Expeiment 1 :- Linear Search : -
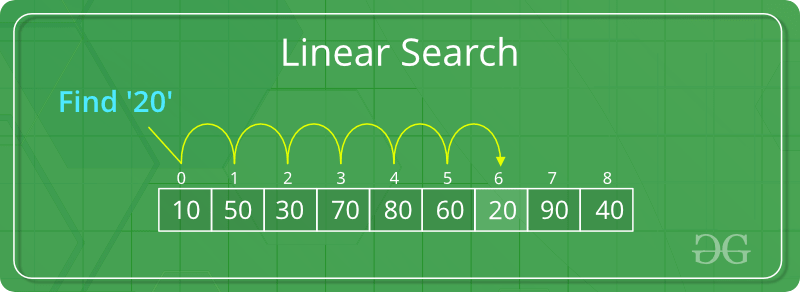
Linear search in C to find whether a number is present in an array. If it's present, then at what location it occurs. It is also known as a sequential search. It is straightforward and works as follows: we compare each element with the element to search until we find it or the list ends. Linear search for multiple occurrences and using a function.
The time complexity of above algorithm is O(n).
Linear search is rarely used practically because other search algorithms such as the binary search algorithm and hash tables allow significantly faster searching comparison to Linear search.
Experiment 2:-
Experiment 3:- write a program to implement singly linked list
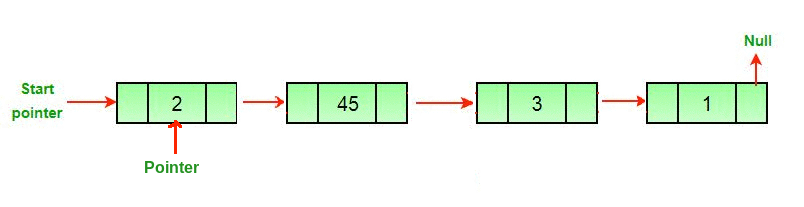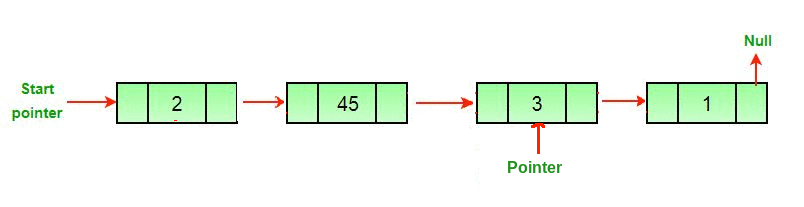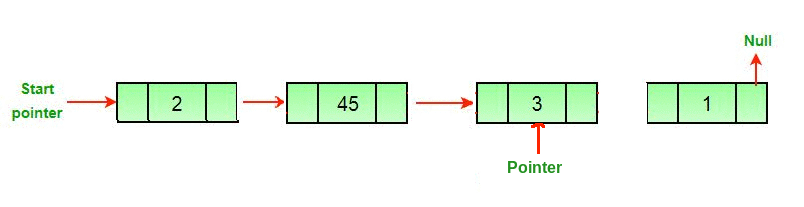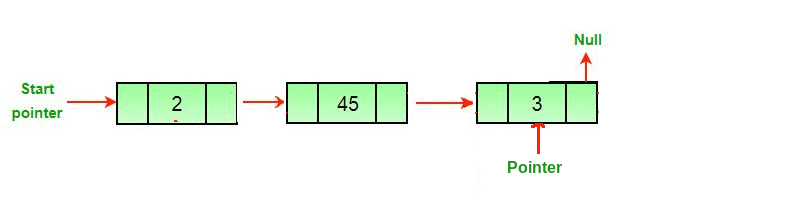
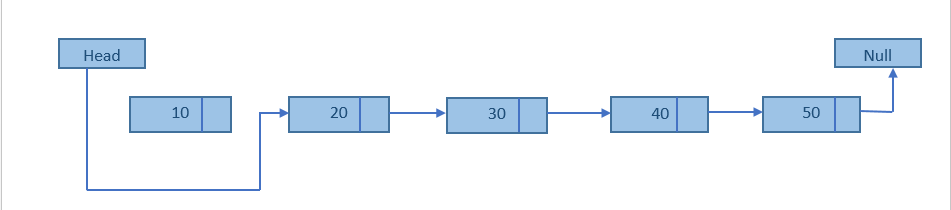
Linked List Linked List can be defined as collection of objects called nodes that are randomly stored in the memory. A node contains two fields i.e. data stored at that particular address and the pointer which contains the address of the next node in the memory. The last node of the list contains pointer to the null. DS Linked List
Uses of Linked List:-
The list is not required to be contiguously present in the memory. The node can reside any where in the memory and linked together to make a list. This achieves optimized utilization of space. list size is limited to the memory size and doesn't need to be declared in advance. Empty node can not be present in the linked list. We can store values of primitive types or objects in the singly linked list.
Why use linked list over array?
Till now, we were using array data structure to organize the group of elements that are to be stored individually in the memory. However, Array has several advantages and disadvantages which must be known in order to decide the data structure which will be used throughout the program.
Array contains following limitations:
The size of array must be known in advance before using it in the program. Increasing size of the array is a time taking process. It is almost impossible to expand the size of the array at run time. All the elements in the array need to be contiguously stored in the memory. Inserting any element in the array needs shifting of all its predecessors. Linked list is the data structure which can overcome all the limitations of an array. Using linked list is useful because,
It allocates the memory dynamically. All the nodes of linked list are non-contiguously stored in the memory and linked together with the help of pointers. Sizing is no longer a problem since we do not need to define its size at the time of declaration. List grows as per the program's demand and limited to the available memory space.
Operations in Singly linked list
Insertion :-
The insertion into a singly linked list can be performed at different positions. Based on the position of the new node being inserted, the insertion is categorized into the following categories.
- Insertion at the beginning : -
It involves inserting any element at the front of the list. We just need to a few link adjustments to make the new node as the head of the list.
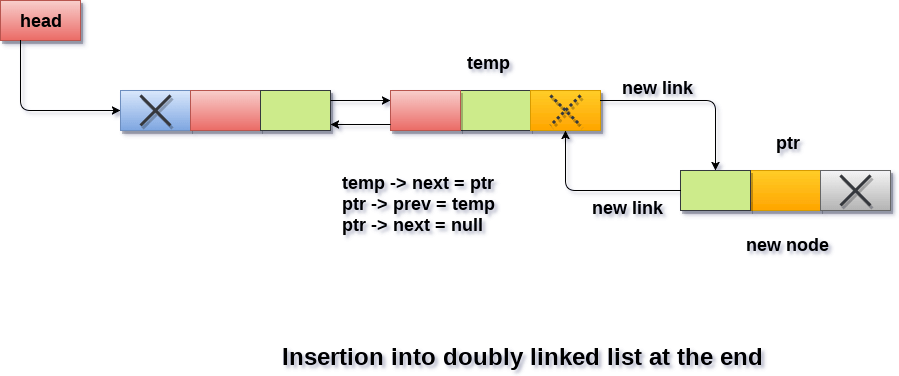
- Insertion at the end of the list :-
It involves insertion at the last of the linked list. The new node can be inserted as the only node in the list or it can be inserted as the last one. Different logics are implemented in each scenario.
- Insertion at the specific node : -
It involves insertion after the specified node of the linked list. We need to skip the desired number of nodes in order to reach the node after which the new node will be inserted. .
Deletion and Traversing:-
The Deletion of a node from a singly linked list can be performed at different positions. Based on the position of the node being deleted, the operation is categorized into the following categories.
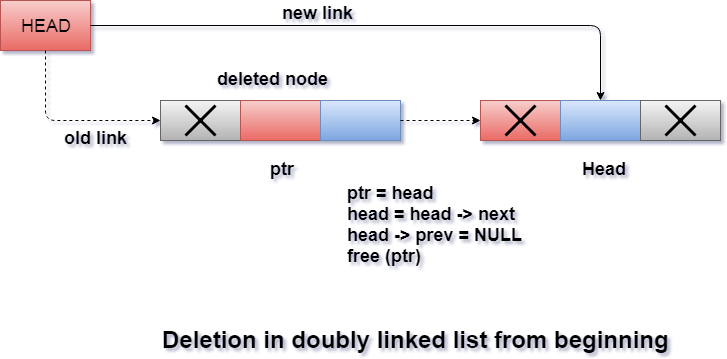
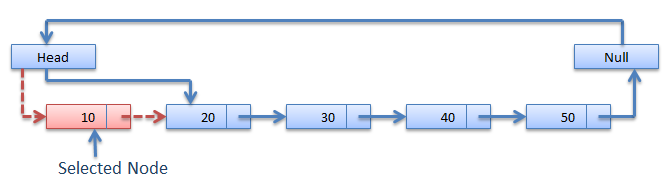
Deletion at the beginning : -
It involves deletion of a node from the beginning of the list. This is the simplest operation among all. It just need a few adjustments in the node pointers.
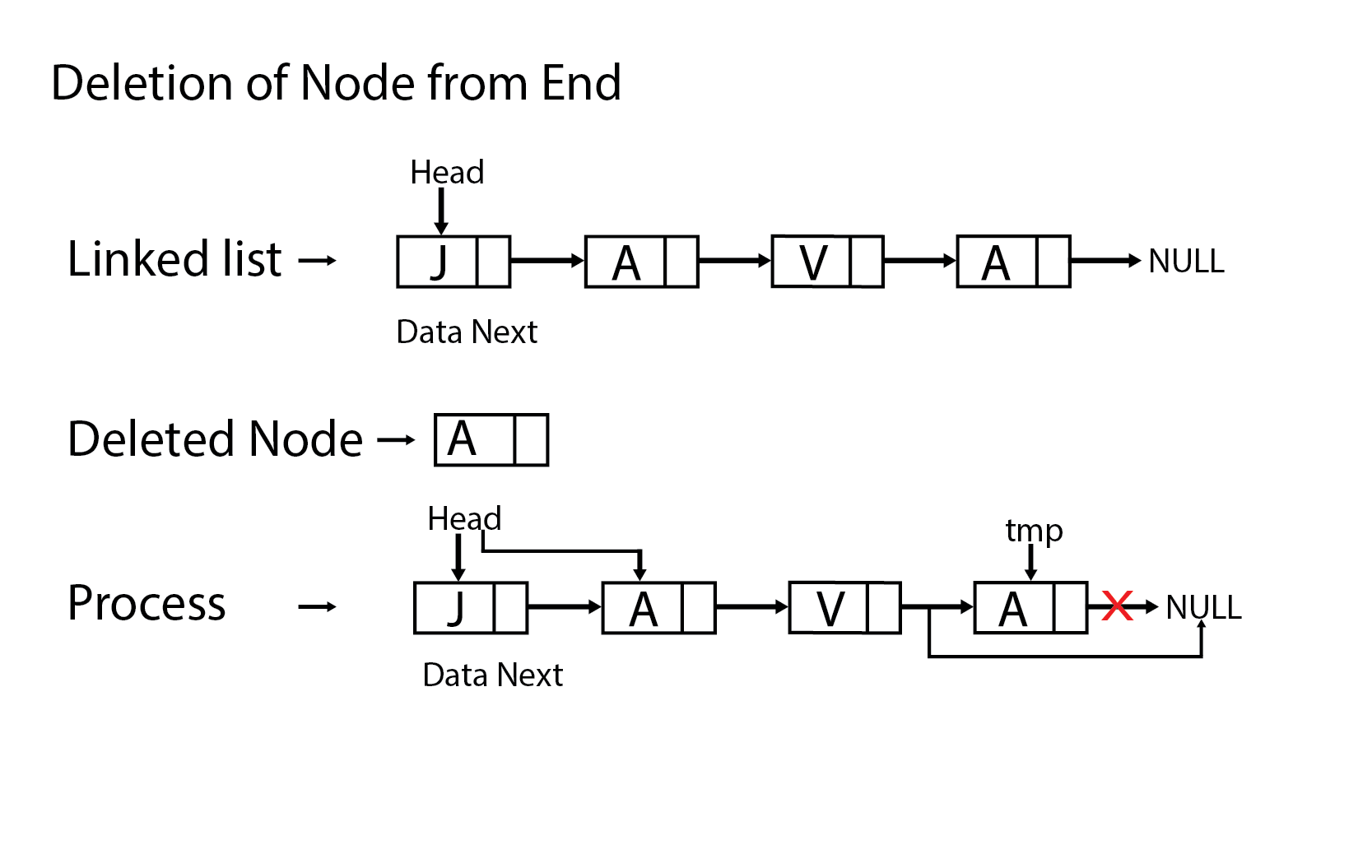
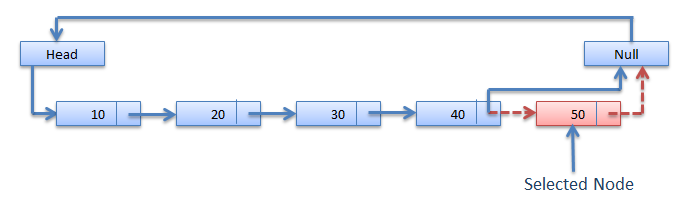
Deletion at the end : -
It involves deleting the last node of the list. The list can either be empty or full. Different logic is implemented for the different scenarios.
Traversing : -
In traversing, we simply visit each node of the list at least once in order to perform some specific operation on it, for example, printing data part of each node present in the list.
Searching: -
In searching, we match each element of the list with the given element. If the element is found on any of the location then location of that element is returned otherwise null is returned. .
Experiment 4 :- write a program to implement doubly linked list
Doubly linked list: -
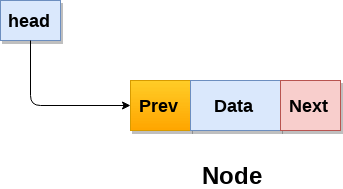
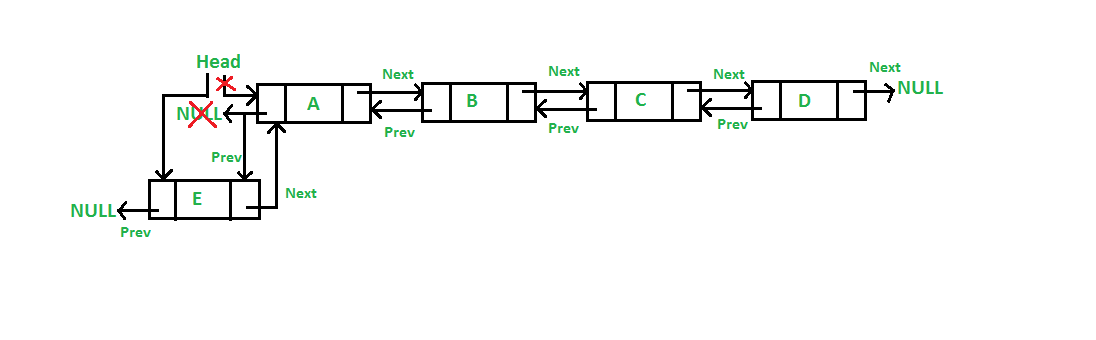
Doubly linked list is a complex type of linked list in which a node contains a pointer to the previous as well as the next node in the sequence. Therefore, in a doubly linked list, a node consists of three parts: node data, pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer) , pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
Operations in doubly linked list
Insertion at the beginning : -
Adding the node into the linked list at beginning.
Insertion at the end : -
Adding the node into the linked list to the end.
Insterion at the specific position : -
Adding the node into the linked list after the specified node.
Deletion: -
- Deletion at the beginng: -
Removing the node from beginning of the list
- Deletion at the end : -
Removing the node from end of the list.
- Deletion of the node having given data : -
Removing the node which is present just after the node containing the given data.
- Traverse: -
Comparing each node data with the item to be searched and return the location of the item in the list if the item found else return null.
- Searching: -
Visiting each node of the list at least once in order to perform some specific operation like searching, sorting, display, etc.
Experiment 5:- write a program to implement circular linked list
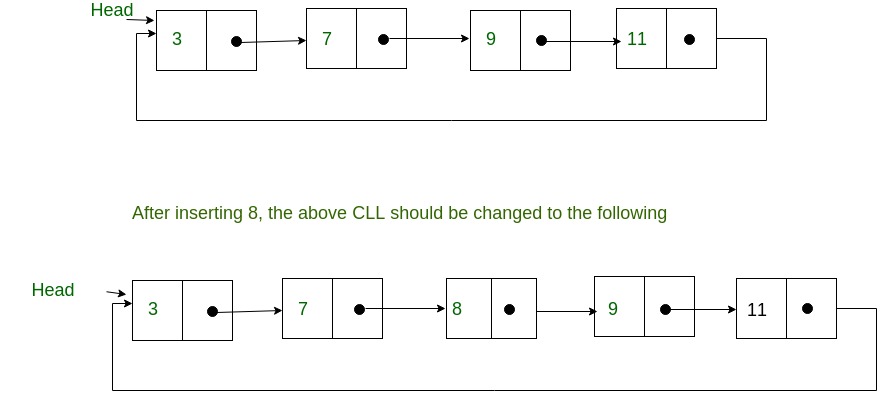
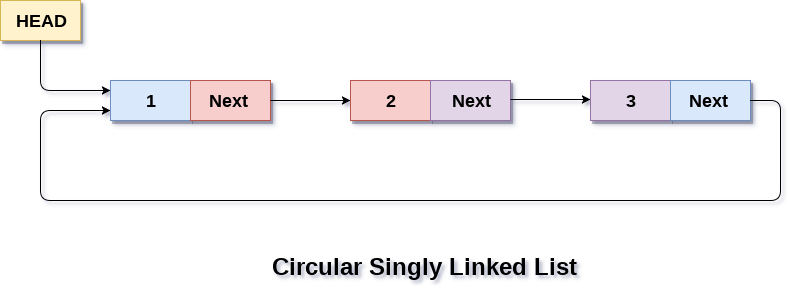
In a circular Singly linked list, the last node of the list contains a pointer to the first node of the list. We can have circular singly linked list as well as circular doubly linked list.
We traverse a circular singly linked list until we reach the same node where we started. The circular singly liked list has no beginning and no ending. There is no null value present in the next part of any of the nodes.
Insertion: -
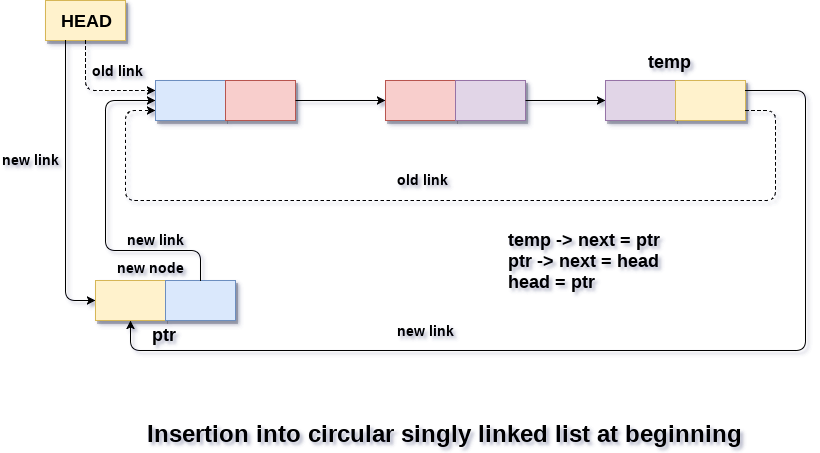
1 Insertion at beginning :-
Adding a node into circular singly linked list at the beginning.
2 Insertion at the end:-
Adding a node into circular singly linked list at the end.
- Deletion at beginning : -
Removing the node from circular singly linked list at the beginning.
- Deletion at the end:-
Removing the node from circular singly linked list at the end.
3 Searching Compare each element of the node with the given item and return the location at which the item is present in the list otherwise return null. 4 Traversing Visiting each element of the list at least once in order to perform some specific operation.
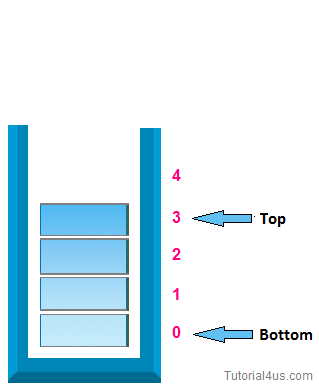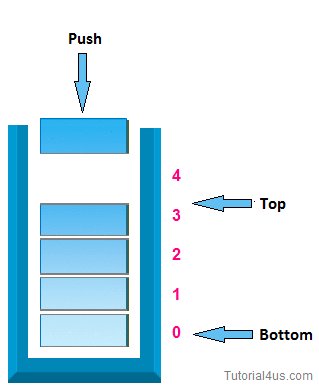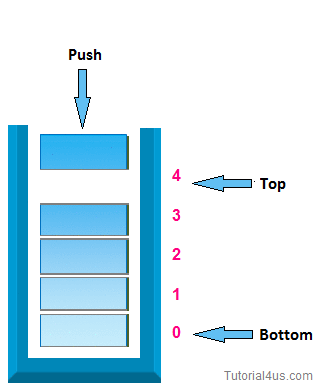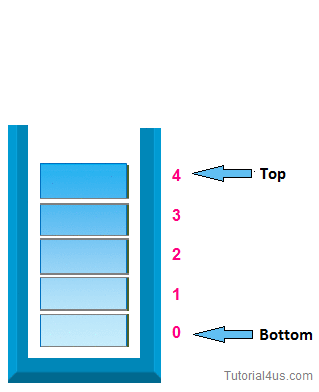
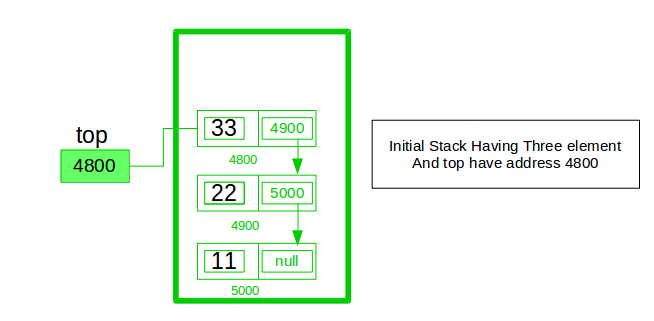
Experiment 6 : Write a program to implement stack as an array
STACK uses Last in First Out approach for its operations. Push and Pop operations will be done at the same end called "top of the Stack"
PUSH function in the code is used to insert an element to the top of stack, POP function used to remove the element from the top of stack.
For push: -
For Pop :-
Experiment 6: -
Write a program to implement stack as a linked list
Experiment 7:-
Aim :-
Write a program to Implement queue using array!!
-------------FIFO(first in first out)---------------------
Implement queue by using
Queue is a linear structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is First In First Out (FIFO). A good example of queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first.
Operations on Queue:
Mainly the following four basic operations are performed on queue:
Enqueue: Adds an item to the queue. If the queue is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition.
Dequeue: Removes an item from the queue. The items are popped in the same order in which they are pushed. If the queue is empty, then it is said to be an Underflow condition.
Front: Get the front item from queue.
Rear: Get the last item from queue.
Applications of queue
-
When a resource is shared among multiple consumers. Examples include CPU scheduling, Disk Scheduling.
-
When data is transferred asynchronously (data not necessarily received at same rate as sent) between two processes. Examples include IO Buffers, pipes, file IO, etc.
IMPLEMENTATION OF QUEUE USING LINKED LIST:-