The source code includes two parts: (1)queries featurization; (2) models training.
This part incudes the following components:
(1) Given the join schema of the database as the input, use a graph embedding method to transform "Tables" into vectors. The join schema is regarded as an undirected graph, each node in the join schema representd a Table in the database. The join schema can be received by the PK and FK relationships among "Tables".
(2) Given the global columns-dependency graph, use the same graph embedding method in (1) to transform "Columns" into vectors. Currently, Fauce only focuses on the columns with real-valued numbers. To build the global columns-dependency graph, it includes 3 steps. 1) For each "Table" in the database, we calculate the Randomized Dependence Coefficient(RDC) values for each pair of "Columns" in each "Table" to build the local columns-dependency graph; 2) Connect the local columns-dependency graph based on the PK and FK relationships among "Tables" to build the global columns-dependency graph; 3) Given the global columns-dependency graph as the input, use the same graph embedding method (the method to represent "Tables" as vectors) to get the embeddings for the "Columns" in the database.
(3) Given the join schema of the database, use the Joins2Vec method to get the embeddings for different join relationships in the database. The algotithm firstly selects all the possible "Join" relationships among different "Tables" in the database. Then, it transform the "Joins" into vectors.
(4) Range representation for each columns with real-valued numbers. The ranges for each column can be achieved by traversing the columns in each "Table".
The queries featurization is done offline. Once the embedding results for the "Tables", "Columns", "Joins", and Ranges are received, give an input query, it can be represented as four tuples: Tables, Columns, Joins, and Ranges, we can directly parse the queries and find the corresponding embding results for each tuple. Finally, we combine the embeding results together to get the queries featurization results.
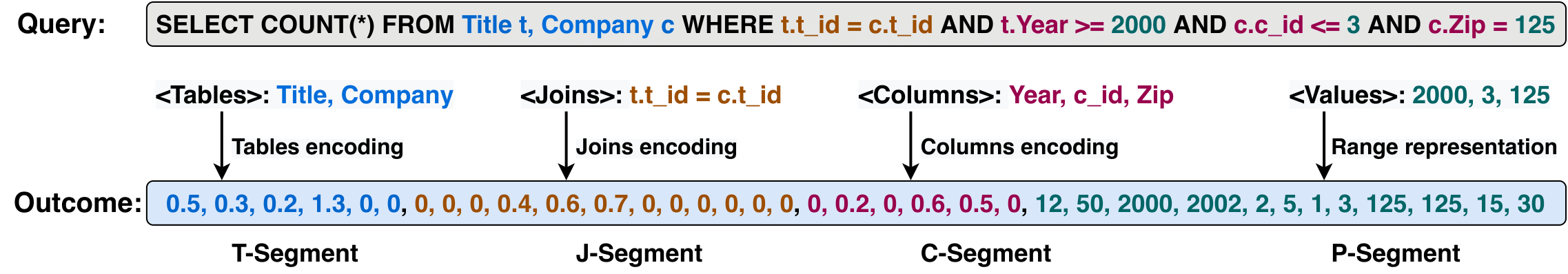
The figure below shows an example of the quey featurization:
The model training part includes the models used in Fauce:
(1) We use the method in NeuroCard proposed by Zongheng Yang, etc to generate the training dataset.
(2) Once the training dataset is generated, we use the embedding results achieved in the queries featurization part to transform each query in the training dataset into vectors, the training dataset is stored in a .csv file.
(3) Use the .csv file as the input training dataset to train the model.