PD-Denoising
PyTorch |Tech Report
This is the official pytorch implementation of the paper 'When AWGN-based Denoiser Meets Real Noises', and parts of the code are initialized from the pytorch implementation of DnCNN-pytorch. We revised the basis model structure and data generation process, and rewrote the testing procedure to make it work for real noisy images. More details can be found in the code implementation.
Abstract
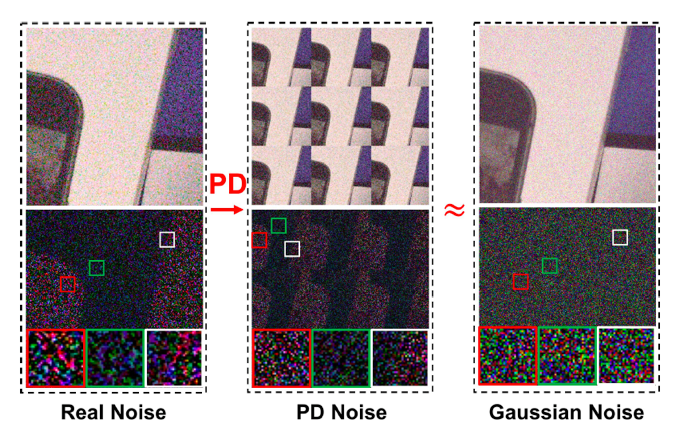
Discriminative learning based image denoisers have achieved promising performance on synthetic noise such as the additive Gaussian noise. However, their performance on images with real noise is often not satisfactory. The main reason is that real noises are mostly spatially/channel-correlated and spatial/channel-variant. In contrast, the synthetic Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) adopted in most previous work is pixel-independent. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to boost the performance of a real image denoiser which is trained only with synthetic pixel-independent noise data. First, we train a deep model that consists of a noise estimator and a denoiser with mixed AWGN and Random Value Impulse Noise (RVIN). We then investigate Pixel-shuffle Down-sampling (PD) strategy to adapt the trained model to real noises. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization ability of the proposed approach. Notably, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on real sRGB images in the DND benchmark.
Basis Model + PD Adaptation
Basis Model
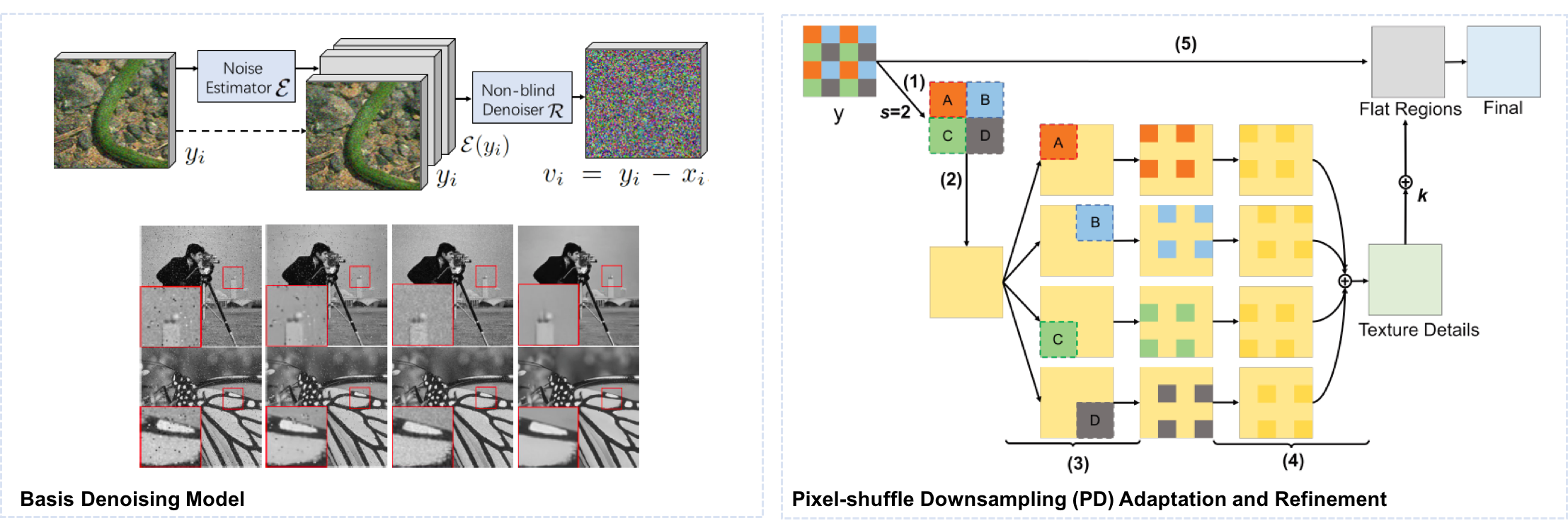
The proposed blind denoising model G consists of a noise estimator E and a follow-up non-blind denoiser R. It is trained on AWGN and RVIN. It can achieve the disentanglement of the two noises as shown.
PD Adaptation
The proposed Pixel-shuffle Down-sampling (PD) refinement strategy: (1) Compute the smallest stride s, which is 2 in this example and more CCD image cases, to match AWGN following the adaptation process, and pixel-shuffle the image into mosaic y_s; (2) Denoise y_s using G; (3) Refill each sub-image with noisy blocks separately and inversely pixel-shuffle them; (4) Denoise each refilled image again using G and average them to obtain the texture details T; (5) Combine the over-smoothed flat regions F to refine the final result.
Denoising Performance on Real Images
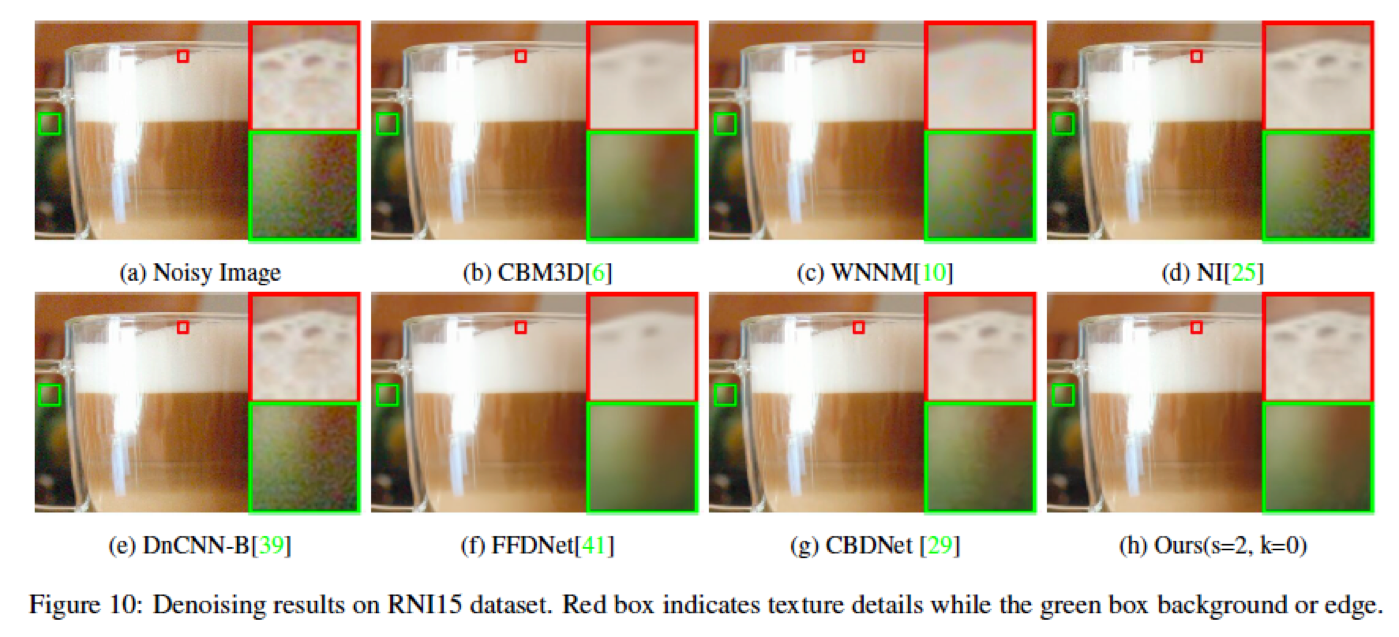
RNI15
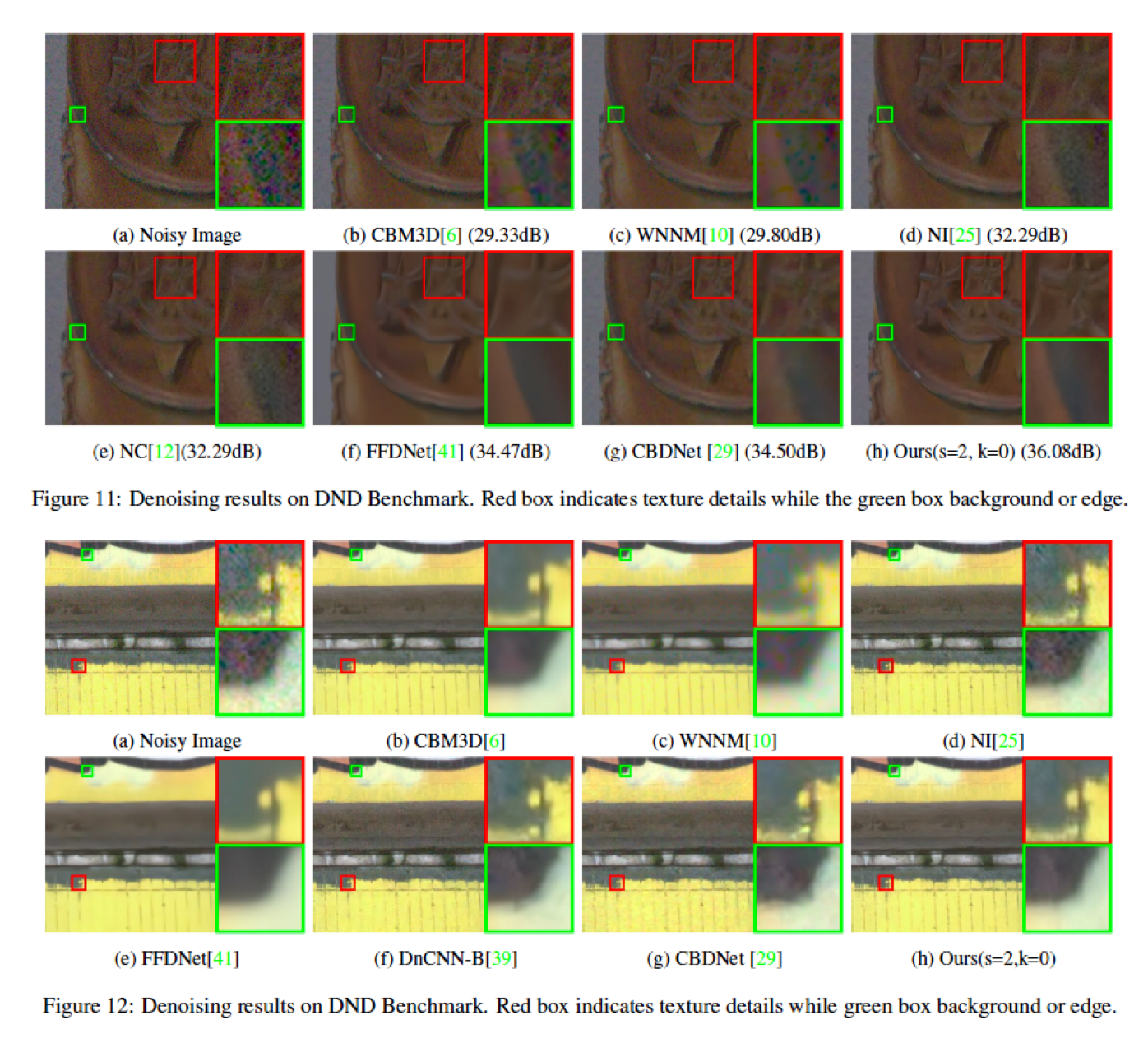
DND Benchmark
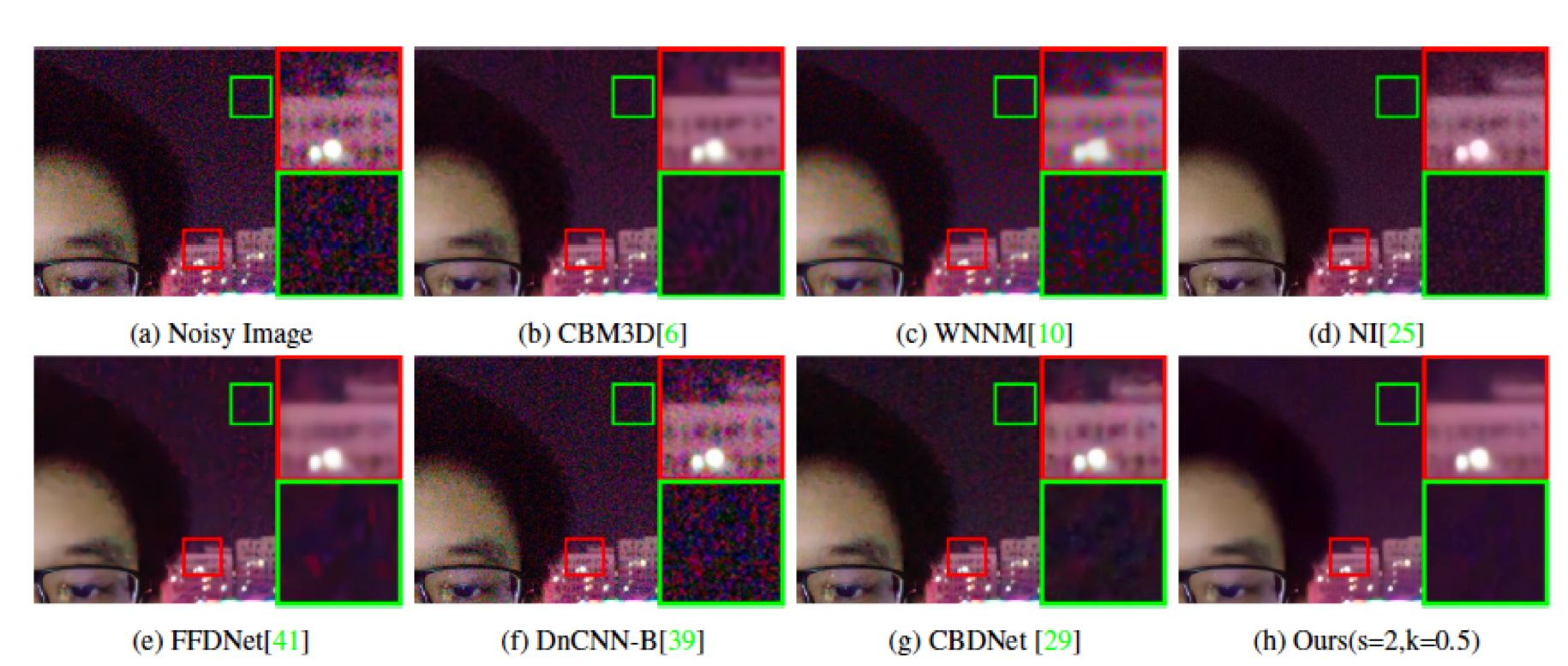
Self-collected Night Photos
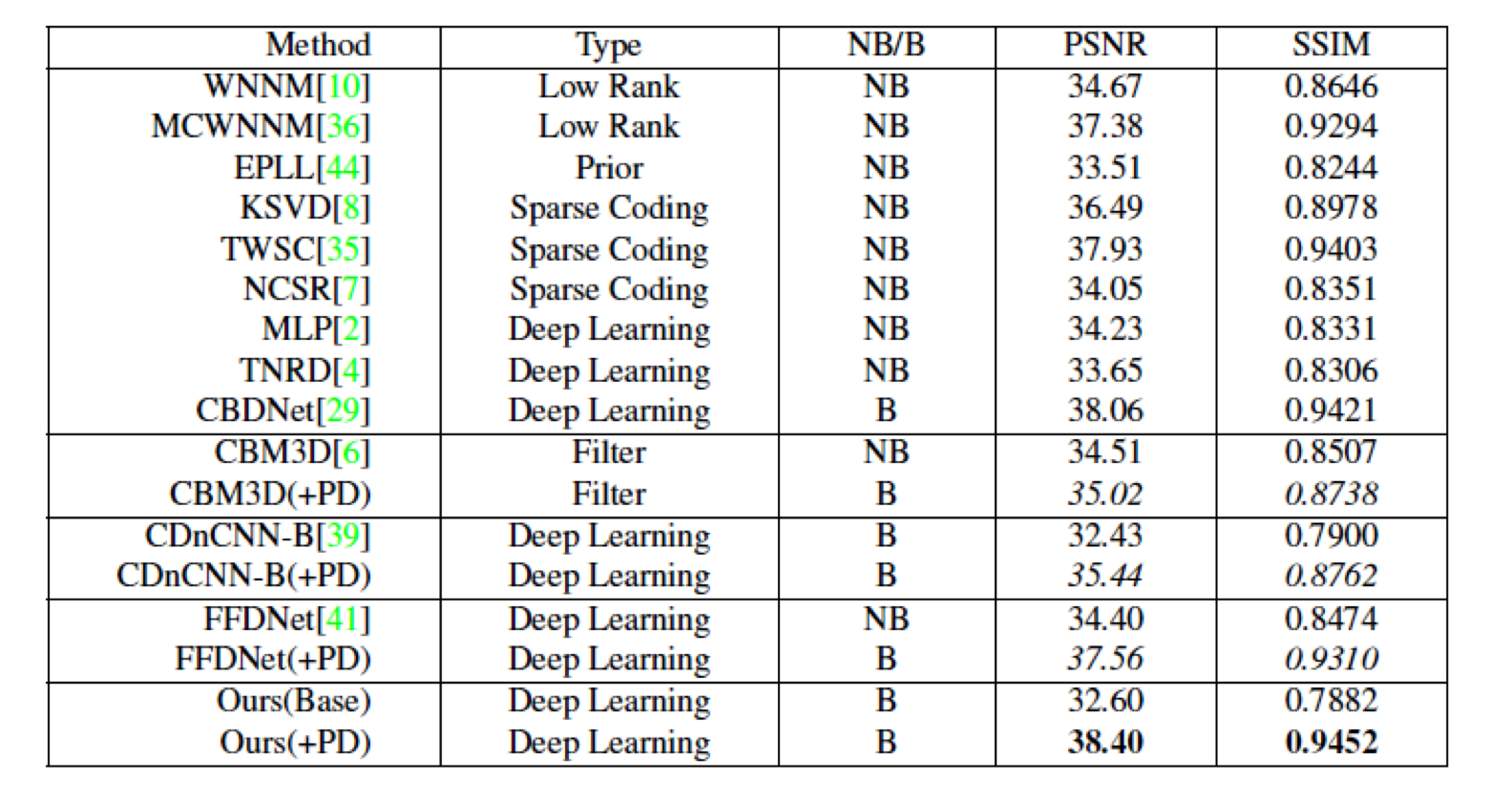
Comparisons with state-of-the-arts
We follow the submission guideline of DND benchmark to achieve the following results.
Requirements and Dependencies
Citation
If you think our model and code useful, please cite
@article{zhou2019awgn,
title={When AWGN-based Denoiser Meets Real Noises},
author={Zhou, Yuqian and Jiao, Jianbo and Huang, Haibin and Wang, Yang and Wang, Jue and Shi, Honghui and Huang, Thomas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.03485},
year={2019}
}
Train
Data Preparation
- Please follow DnCNN-pytorch to generate training data of gray image model.
- For color images, you can save your images inside the train_c folder and process it to train_c.h5 by setting preprocess=1. In the paper, we used CBSD(500-68) as the training data set. Training data can be downloaded here
- If you've already built the training and validation dataset (i.e. train.h5 & val.h5 files), set preprocess to be False.
Train the Baseline Model
The baseline model is the one without explicit noise estimation. We directly trained the model with AWGN, RVIN and mixed-AWGN-RVIN.
python train.py \
--preprocess 1\
--num_of_layers 20\
--mode B\
--color 0\
--outf logs/baseline_model
Train the Basis Model with Noise Estimation
python train.py \
--preprocess 1\
--num_of_layers 20 \
--mode MC\
--color 0\
--outf logs/gray_MC_model
You can also directly run
bash run_train.sh
NOTE
- For color version, directly set the color option to 1, and change the output folder name.
- The layer number of estimation model is default 3.
Test on Pretrained model
We provide the pretrained model saved in the logs folder. To replicate the denoising results on real images in DND benchmark and other real images, simply run
python test.py\
--scale 1\
--ps 2 --ps_scale 2\
--real 1\
--k 0\
--mode MC\
--color 1\
--output_map 0\
--zeroout 0 --keep_ind 0\
--num_of_layers 20\
--delog logs/logs_color_MC_AWGN_RVIN\
--cond 1 --refine 0 --refine_opt 1\
--test_data real_night\
--out_dir results/real_night
or simiply run,
bash run_test_on_real_patches.sh
NOTE
- test_data can be changed to other folder name with your own data.
- ps can be set to 1 to get the adaptive pixel-shuffle stride. For CCD camera images, it is better to be set to 2.
- k can be interactively adjusted to balance the details and background, providing a flexibile denoising performance. k=1 for flat regions, and k=0 for textural details (default).
- This version of testing script may cause exceeding memory issues in GPU while testing on large images. A testing_on_full image version will be released soon.
Acknowledgments
Code borrows from DnCNN-pytorch.