This is a C framework for comparing page replacement algorithms on x86 architecture by using test suites. Testing such algoritms on a running operating system would be inaccurate, because the results would be influenced by many parts of a operating system. Therefore this framework runs on a bare machine by implementing a bootloader and a custom kernel for running test suites and page replacement algorithms.
Since this project compiles C code for specific architecture one of the dependencies is a GCC cross-compiler. For ease-of-use, you can use our CLI tool to download and install a supported GCC toolchain.
Once you have installed the CLI tool, you can run this command to automatically download this framework and the GCC toolchain.
prac initOther dependencies include NASM for assembling bootloader source code and other assembly files. For creating final bootable ISO file, you're gonna need a mkisofs tool. Finally, to execute the code you will need a QEMU for i386.
To install these dependencies on Ubuntu, execude this commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential nasm mkisofs qemu-system-i386Optional dependencies for running framework tests are 32-bit GCC, which can be installed by executing this command for Ubuntu based systems:
sudo apt install gcc-multilibThe standard usage of this framework consists of these steps:
- Create a new project
- Write custom test programs and test suite
- Write custom page replacement algorithms (optional)
- Execute the project to see results of comparison
- Analyze and display the results graphically via the VS Code extension
To create a new project, just run
prac createThis will initialize a new project in your current working directory.
After creating a new project, your project directory structure will look like this.
.prac/– build folder, that contains framework sources and compiled files or analysis resultssrc/– source folder where your sources will go (test programs, test suites or page replacement algorithms)prac.int– configuration file with framework options
To make creating test programs easier, there will be already a sample implementation of a test suite with two test programs.
Creating a test program is easy. It is just a function with no arguments and no return value that implements all the code you want to test (i.e. a sorting algorithm).
To run such a test program, we also need to define a test suite. This is done by creating a test_configuration_t structure that contains which test programs are to be executed, what parameters to use and which page replacement algoritms to use.
After creating such configuration, you can execute it by calling run_test_suite(configuration);
A very simple example of configuration definition si shown below.
void setup()
{
test_execution_t execution =
{
.name = "Bubble Sort",
.callback = test_bubble_sort
};
page_replacement_algorithm_e algorithm = pra_fifo;
test_parameters_t parameters =
{
.pages_limit = 10,
.allocation_spread = 15,
.seed = 1
};
test_configuration_t configuration =
{
.tests = &execution,
.tests_length = 1,
.algorithms = &algorithm,
.algorithms_length = 1,
.parameters = ¶meters,
.parameters_length = 1
};
run_test_suite(configuration);
}To use an "allocation spread" parameter in your test programs, use void* user_memory_random_allocate(size_t size) function to allocate your memory randomly in selected allocation spread.
This framework already implements some page replacement algorithms that you can use. You can find a list of these algoritms in API reference. To write a new page replacement algorithms, you need to create and implement a function that will handle page faults.
This function signature is defined like this:
typedef void (*page_replacement_function_t)(uint32_t error_code, page_fault_handler_result_t *result);First parameter error_code is an error code specified by system when generating a page fault exception. You can read more about the structure of this error code here.
Second parameter result is a pointer to a structure that will be used to aggregate statistical information about your page replacement algorithm. To get accurate results, you must use correctly fill the result structure when necessary. To ease filling this structure with all the information manually, you can use page_fault_handler_result_fill function to fill the results automatically by supplying the victim page_table_entry_t as a parameter.
There are two other optional functions that you can implement. Those are page_replacement_init_function_t and page_replacement_destroy_function_t functions. Initialization function will be called before each test program is executed. You can use this function to initialize variables that are needed for page fault handler algorithm. Destroy function is called after each test program execution is finished and must destroy all initalized data to provide accurate results.
You can see an implementation of Random page replacement algorithm here.
Executing a project is as simple as using a CLI tool. You can also build or clean your project with prac clean and prac build commands. To execute a project, just run this command in current project
prac runThis will build your project, execute the test suite you specified and display a results. If you want to see better comparison of these results, we recommend you use a VS Code extension and it's provided functionality.
The recommended usage of this framework is with a VS Code extension that supports editing, building and analyzing your projects. To download and install the extension, follow these instructions.
When you have successfully installed the extension and have a existing project, you can open the folder in VS Code and the extension will be automatically activated. All commands that you can run use PRAC prefix. You can build, clean, run on analyze your project by running these commands from your command palette.
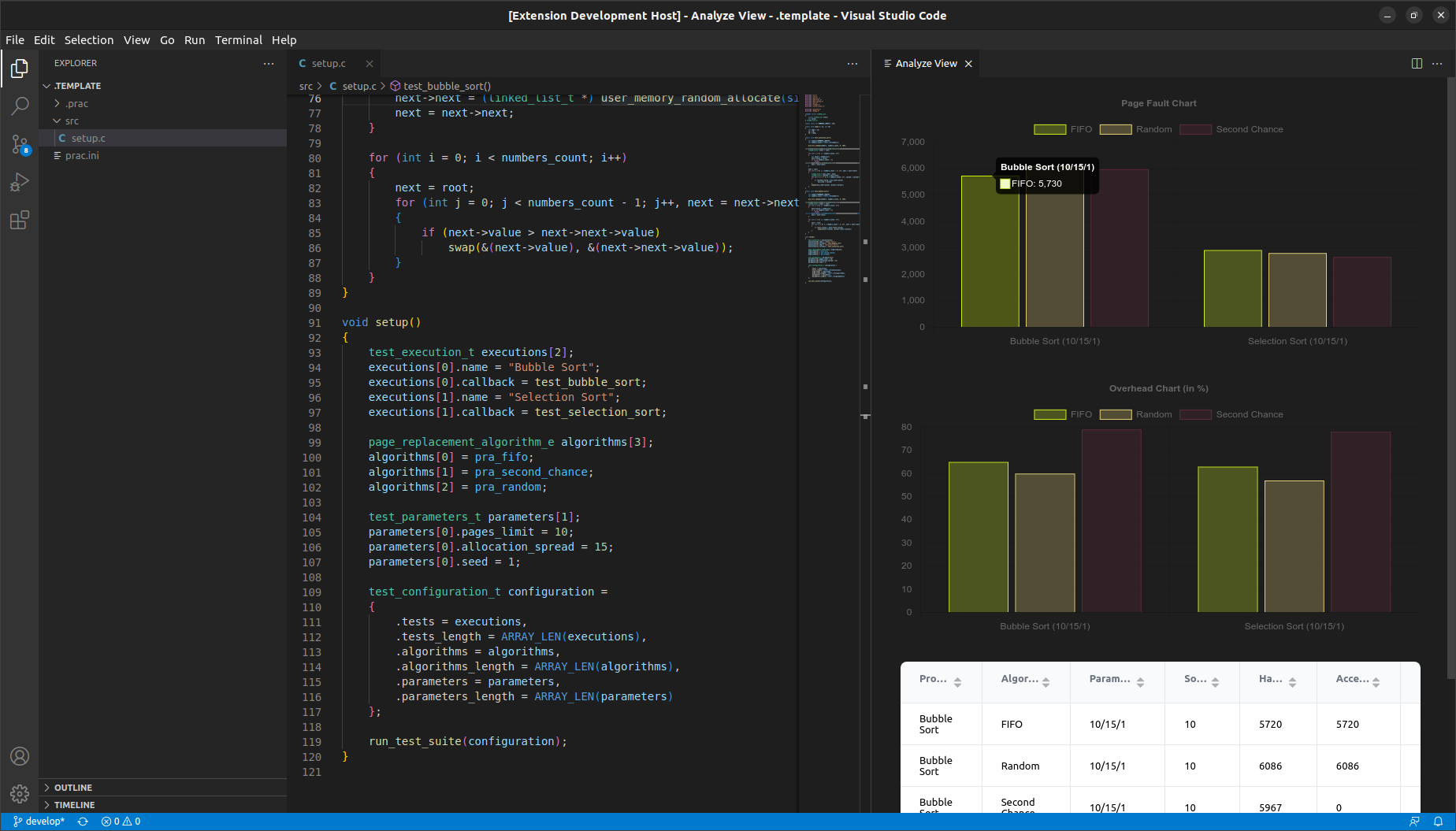
The main benefit of this extension comes from ability to analyze the results of the test suite. To analyze your project, just execute the command PRAC: Analyze, which will build your project, execute it and parse the results to show in charts and tables.
To run framework tests, you can execute make test, which will execude all tests in the test folder and display the results.
⚠️ If you are on a x64_86 machine, you need to first install 32-bit GCC version
For more technical documentation and implementation details, check out the API reference.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.txt for more information.