Implementation of a Genetic Algorithm using Clojure. See the literate programming page: Docs
"Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city and returns to the origin city?"
This implementations uses a genetic algorithm to find the shortest route between cities.
- Clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/vascoferreira25/travelling-salesman-problemFirst make the project folder your working directory:
cd travelling-salesman-problemAnd then, either run it directly with:
lein runor use the REPL and execute the main function:
lein repluncomment the last line
(-main)and execute the function.
This project has a literate programming page that walks the entire code to explain everything that is done at each step.
Check it at: Docs
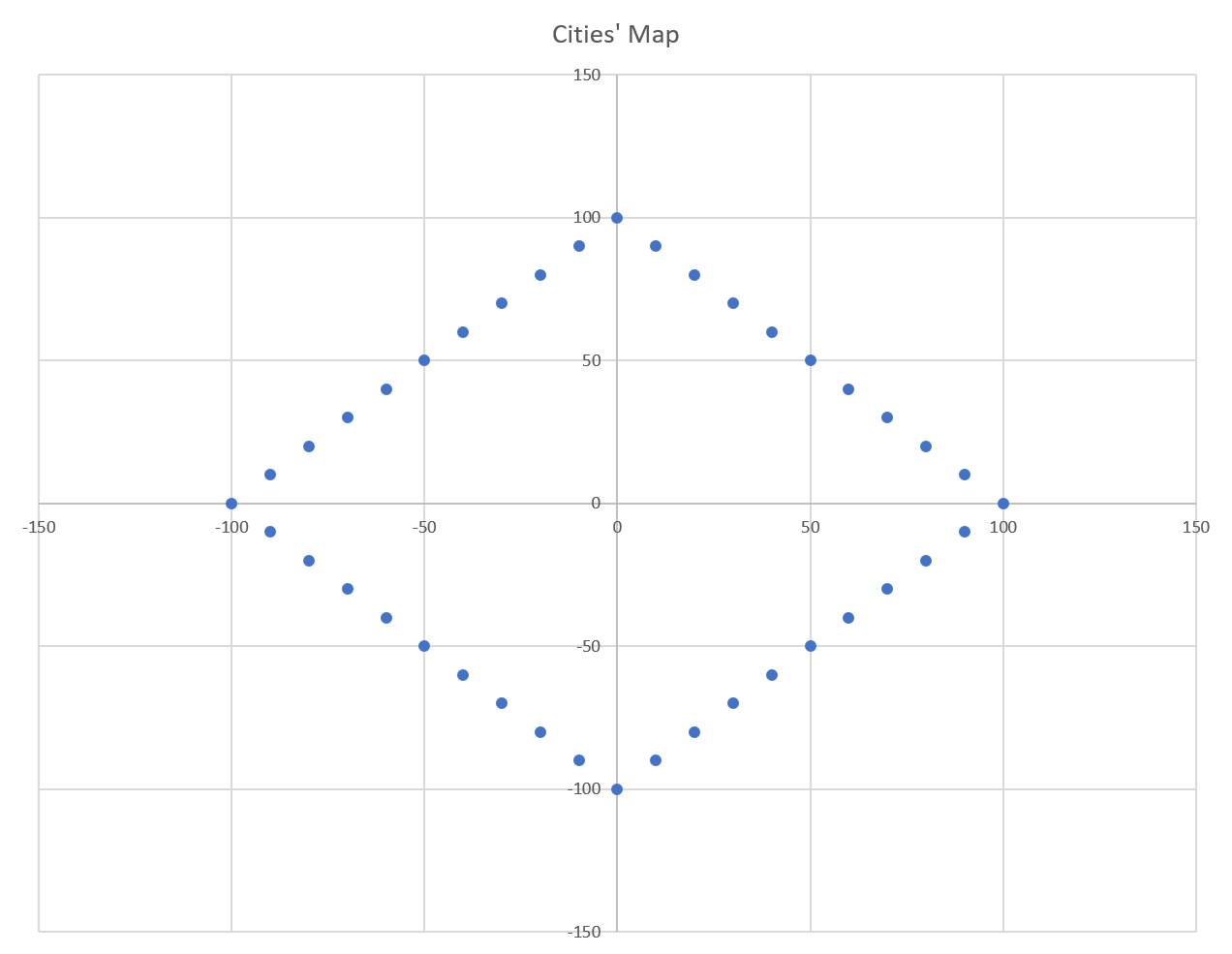
Find the best possible route for a list of cities. The cities are represented in the following chart:
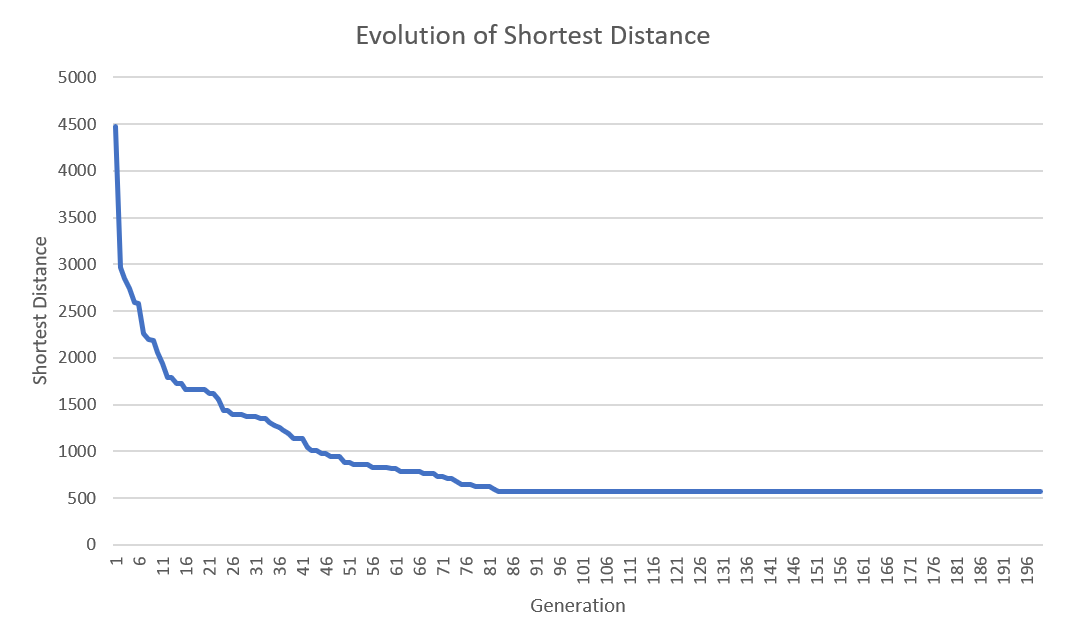
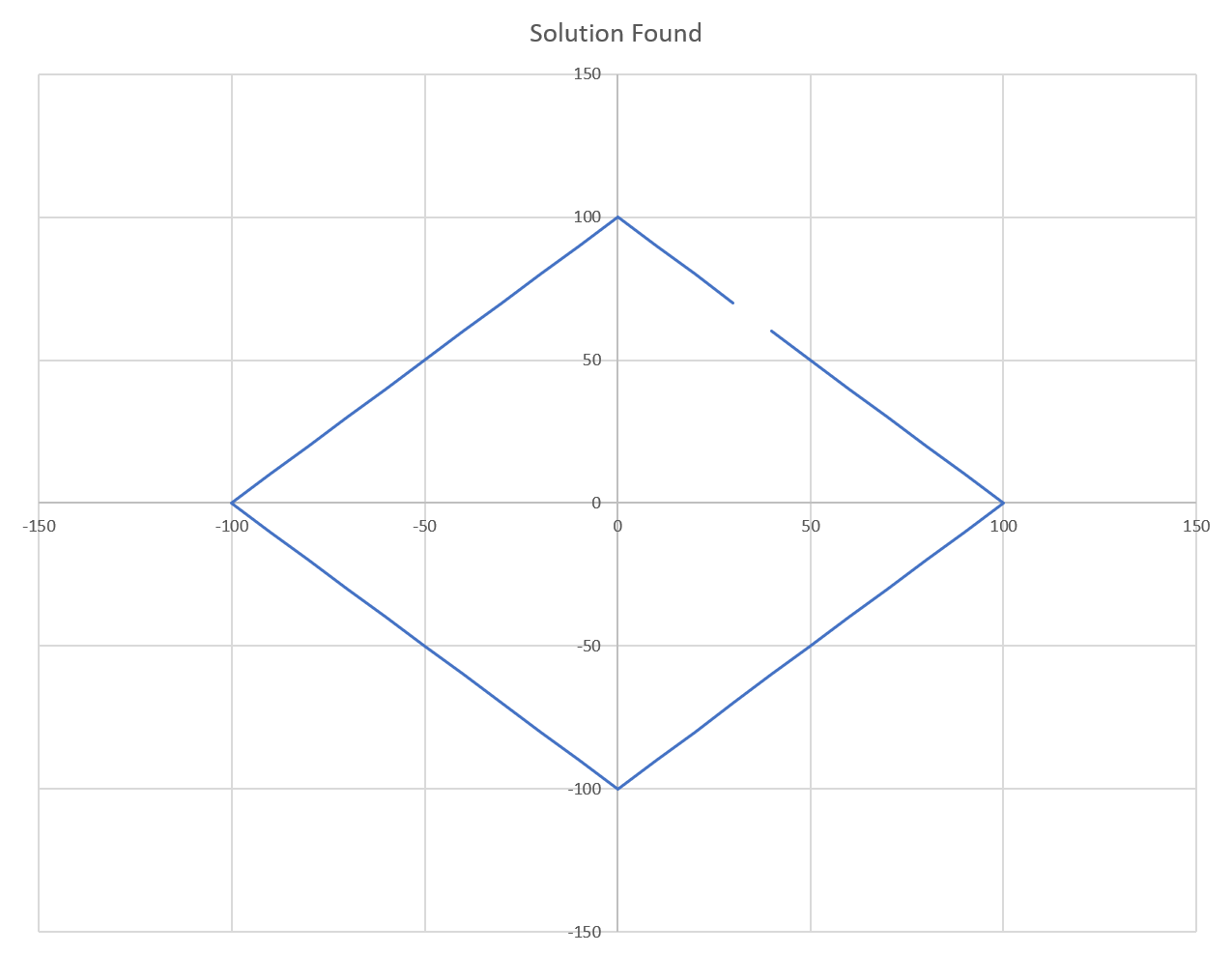
With the following parameters, the algorithm reached the result of 565.685424949238:
- Generations: 200,
- Population Size: 500,
- Mutation Rate: 0.02.
Copyright © 2019
This program and the accompanying materials are made available under the terms of the Eclipse Public License 2.0 which is available at http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-2.0.
This Source Code may also be made available under the following Secondary Licenses when the conditions for such availability set forth in the Eclipse Public License, v. 2.0 are satisfied: GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version, with the GNU Classpath Exception which is available at https://www.gnu.org/software/classpath/license.html.