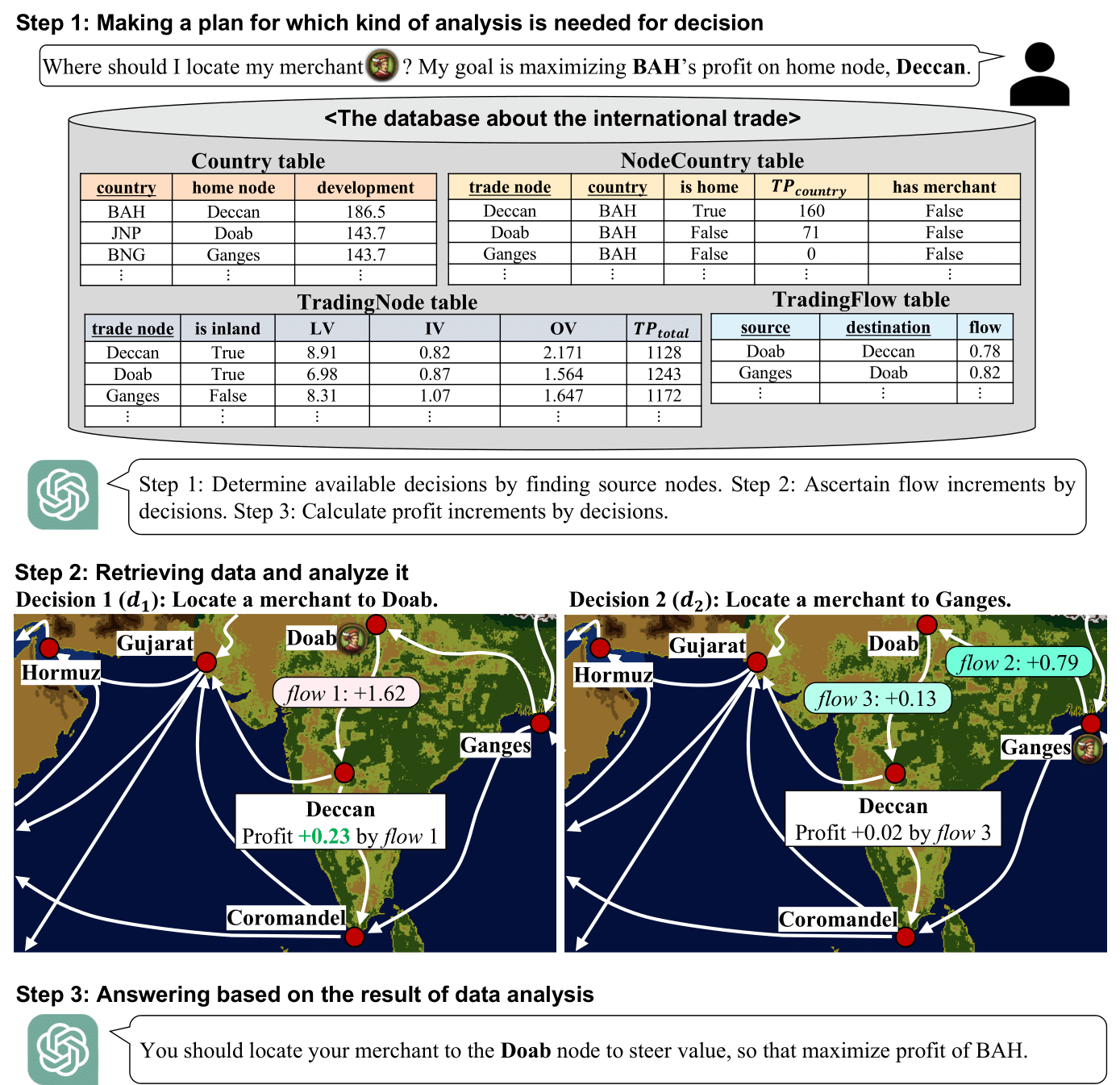
PlanRAG: A Plan-then-Retrieval Augmented Generation for Generative Large Language Models as Decision Makers
Accepted at NAACL 2024 Main: https://aclanthology.org/2024.naacl-long.364/
Our RAG-based decision makers use Neo4j as a tool to access Labeled Property Graph (LPG) data in DQA benchmark. Therefore, you should prepare Neo4j with the following commands and instructions:
# Ubuntu
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
sudo curl -fsSL https://debian.neo4j.com/neotechnology.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://debian.neo4j.com stable 4.1"
sudo apt install neo4j-enterprise
sudo apt install cypher-shell
# Login with the default user/password 'neo4j'/'neo4j'.
cypher-shell -u neo4j
# Then, change to a new password and enter ':exit' to return to the terminal.For relational data in DQA benchmark, you should prepare MySQL with the following commands and instructions:
# Ubuntu
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.14-1_all.deb
sudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.14-1_all.deb
# Then, select 'OK' to proceed to the next step.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y mysql-server
# Login with root user to create the default database 'DQA_rdb'.
sudo mysql -u root
mysql> CREATE DATABASE DQA_rdb;
# (Optional) Make MySQL accessible without sudo privilege in the Python environment.
mysql> USE mysql;
mysql> update user set plugin='mysql_native_password' where user='root';
mysql> flush privileges;
# Then, enter ':exit' to return to the terminal.Please fill the values in "config.json" file with database connection information and your API key you want to use.
Note: Our decision makers in the paper use OpenAI's GPT-4.0 as a generative LM. Due to the performance, we strongly recommend using OpenAI's GPT-4.0.
{
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "Your OpenAI API key",
"HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN": "Your Hugging Face Hub API key",
"NEO4J": {
"HOST": "Neo4j host address (default: 'bolt://localhost:7687')",
"USER": "User id (default: 'neo4j')",
"PASSWORD": "User password (Do not fill with the default password 'neo4j')"
}
"MYSQL": {
"HOST": "MySQL host address (default: 'localhost')",
"USER": "User id (default: 'root')"
}
}conda create -n planRAG -y python=3.8 && conda activate planRAG
pip install -r requirements.txt- PlanRAG (ours)
# locating scenario with relational database python src/main.py \ --technique PlanRAG \ --scenario locating \ --database relational \ --question_num 1 \ --model gpt-4 \ --model_method openai # building scenario with graph database python src/main.py \ --technique PlanRAG \ --scenario building \ --database graph \ --question_num 1 \ --model gpt-4 \ --model_method openai
- Iterative RAG
python src/main.py \ --technique IterRAG \ --scenario locating \ --database relational \ --question_num 1 \ --model gpt-4 \ --model_method openai - Single-turn RAG
python src/main.py \ --technique SingleRAG \ --scenario locating \ --database relational \ --question_num 1 \ --model gpt-4 \ --model_method openai
python src/main.py \
--technique PlanRAG \
--scenario locating \
--database relational \
--question_num 1 \
--model gpt-4 \
--model_method openai \
--mode few-shotNote: As DQA has relatively long questions, we recommend to use one-shot execution only with GPT-4 or GPT-3.5
For using open models in our experiment, you should install vllm library in your environment (e.g. conda environment). You can install it by following command.
pip install vllmYou can also check the official documentation in here.
Following code is an example for executing our code by using meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-chat-hf model.
# First, you should deploy your model as a server by vllm.
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server --model meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-chat-hf
# Now, you can try open-model experiments.
python src/main.py \
--technique IterRAG \
--scenario locating \
--database relational \
--question_num 1 \
--model meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-chat-hf \
--model_method vllmYou can also try to use Huggingface library. Following code is for executing meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf and do experiment by Huggingface pipeline function:
python src/main.py \
--technique IterRAG \
--scenario locating \
--database relational \
--question_num 1 \
--model meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf \
--model_method huggingfaceNote: As this code is reletively slow rather than vllm's one, we are not recommended to run this.
To generate questions for the locating scenario, you will need a Europa Universalis IV game savefile. We provide three raw files: raw1445.eu4, raw1618.eu4 and raw1701.eu4 in /data/locating/raw/ for data generation.
You can create the simulated_question.json in /data/locating/questions/ by sequentially executing the following code:
export PYTHONPATH=.
python ./src/data_parsers/locating/queries_gen/simulator.py
python ./src/data_parsers/locating/example_gen/main.py
Note: Executing Locating simulator usually takes around 30 minutes.
To generate questions for the building scenario, you will need a Victoria 3 game savefile. We provide three raw files: raw1836.v3 and raw1849.v3 in /data/building/raw/ for data generation.
You can create the simulated_questions.json in /data/building/questions/ by sequentially executing the following code:
export PYTHONPATH=.
python ./src/data_parsers/building/queries_gen/simulator.py
python ./src/data_parsers/building/example_gen/main.py
Note: Executing Building simulator usually takes around one hour.
In locating scenario, columns named "upstream" and "downstream" mean "source" and "destination" in our paper, respectively (i.e., The business logic is identical.) Also, "base_trading_power" and "calculated_trading_power" are both mean "TP_country" in our paper.