CCPi-Regularisation Toolkit (Software X paper)
| Master | Development | Anaconda binaries |
|---|---|---|
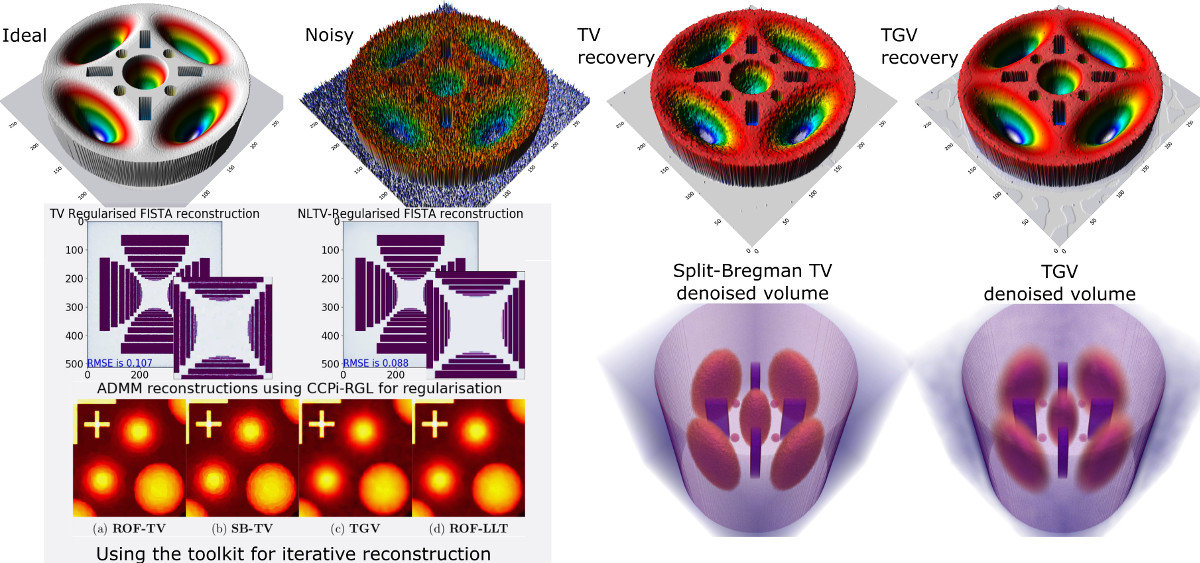
Iterative image reconstruction (IIR) methods frequently require regularisation to ensure convergence and make inverse problem well-posed. The CCPi-Regularisation Toolkit (CCPi-RGL) toolkit provides a set of 2D/3D regularisation strategies to guarantee a better performance of IIR methods (higher SNR and resolution). The regularisation modules for scalar and vectorial datasets are based on the proximal operator framework and can be used with proximal splitting algorithms, such as PDHG, Douglas-Rachford, ADMM, FISTA and others. While the main target for CCPi-RGL is tomographic image reconstruction, the toolkit can be used for image denoising problems. The core modules are written in C-OMP and CUDA languages and wrappers for Matlab and Python are provided. With CuPy dependency installed for Python, one can use regularisers directly without the need for explicit compilation. We recommend this option as the simplest to start with if you've got a GPU. This software can also be used by running in parallel across multiple GPU devices on a PC or a cluster compute node.
- MATLAB OR
- Python (tested ver. 3.5/2.7); Cython
- C compilers
- nvcc (CUDA SDK) compilers
- CuPy for the GPU-enabled methods
- Rudin-Osher-Fatemi (ROF) Total Variation (explicit PDE minimisation scheme) 2D/3D CPU/GPU + CuPy (Ref. 1)
- Fast-Gradient-Projection (FGP) Total Variation 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 2)
- Split-Bregman (SB) Total Variation 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 5)
- Primal-Dual (PD) Total Variation 2D/3D CPU/GPU + CuPy (Ref. 13)
- Total Generalised Variation (TGV) model for higher-order regularisation 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 6,13)
- Linear and nonlinear diffusion (explicit PDE minimisation scheme) 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 8)
- Anisotropic Fourth-Order Diffusion (explicit PDE minimisation) 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 9)
- A joint ROF-LLT (Lysaker-Lundervold-Tai) model for higher-order regularisation 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 10,11)
- Nonlocal Total Variation regularisation (GS fixed point iteration) 2D CPU/GPU (Ref. 12)
- Fast-Gradient-Projection (FGP) Directional Total Variation 2D/3D CPU/GPU (Ref. 3,4,2)
- Total Nuclear Variation (TNV) penalty 2D+channels CPU (Ref. 7)
The package comes as a CMake project and additional wrappers for Python and Matlab. Please see more detailed Installation information.
To install precompiled binaries, you need conda and install from the ccpi channel using :
conda install ccpi-regulariser -c ccpi -c conda-forge
One can also use some of the GPU modules with the provided CuPy interfaces. The functions in ccpi-regularisation-cupy package work with CuPy arrays as an input and return a CuPy array for output.
conda install -c httomo ccpi-regularisation-cupy
Once installed please see Demos. Please note that not all modules are yet supported as this is an ongoing development. One can install both CuPy-driven and the ccpi-regulariser packge in one environment, but please be aware that the functions carry the identical names.
-
Kazantsev, D., Jørgensen, J.S., Andersen, M., Lionheart, W.R., Lee, P.D. and Withers, P.J., 2018. Joint image reconstruction method with correlative multi-channel prior for X-ray spectral computed tomography. Inverse Problems, 34(6) Results can be reproduced using the following SOFTWARE
- The Core Imaging Library by CCPi
- TOmographic MOdel-BAsed Reconstruction (ToMoBAR)
- Joint image reconstruction method with correlative multi-channel prior for X-ray spectral computed tomography (MATLAB code)
CCPi-RGL software is a product of the CCPi group and STFC SCD software developers. Any relevant questions/comments can be e-mailed to Daniil Kazantsev at dkazanc@hotmail.com