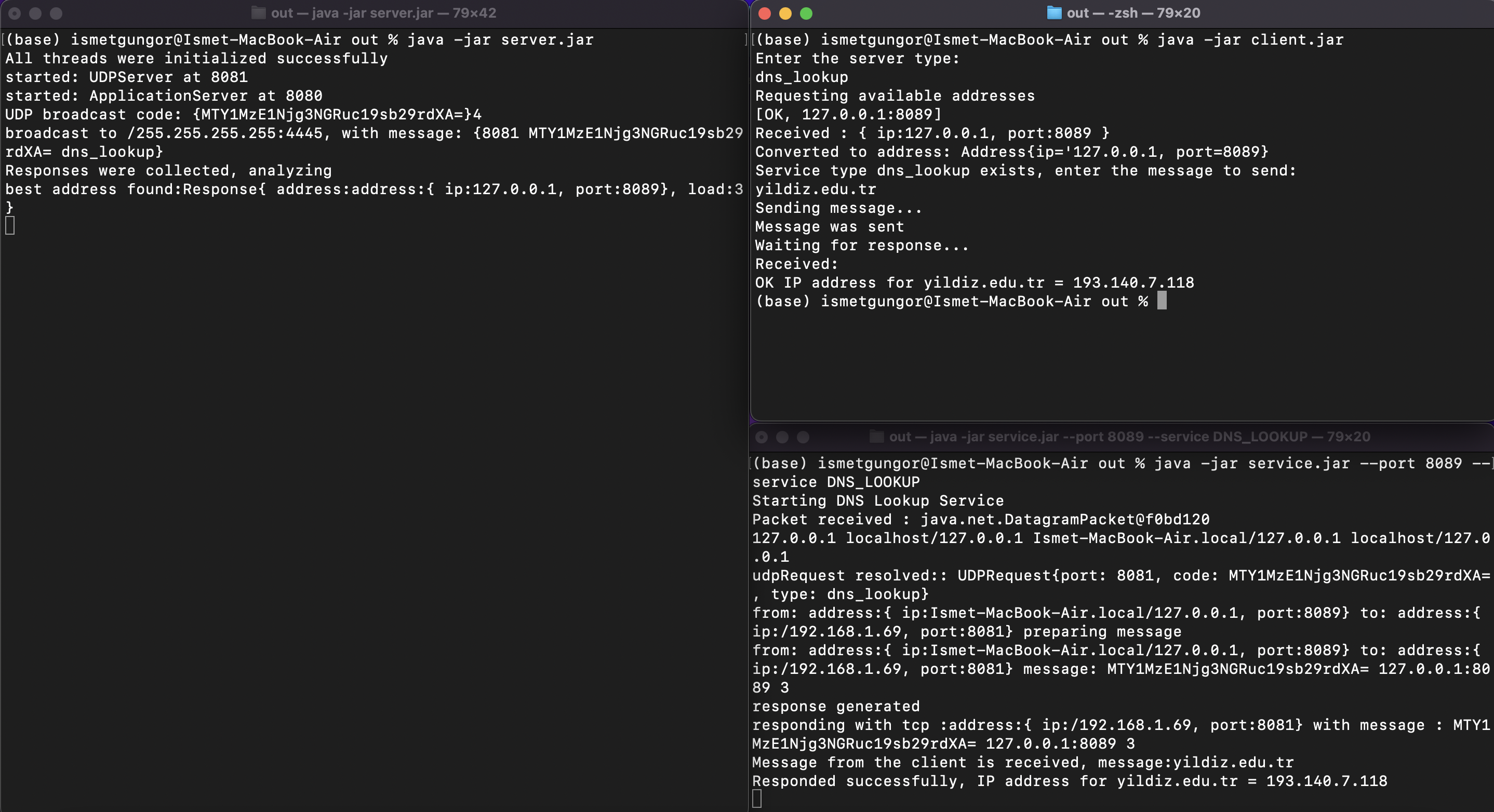
- DNS Lookup service running on MacOS.
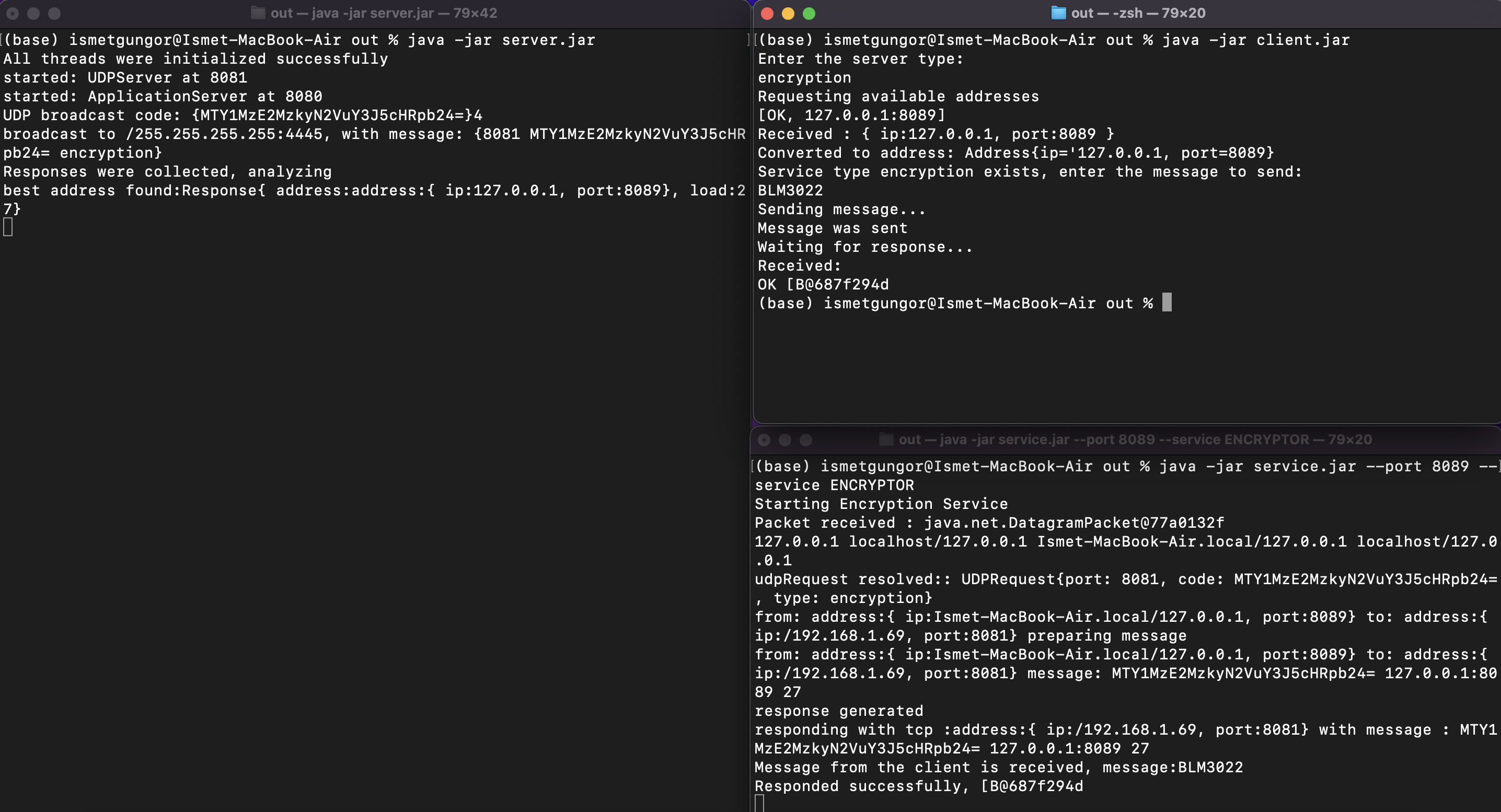
- Encryption service running on MacOS.
- Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/umutsevdi/service-discovery.git- Run following command to create Load Balance and Discovery server.
java -jar out/server.jar- Run following command on a seperate terminal to run client.
java -jar out/client.jar- Run following command on a seperate terminal to execute a service.
java -jar out/service.jar --port 8083 --service DNS_LOOKUPRead the full documentation from here.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
You can contact any developer of this project for any suggestion or information.
Project: umutsevdi/service-discovery
Developed by Umutcan Sevdi, İsmet Güngör, Metin Usta and Emre Arslanoğlu.