This is the implementation for Full Parameter Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources and AdaLomo: Low-memory Optimization with Adaptive Learning Rate.
LOMO and AdaLomo are integrated in CoLLiE library, which supports Collaborative Training of Large Language Models in an Efficient Way.
You can also install lomo-optim from PyPI using pip.
pip install lomo-optimThen, import Lomo or AdaLomo.
from lomo_optim import Lomo
from lomo_optim import AdaLomoThe usage of Lomo and AdaLomo is similar but not the same as PyTorch's optimizers
(example).
We recommend to use AdaLomo without gradnorm to get better performance and higher throughput.
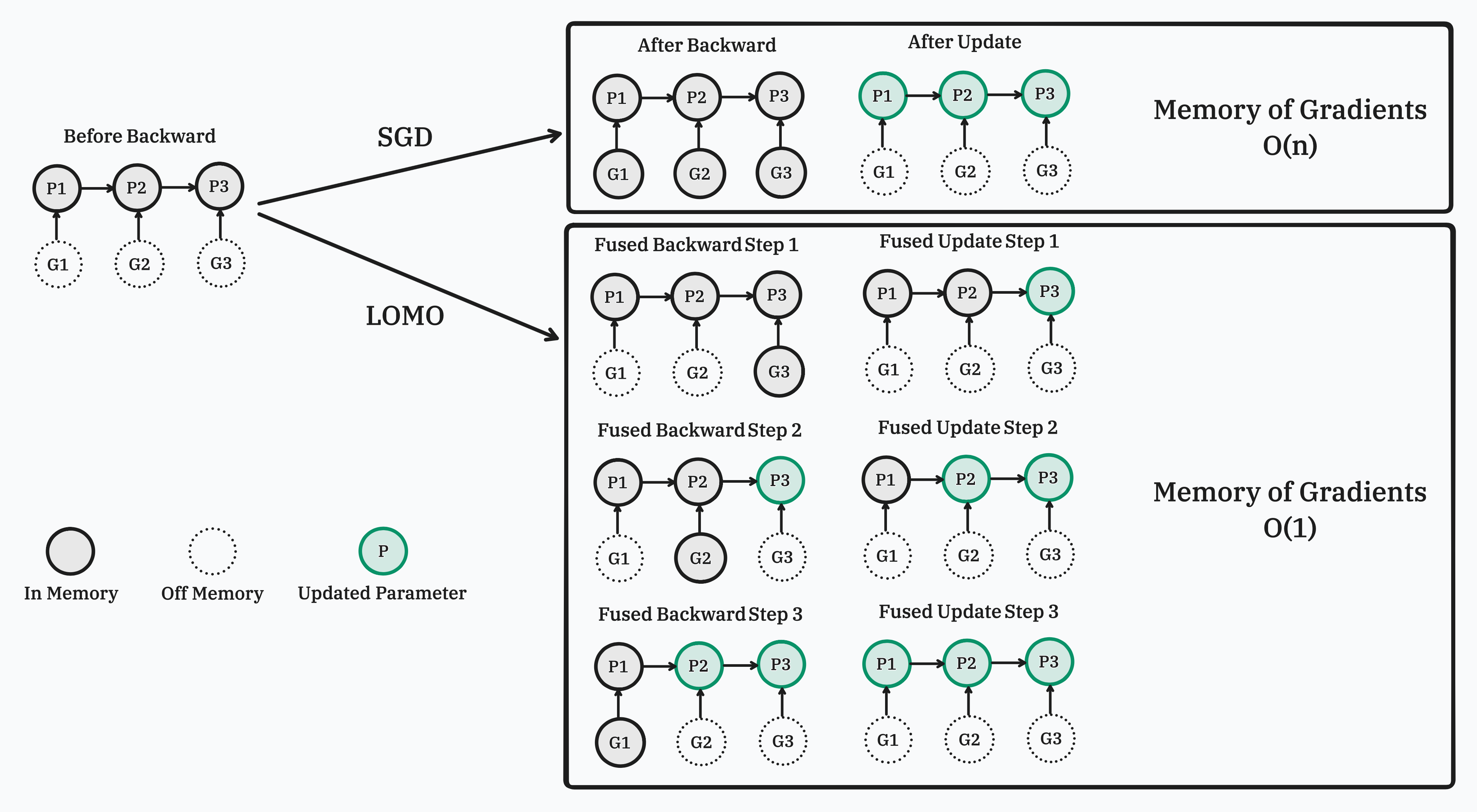
In this work, we propose a new optimizer, LOw-Memory Optimization (LOMO), which fuses the gradient computation and the parameter update in one step to reduce memory usage. Our approach enables the full parameter fine-tuning of a 7B model on a single RTX 3090, or a 65B model on a single machine with 8×RTX 3090, each with 24GB memory.
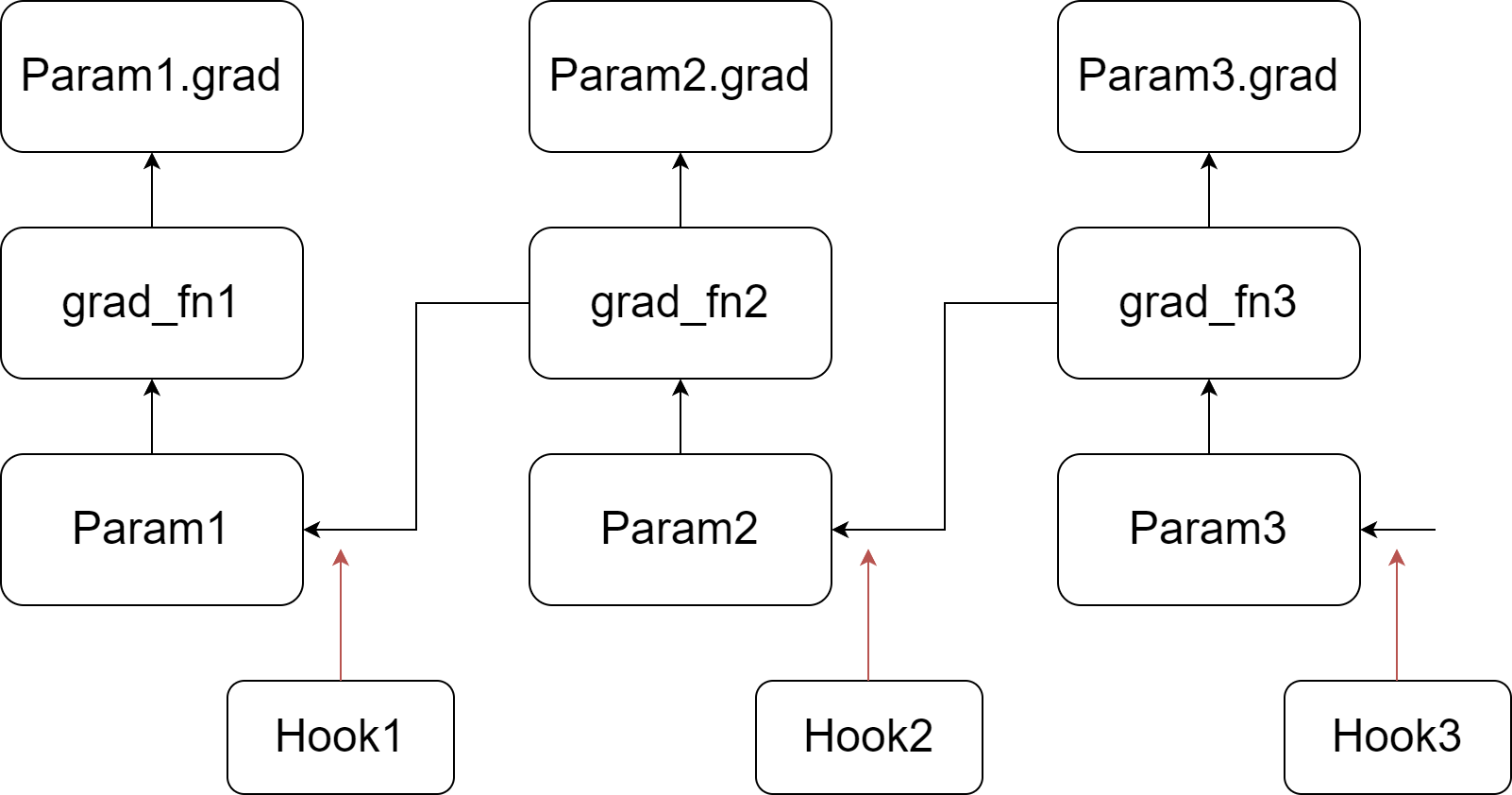 Our implementation relies on injecting hook functions into PyTorch's backward pass. As depicted in the figure, we register a customized hook function for each parameter. When the gradient of a parameter is computed (prior to writing it to the .grad attribute), its corresponding hook function is invoked. For more information about hook functions and the backward pass of the autograd graph, please refer to PyTorch's documentation. In summary, during the backward pass, we go through a tensor and its grad_fn, write the gradient into the .grad attribute, and then pass to the next tensor.
Our implementation relies on injecting hook functions into PyTorch's backward pass. As depicted in the figure, we register a customized hook function for each parameter. When the gradient of a parameter is computed (prior to writing it to the .grad attribute), its corresponding hook function is invoked. For more information about hook functions and the backward pass of the autograd graph, please refer to PyTorch's documentation. In summary, during the backward pass, we go through a tensor and its grad_fn, write the gradient into the .grad attribute, and then pass to the next tensor.
Our customized hook function scans all the parameters, updating a parameter if its .grad attribute is not empty, and then clears and frees the .grad attribute. Since the hook function for a parameter is called before its .grad attribute is set, the .grad attribute of the last parameter in the autograd graph is not ready when the last hook function is invoked. Therefore, we perform an additional scan to update the last parameter.
The code for LOMO is in lomo folder.
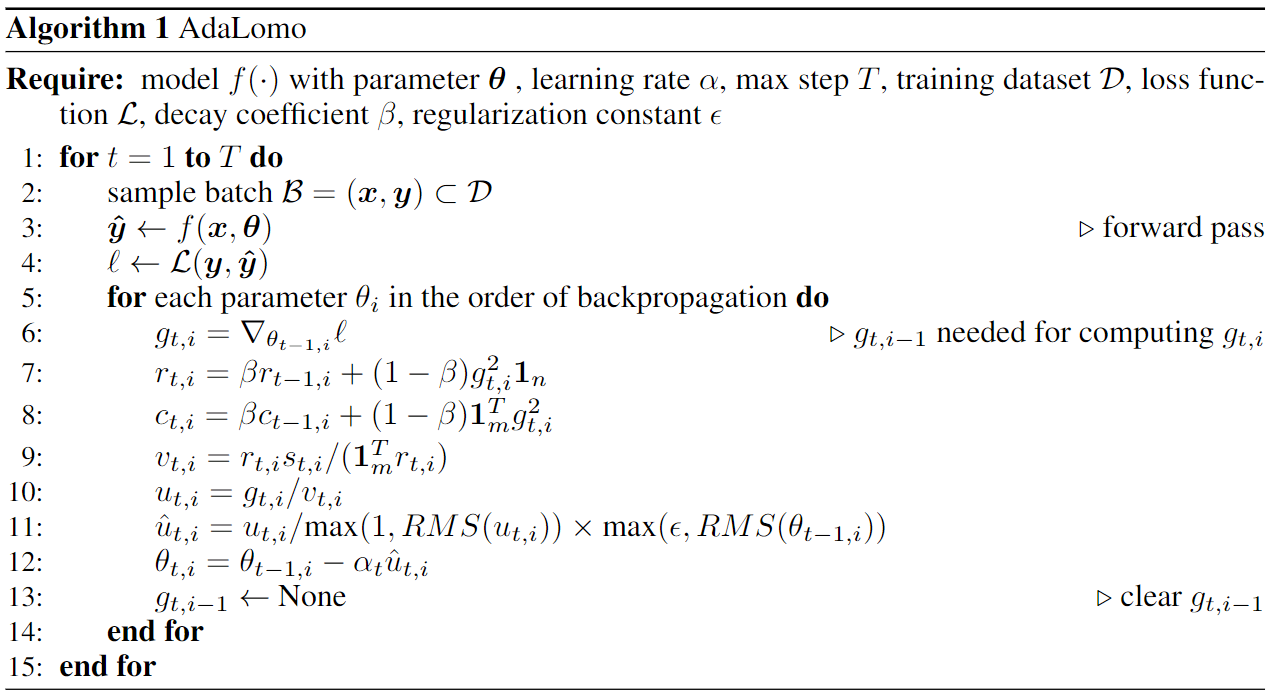
In this work, we examined the distinctions between the LOMO and Adam optimization techniques and introduce AdaLomo, which provides an adaptive learning rate for each parameter and utilizes grouped update normalization while maintaining memory efficiency. AdaLomo achieves results comparable to AdamW in both instruction-tuning and further pre-training with less memory footprint.
The code for AdaLomo is in adalomo folder.
@article{lv2023full,
title={Full Parameter Fine-tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources},
author={Lv, Kai and Yang, Yuqing and Liu, Tengxiao and Gao, Qinghui and Guo, Qipeng and Qiu, Xipeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.09782},
year={2023}
}