This project shows how to use django-bitcoin to receive and send money in your Python + Django application.
It shows how to create a bitcoin wallet, accept incoming bitcoins and then spend them. This all is done interactively from the command line and Python prompt.
This tutorial was written on OSX. It should work on Linux unmodified. Windows: don't know and don't care.
Note
LocalBitcoins is hiring open source freelancers to working on various open source projects we are using. If you have decent Python and UNIX experience please contact to mikko@localbitcoins.com, CV included.
Contents
All code is MIT licensed.
- Bitcoin is money with API: very easy to handle programmatically. You can do it even from UNIX command line.
- No upfront contracts or paperwork needed.
- Bitcoin market liquity has risen to a level, so that it is easy for everyone to obtain bitcoins from LocalBitcoins.com. You can also convert bitcoins easily back to fiat currency, when you need to pay taxes.
- It is free from chargeback fraud. The system is based on mathematics instead of trust.
- Very low fees (0.01% compared to 2-5% by credit card, PayPal)
In order to understand this tutorial, you need to have mastered
- Python 2.7
- virtualenv
- memcached
- bitcoind
- Django basics: how to configure Django project, MySQL, models, South migrations, using interactive Python shell.
- How to consume piles of open source code from Github
Setup a configure memcached first.
Installation (virtualenv based):
git clone git@github.com:miohtama/django-bitcoin-example.git cd django-bitcoin-example virtualenv venv # Create virtualenv folder caller venv . venv/bin/activate # Active virtualenv
Install Python dependencies using pip:
pip install -r requirements.txt
django-bitcoin creates a so called bitcoin web wallet in your Django project.
- You need to have a bitcoind installed on your desktop / server.
django-bitcoinreads transactions frombitcoindand duplicates them as Django models for easy handlingdjango-bitcoincan send bitcoins from the system- Bitcoin addresses are created and used on demand. The sending and receiving addresses do not have relationship between them. When you receive bitcoins to your system they do not leave out from the same address. This is who most bitcoin web wallets behave.
Install bitcoind.
Note that the initial installation takes hefty 10-20 GB disk space for the block chain data. Blockchain contains all transaction history of bitcoin ever. Downloading this data while take a while.
- django-bitcoin communites with bitcoind over JSON-RPC protocol. You set the bitcoind address in
settings.py bitcoindtransaction handling is done as polling, using Django management commands
Configure your bitcoind to accept connection with username and password.
Create file ``example/localsettings.py` and let's put there in confidential settings (not stored on Github):
BITCOIND_CONNECTION_STRING = "http://miguel:passwor@example.com:8332" # How many bitcoin network confirmations are required until django-bitcoin considers the transaction # as received BITCOIN_MINIMUM_CONFIRMATIONS = 1 # Use Django signals to tell the system when new money has arrived to your wallets BITCOIN_TRANSACTION_SIGNALING = True
django-bitcoin uses South for its schema management.
Create a database (sqlite test.db file by default):
python manage.py syncdb python manage.pt migrate django_bitcoin
Let's open the development web server and see that the Django admin is up with django-bitcoin:
python manage.py runserver_plus
Visit http://localhost:8000/admin to see the Django admin interface having addresses,
wallets and such:
A wallet, django_bitcoin.models.Walletx,
is a combination of receiving and sending bitcoin addresses and
stores the bitcoin value associated with these addresses.
A wallet can have infinite number of sending and receiving bitcoin addresses.
Let's start interactive IPython prompt:
python manage.py shell_plus
Then we create a wallet with an label. Usually if the application has only one wallet (not per user wallets) you call this wallet instance to master wallet:
master_wallet, created = Wallet.objects.get_or_create(label="master_wallet")
Then we need to have an receiving bitcoin address where this wallet can receive bitcoins:
recv_address = master_wallet.receiving_address(fresh_addr=False) print recv_address
Write down the bitcoin address you got.
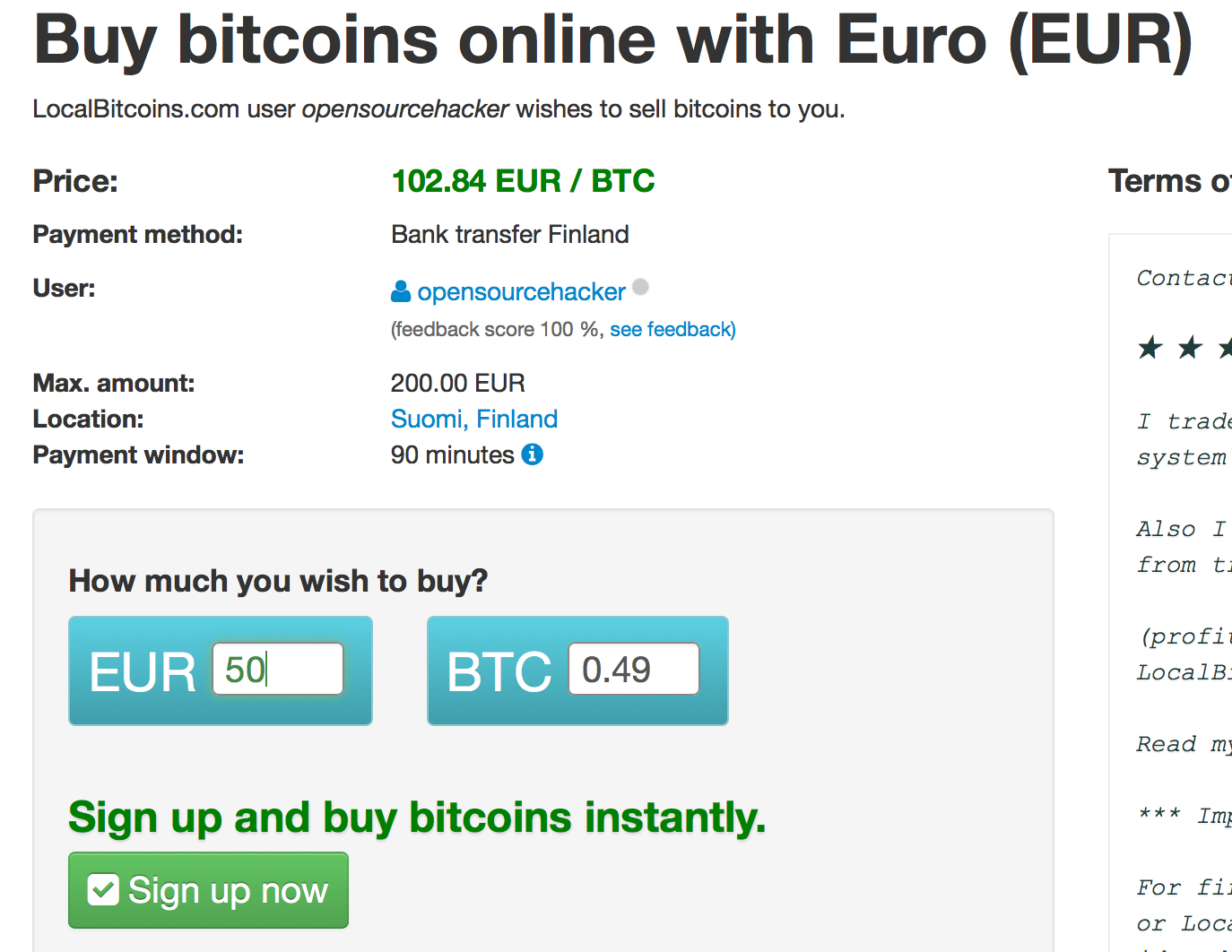
Go to LocalBitcoins.com and buy some bitcoins. LocalBitcoins.com is a person-to-person bitcoin exchange where you are not buying bitcoins from the organization, but from another user. This is definitely the easiest and fastest way to obtain your first bitcoins. Think LocalBitcoins as eBay of bitcoins.
LocalBitcoins.com provides diffferent online payment methods. The recommended methods are:
- Cash deposit (inverse ATM popular in US) - no id needed
- National bank transfer - the bitcoin seller may require you to show an id
If you are living a big city you can also try cash trade.
You can buy small amounts of bitcoins from me. If you want to purchase bitcoins with PayPal agree it with beforehand, as PayPal bitcoin sell advertisements are hidden by default to avoid frauduleint buy requests.
We have the receiving bitcoin address of our master wallet from before. Now we are going to send the bitcoins there from LocalBitcoins:
When you hit the Send on LocalBitcoins.com, the site submits the transaction to the bitcoin network. Bitcoin network consists of nodes which will confirm your transaction. After the certain transaction confirmation threshold is exceeded you can assume the transaction was safe and not double spent attempt. Usually this confirmation threshold is six confirmations, but you can set it lower if you want to have faster customer experience. It takes 5-30 minutes to process a transaction with six confirmations.
Now, in our own example application polls bitcoind which listens
to bitcoin network. bitcoind exposes a bunch of commands
over JSON-RPC protocol.
You can call these commands even from the UNIX command line.
We have a Django management command for polling bitcoind.
On each poll, we check the incoming transaction for receiving
bitcoin addresses we have in our database. When the bitcoin
network keeps confirming our transaction, the confirmation count
of the transaction increases. When the threshold is exceeded,
django-bitcoin writes down the transaction to the database
as DepositTransaction and the amount of bitcoins in the
wallet is increased.
For this example we run the polling command by hand. Usually this is a task delegated to Celery task scheduler:
python manage.py CheckTransactions
CheckTransactions fires the Django signal handlers
notifying the Django project for incoming transactions.
For the simplicity, we do not use Django signalling in this example.
Instead, we manually run CheckTransactions
and after 20 minutes and see
that the bitcoins have been received in our wallet:
python manage.py shell_plus master_wallet = Wallet.objects.get(label="master_wallet") print master_wallet.total_balance()
Now, we got the coins! Time to make some purchases. We go to an online shop selling high quality Brazilian music.
Then we'll send the bitcoins from our wallet to buy this wondeful piece of art.
All bitcoin amounts are stored in Python decimal.Decimal instead of
floats to avoid floating point rounding errors.
We fire up the Python shell again and send the bitcoins to the target address:
python manage.py shell_plus
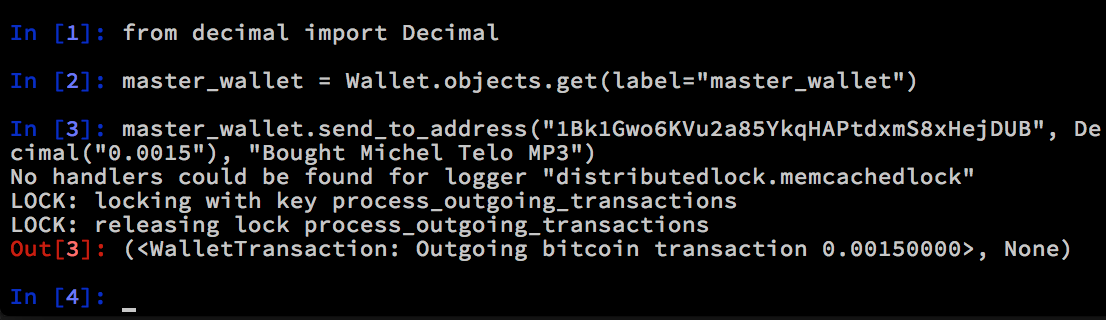
from decimal import Decimal
master_wallet = Wallet.objects.get(label="master_wallet")
master_wallet.send_to_address("1Bk1Gwo6KVu2a85YkqHAPtdxmS8xHejDUB", Decimal("0.0505"), "Bought Michel Telo MP3")
Note that for every outgoing transaction there is a bitcoin network fee
to compensate the bitcoin miners for confirming your transaction.
The network fee is configured to be 0.0005 BTC in django_bitcoind by default.
So the total amount to be send is the checkout price + network fee.
Higher the paid network fee, faster the transaction is processed by bitcoin network.
We can check the outgoing transactions from our wallet:
for t in WalletTransaction.objects.filter(from_wallet=master_wallet): print t, t.to_bitcoinaddress
If you enter the receiving address to blockchain.info you can see its transaction statuses in the bitcoin network.
And that's it. Nossa!