US Department of Transportation (USDOT) Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) Joint Program Office (JPO) Intersection GeoJSON Converter
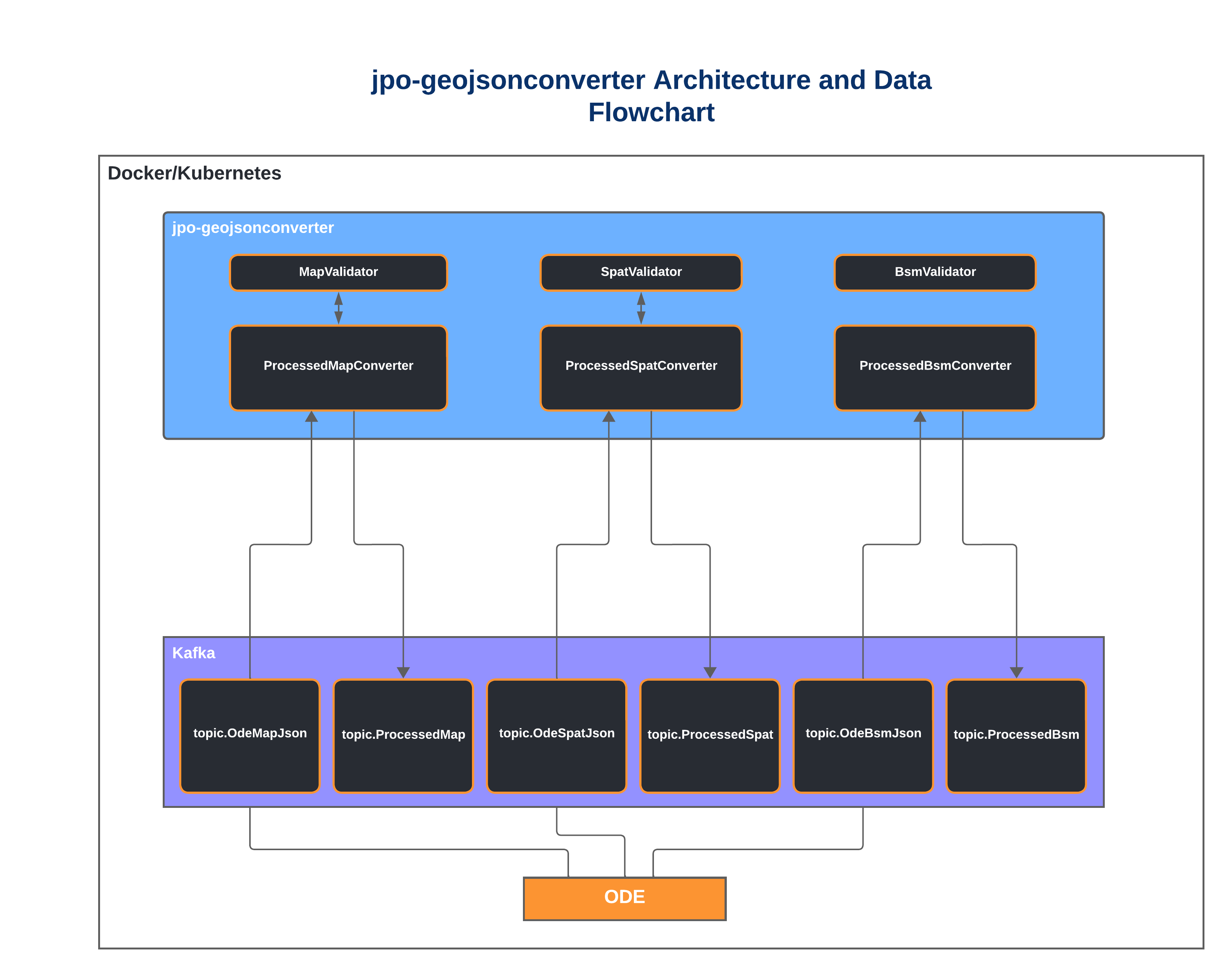
The JPO Intersection GeoJSON Converter is a real-time validator and data converter of JPO-ODE MAP and SPaT JSON based on the SAE J2735 message standard. Messages are consumed from Kafka and validated based on both the SAE J2735 standard and the more robust Connected Transportation Interoperability (CTI) Intersection Implementation Guide Message Requirements (Section 3.3.3). Message validation occurs simultaneously as the GeoJSON converter converts the JPO-ODE MAP and SPaT messages into mappable geoJSON. The JPO Intersection GeoJSON Converter outputs the resulting geoJSON onto Kafka topics. These messages contain validation information that identifies all issues encountered with validation, if any.
The message validation has been included in the jpo-geojsonconverter in order to prevent too many small microservices from being created. The extent of the current validation that occurs is surface level and is supported by simple verification against a schema that is based on J2735 and the CTI Intersection Implementation Guide. There may be reason to eventually break this feature out into a new, separate repository if more complex validation must be performed.
All stakeholders are invited to provide input to these documents. To provide feedback, we recommend that you create an "issue" in this repository (https://github.com/usdot-jpo-ode/jpo-geojsonconverter/issues). You will need a GitHub account to create an issue. If you don’t have an account, a dialog will be presented to you to create one at no cost.
The current version and release history of the JPO GeoJSON Converter: Release Notes
- Usage Example
- Configuration
- Installation
- File Manifest
- Development Setup
- Contact Information
- Contributing
The jpo-geojsonconverter is used to convert the ODE JSON output of MAP and SPaT messages into GeoJSON ProcessedMap messages and enhanced ProcessedSpat messages. In order to verify your jpo-geojsonconverter is functioning, you must run the jpo-ode, then the jpo-geojsonconverter, and then send the jpo-ode raw ASN1 encoded MAP and SPaT data.
Follow the configuration section to properly configure and launch your jpo-ode and jpo-geojsonconverter.
Run one of the UDP sender Python scripts from the jpo-ode repository to generate some example MAP and SPaT messages. Make sure to set your DOCKER_HOST_IP environment variable so the script will properly send the ASN1 encoded messages to your locally running JPO-ODE.
Once the message has been sent to the jpo-ode, it will be eventually be decoded and serialized into a JSON string. This string will be placed into the Kafka topics topic.OdeMapJson and topic.OdeSpatJson. The jpo-geojsonconverter will then transform them into geoJSON. If a user needs WKT formatted GeoJSON, it is possible to turn this on by specifying the geometry.output.mode environment variable to "WKT".
When an OdeMapJson message is processed through the jpo-geojsonconverter, a ProcessedMap message is created. This message is a single JSON object that contains two geoJSON FeatureCollection objects and one regular JSON object.
- mapFeatureCollection - Feature Collection for storing all of the unique metadata and geographic data for each lane in an intersection. Mapping this object would display all defined lanes in an OdeMapJson object.
- connectingLanesFeatureCollection - Feature Collection for storing all geographic data for connecting lanes within an intersection. When mapped, the feature collection displays a bunch of two point lines connecting each egress lane to all possible and legal traversals to ingress lanes. Useful for visualizing ProcessedSpat data.
- properties - General metadata and property values that are important to keep with the processed MAP message but aren't related to any single lane in the intersection. RSU IP, intersection ID, and validation messages are stored here.
ProcessedMap schema can be found here.
When an OdeSpatJson message is processed through the jpo-geojsonconverter, a ProcessedSpat message is created. This message is a single JSON object that contains all of the important information within a SPaT message for matching it to a corresponding ProcessedMap message and for identifying its state. There is no geoJSON component to a ProcessedMap message on its own.
ProcessedSpat schema can be found here.
Example ProcessedSpat message:
{
"messageType": "SPAT",
"odeReceivedAt": "2023-06-20T06:18:20.577365Z",
"originIp": "10.0.0.2",
"intersectionId": 12108,
"cti4501Conformant": false,
"validationMessages": [
{
"message": "$.metadata.receivedMessageDetails.locationData: is missing but it is required",
"jsonPath": "$.metadata.receivedMessageDetails",
"schemaPath": "#/$defs/OdeSpatMetadata/properties/receivedMessageDetails/required"
}
],
"revision": 0,
"status": {
"manualControlIsEnabled": false,
"stopTimeIsActivated": false,
"failureFlash": false,
"preemptIsActive": false,
"signalPriorityIsActive": false,
"fixedTimeOperation": false,
"trafficDependentOperation": false,
"standbyOperation": false,
"failureMode": false,
"off": false,
"recentMAPmessageUpdate": false,
"recentChangeInMAPassignedLanesIDsUsed": false,
"noValidMAPisAvailableAtThisTime": false,
"noValidSPATisAvailableAtThisTime": false
},
"utcTimeStamp": "2023-06-20T06:18:17.679Z",
"states": [
{
"signalGroup": 1,
"stateTimeSpeed": [
{
"eventState": "STOP_AND_REMAIN",
"timing": {
"minEndTime": "2023-06-20T06:18:17.6Z",
"maxEndTime": "2023-06-20T06:18:17.6Z"
}
}
]
},
{
"signalGroup": 2,
"stateTimeSpeed": [
{
"eventState": "PROTECTED_MOVEMENT_ALLOWED",
"timing": {
"minEndTime": "2023-06-20T06:18:21.6Z",
"maxEndTime": "2023-06-20T06:18:37.6Z"
}
}
]
}
]
}
Recommended machine specs running Docker to run the GeoJsonConverter:
- Minimum RAM: 16 GB
- Minimum storage space: 100 GB
- Supported operating systems:
- Ubuntu 18.04 Linux (Recommended)
- Windows 10 Professional (Professional version required for Docker virtualization)
- OSX 10 Mojave
The GeoJsonConverter software can run on most standard Window, Mac, or Linux based computers with Pentium core processors. Performance of the software will be based on the computing power and available RAM in the system. Larger data flows can require much larger space requirements depending on the amount of data being processed by the software. The GeoJsonConverter software application was developed using the open source programming language Java. If running the GeoJsonConverter outside of Docker, the application requires the Java 11 runtime environment.
The GeoJsonConverter is a micro service that runs as an independent application but serves the sole purpose of converting JSON objects created by the JPO-ODE via Apache Kafka. To support these JSON objects, the GeoJsonConverter application utilizes some classes from the JPO-ODE repository. This is included into the GeoJsonConverter as a submodule but the JPO-ODE should also be run independently of the jpo-geojsonconverter. The JPO-ODE is still required to launch Kafka, Zookeeper, the ASN1 decoder and create the required Kafka topics. All other required dependencies will automatically be downloaded and installed as part of the Docker build process.
- Docker: https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/
- Docker-Compose: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
Read the following guides to familiarize yourself with GeoJsonConverter's Docker and the ODE managed Kafka modules.
Installation and Deployment:
- Docker builds may fail if you are on a corporate network due to DNS resolution errors.
- Windows users may find more information on installing and using Docker here.
- Users interested in Kafka may find more guidance and configuration options here.
Configuration:
The GeoJsonConverter configuration is customized through the environment variables provided to Docker when Docker-Compose runs the Docker built GeoJsonConverter image. You may customize the Kafka broker endpoint.
Important!
You must rename sample.env to .env for Docker to automatically read the file. Do not push this file to source control.
The following instructions describe the minimal procedure to fetch, build, and run the main GeoJsonConverter application.
If running on Windows, please make sure that your global git config is set up to not convert end-of-line characters during checkout.
Disable git core.autocrlf (One Time Only)
git config --global core.autocrlf falseNote: to avoid cloning redundant local copies of submodules, if you intend to run the entire ConflictVisualizer system, you should instead start with step 1 of the ConflictVisualizer Installation Guide before returning to step 2 below.
The jpo-geojsonconverter software system consists of the following modules hosted in separate Github repositories:
| Name | Visibility | Description |
|---|---|---|
| jpo-geojsonconverter | public | Contains the public components of the application code. |
| jpo-ode | public | Contains the public classes and libraries of the jpo-ode used in the GeoJsonConverter. |
You may download the stable, default branch for ALL of these dependencies by using the following recursive git clone command:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/usdot-jpo-ode/jpo-geojsonconverter.gitOnce you have these repositories obtained, you are ready to build and deploy the application.
Navigate to the root directory of the jpo-ode project and run the following command:
docker-compose up --build -d
docker-compose psVerify the jpo-ode, kafka, zookeeper, asn1-decoder and asn1-encoder are running before performing step 3.
Notes:
- Docker builds may fail if you are on a corporate network due to DNS resolution errors.
- In order for Docker to automatically read the environment variable file, you must rename it from
sample.envto.env. This file will contain private keys, do not put add it to version control. - Unless you intend to run geojsonconverter without jpo-ode, replace the contents of docker-compose.yml with those of docker-compose-standalone.yml.
Navigate to the root directory of the jpo-geojsonconverter project and run the following command:
docker-compose up --build -d
docker-compose psTo bring down the services and remove the running containers run the following command:
docker-compose downFor a fresh restart, run:
docker-compose down
docker-compose up --build -d
docker-compose psTo completely rebuild from scratch, run:
docker-compose down
docker-compose rm -fvs
docker-compose up --build -d
docker-compose ps- The DOCKER_HOST_IP environment variable is used to communicate with the bootstrap server that the instance of Kafka is running on.
In order to utilize Confluent Cloud:
- DOCKER_HOST_IP must be set to the bootstrap server address (excluding the port)
This section outlines the software technology stacks of the GeoJsonConverter.
Install the IDE of your choice:
- Eclipse: https://eclipse.org/
- STS: https://spring.io/tools/sts/all
- IntelliJ: https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/
Contact the developers of the GeoJsonConverter application by submitting a Github issue.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either expressed or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Please read our contributing guide to learn about our development process, how to propose pull requests and improvements, and how to build and test your changes to this project.
- Main repository on GitHub (public)
- USDOT ITS JPO ODE on Github (public)