This repository implements an Event Source for Knative Eventing defined with a CustomResourceDefinition (CRD). This Event Source represents Google Cloud Scheduler. Point is to demonstrate an Event Source that does not live in the Knative Eventing Sources that can be independently maintained, deployed and so forth.
This particular example demonstrates how to perform basic operations such as:
- Create a Cloud Scheduler Job when a Source is created
- Delete a Job when that Source is deleted
- Update a Job when the Source spec changes
Actual implementation contacts the Cloud Scheduler API and creates a Job as specified in the CloudSechedulerSource CRD Spec. Upon success a Knative service is created to receive calls from the Cloud Scheduler and will then forward them to the Channel.
Provide an Event Source that allows subscribing to Cloud Scheduler and processing them in Knative.
Another purpose is to serve as an example of how to build an Event Source using a [Warm Image[(https://github.com/mattmoor/warm-image) as a starting point.
-
Create a Google Cloud project and install the
gcloudCLI and rungcloud auth login. This sample will use a mix ofgcloudandkubectlcommands. The rest of the sample assumes that you've set the$PROJECT_IDenvironment variable to your Google Cloud project id, and also set your project ID as default usinggcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID. -
Setup Knative Serving
-
Configure static IP
-
Configure custom dns
-
Configure outbound network access
-
Setup Knative Eventing using the
release.yamlfile. This example does not require GCP.
-
Enable Google Cloud Scheduler API
gcloud services enable cloudscheduler.googleapis.com -
Create a GCP Service Account. This sample creates one service account for both registration and receiving messages, but you can also create a separate service account for receiving messages if you want additional privilege separation.
-
Create a new service account named
csr-sourcewith the following command:gcloud iam service-accounts create csr-source
-
Give that Service Account the Editor' role on your GCP project:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member=serviceAccount:csr-source@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com \ --role roles/cloudscheduler.admin
-
Download a new JSON private key for that Service Account. Be sure not to check this key into source control!
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create csr-source.json \ --iam-account=csr-source@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com -
Create a namespace for where the secret is created and where our controller will run
kubectl create namespace cloudschedulersource-system
-
Create a secret on the kubernetes cluster for the downloaded key. You need to store this key in
key.jsonin a secret namedgcppubsub-source-keykubectl -n cloudschedulersource-system create secret generic cloudschedulersource-key --from-file=key.json=csr-source.json
The name
cloudschedulersource-keyandkey.jsonare pre-configured values in the controller which manages your Cloud Scheduler sources.
-
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vaikas-google/csr/master/release.yamlFirst list the available sources, you might have others available to you, but this is the one we'll be using in this example
kubectl get crds -l "eventing.knative.dev/source=true"You should see something like this:
vaikas@penguin:~/projects/go/src/github.com/vaikas-google/csr$
NAME AGE
cloudschedulersources.sources.aikas.org 29dyou can then get more details about it, for example what are the available configuration options for it:
kubectl get crds cloudschedulersources.sources.aikas.org -oyamlAnd in particular the Spec section is of interest:
validation:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
apiVersion:
type: string
kind:
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
properties:
body:
description: Optional body to send in the event
type: string
googleCloudProject:
description: Google Cloud Project ID to create the scheduler job in.
type: string
httpMethod:
description: Optional HTTP method to use when delivering the event.
If omitted, uses POST
type: string
location:
description: 'Google Cloud Platform region to create the scheduler job
in. For example: us-central1.'
type: string
schedule:
description: 'Schedule in cron format. For example: ''* * * * *'' (once
a minute), or human readable: ''every 1 mins'''
type: string
serviceAccountName:
description: Service Account to run Receive Adapter as. If omitted,
uses 'default'.
type: string
sink:
type: object
timezone:
description: Optional timezone of the schedule. If omitted, uses UTC.
type: string
required:
- googleCloudProject
- location
- scheduleTo verify the Cloud Scheduler is working, we will create a simple Knative
Service that dumps incoming messages to its log. The service.yaml file
defines this basic service. Image might be different if a new version has been released.
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: github-message-dumper
spec:
runLatest:
configuration:
revisionTemplate:
spec:
container:
image: us.gcr.io/probable-summer-223122/eventdumper-833f921e52f6ce76eb11f89bbfcea1df@sha256:7edb9fc190dcf350f4c49c48d3ff2bf71de836ff3dc32b1d5082fd13f90edee3Enter the following command to create the service from service.yaml:
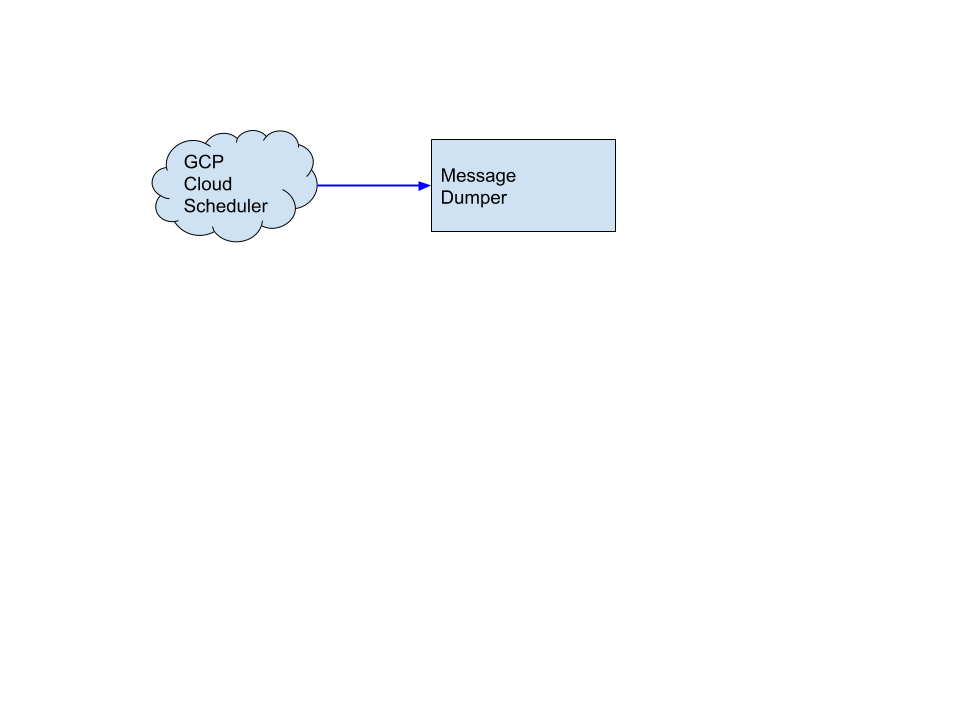
kubectl --namespace default apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vaikas-google/csr/master/service.yamlThe simplest way to consume events is to wire the Source directly into the consuming function. The logical picture looks like this:
Create a Cloud Scheduler instance targeting your function with the following:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vaikas-google/csr/master/one-to-one-csr.yaml | \
sed "s/MY_GCP_PROJECT/$PROJECT_ID/g" | kubectl apply -f -kubectl get cloudschedulersourcesAnd you should see something like this:
vaikas@penguin:~/projects/go/src/github.com/vaikas-google/csr$ kubectl get cloudschedulersources
NAME AGE
scheduler-test 1mgcloud beta scheduler jobs listYou should see something like this:
vaikas@penguin:~/projects/go/src/github.com/vaikas-google/csr$ gcloud beta scheduler jobs list
ID LOCATION SCHEDULE (TZ) TARGET_TYPE STATE
filter-source us-central1 every 1 mins (UTC) HTTP ENABLEDThen wait a couple of minutes and you should see events in your message dumper.
Note this might take couple of minutes after the creation while the Cloud Scheduler gets going
kubectl -l 'serving.knative.dev/service=message-dumper' logs -c user-containerAnd you should see an entry like this there
2018/12/20 00:23:00 Received Cloud Event Context as: {CloudEventsVersion:0.1 EventID:2cd5d2ed-d2d1-94a1-bee7-d542d7ab834e EventTime:2018-12-20 00:23:00.498638175 +0000 UTC EventType:GoogleCloudScheduler EventTypeVersion: SchemaURL: ContentType:application/json Source:GCPCloudScheduler Extensions:map[]}
2018/12/20 00:23:00 Received event data as: {"data": "test does this work"}Where the first line is displaying the Cloud Events Context and the second line is the actual data line.
kubectl delete cloudschedulersources scheduler-test
kubectl delete services.serving message-dumpergcloud beta scheduler jobs listThe specification for a scheduler job looks like:
apiVersion: sources.aikas.org/v1alpha1
kind: CloudSchedulerSource
metadata:
name: scheduler-test
spec:
googleCloudProject: quantum-reducer-434
location: us-central1
schedule: "every 1 mins"
body: "{test does this work}"
sink:
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Channel
name: scheduler-demoWith the above in foo.yaml, you would create the Cloud Scheduler Job with:
kubectl create -f foo.yamlYou can see what Cloud Scheduler Jobs have been created:
$ kubectl get cloudschedulersources
NAME AGE
scheduler-test 4mYou can upgrade foo.yaml jobs by updating the spec. For example, say you
wanted to change the above job to send a different body, you'd update
the foo.yaml from above like so:
apiVersion: sources.aikas.org/v1alpha1
kind: CloudSchedulerSource
metadata:
name: scheduler-test
spec:
googleCloudProject: quantum-reducer-434
location: us-central1
schedule: "every 1 mins"
body: "{test does this work, hopefully this does too}"
sink:
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Channel
name: scheduler-demoAnd then update the spec.
kubectl replace -f foo.yamlOf course you can also do this in place by using:
kubectl edit cloudschedulersources scheduler-testAnd on the next run (or so) the body send to your function will by changed to '{test does this work, hopefully this does too}' instead of '{test does this work}' like before.
You can remove a Cloud Scheduler jobs via:
kubectl delete cloudschedulersources scheduler-test