BAPCtools is a tool for creating and developing problems following the CLICS (DOMjudge/Kattis) problem format specified here.
The aim of this tool is to run all necessary compilation, validation, and testing commands while working on an ICPC-style problem. Ideally one should never have to manually run any compilation or testing command themselves.
I'm interested to know who's using this, so feel free to inform me (e.g. via an issue) if so ;) The current state is relatively stable, but things do change from time to time since I'm not aware of usage outside of BAPC yet.
You can install the bapctools-git AUR package, mirrored here, or use the Docker image.
Otherwise, clone this repository and install the required dependencies manually. (If you know how to make a Debian package, feel free to help out.)
-
Python 3 (>= 3.6).
-
The yaml library via
pip install pyyamlor thepython[3]-yamlArch Linux package. -
The colorama library via
pip install coloramaor thepython[3]-coloramaArch Linux package. -
The
argcompletelibrary for command line argument completion. Install viapython[3]-argcomplete.-
Note that actually using
argcompleteis optional, but recommended. Detailed instructions are here.TL;DR: Put
eval "$(register-python-argcomplete[3] tools.py)"in your.bashrcor.zshrc.
-
Optional dependencies, required for some subcommands:
- The ruamel.yaml library via
pip install ruamel.yamlor thepython-ruamel-yamlArch Linux package (python3-ruamel.yamlon Debian derivatives).- This is only needed for commands that update
generators.yaml.
- This is only needed for commands that update
- The
latexmkandpdflatexcommands, provided bytexlive-binon Arch Linux and potentially some specific LaTeX packages (like tikz) provided bytexlive-extra. These are only needed for buildingpdffiles, not forrunandvalidateand such. - The matplotlib library via
pip install matplotlibor thepython[3]-matplotlibLinux package.- This is optional and only used by the
solve_statscommand.
- This is optional and only used by the
- The requests library via
pip install requestsor thepython[3]-requestsLinux package.- This is optional and only used by the commands that call the DOMjudge API (
export,solutions --order-from-css, andsolve_stats) or the Slack API (create_slack_channelscommand).
- This is optional and only used by the commands that call the DOMjudge API (
- The questionary library via
pip install questionary.- This is optional and only used by the
new_contestandnew_problemcommands.
- This is optional and only used by the
After cloning the repository, symlink bin/tools.py to somewhere in your $PATH. E.g., if ~/bin/ is in your $PATH, you can do:
% ln -s ~/git/BAPCtools/bin/tools.py ~/bin/bt
For Windows, you'll need the following in your
path:
Pythonfor Python 3g++to compile C++javacandjavato compile and runjava.
Resource limits (memory limit/hard cpu time limit) are also not supported.
BAPCtools makes use of symlinks for building programs. By default users are not allowed to create symlinks on Windows.
This can be fixed by enabling Developer Mode on Windows (Only since Windows 10, version 1703 or newer).
In case you're still having problems with symlinks in combination with Git after enabling this setting,
please try the suggestions at https://stackoverflow.com/a/59761201.
Specifically, git config -g core.symlinks true should do the trick,
after which you can restore broken symlinks using git checkout -- path/to/symlink.
A docker image containing this git repo and dependencies, together with commonly used languages, is provided at ragnargrootkoerkamp/bacptools. This version may be somewhat outdated. Ping me if you'd like it to be updated.
This image can be used for e.g.:
- running CI on your repo. Also see
bt gitlabciwhich generates a.gitlab-ci.yamlfile. Make sure to clear the entrypoint, e.g.entrypoint: [""]. - running
bton your local problems. Use this command to mount your local directory into the docker image and run a command on it:docker run -v $PWD:/data --rm -it ragnargrootkoerkamp/bapctools <bt subcommands>
To update the image:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
$ docker pull archlinux:latest
$ docker login
$ docker build . -t ragnargrootkoerkamp/bapctools
$ docker push ragnargrootkoerkamp/bapctools
$ ssh <server> sudo docker pull ragnargrootkoerkamp/bapctools
The last step is needed when your CI server is not automatically pulling the latest version.
BAPCtools can be run either from a problem directory or a contest directory. This
is automatically detected by searching for the problem.yaml file.
The most common commands and options to use on an existing repository are:
bt run [-v] [submissions [submissions ...]] [testcases [testcases ...]]bt test <submission> [--interactive | --samples | [testcases [testcases ...]]]bt generate [-v] [--jobs JOBS]bt validate [-v] [--input | --answer] [--remove | --move-to DIR] [testcases [testcases ...]]bt pdf [-v]
The list of all available commands and options is at doc/commands.md#synopsis, and more information regarding the implementation is at doc/implementation_notes.md.
bt run [-v] [submissions [submissions ...]] [testcases [testcases ...]]
Without arguments, the run command runs all submissions against all testcases.
Specify one or more submissions and one or more testcases to only run the given submissions against the given testcases.
Before running the given submissions, this command first makes sure that all generated testcases are up to date (in case generators/generators.yaml was found).
By default, bt run only prints one summary line per submission, and one additional line for each testcase with an unexpected result. Use -v to print one line per testcase instead.
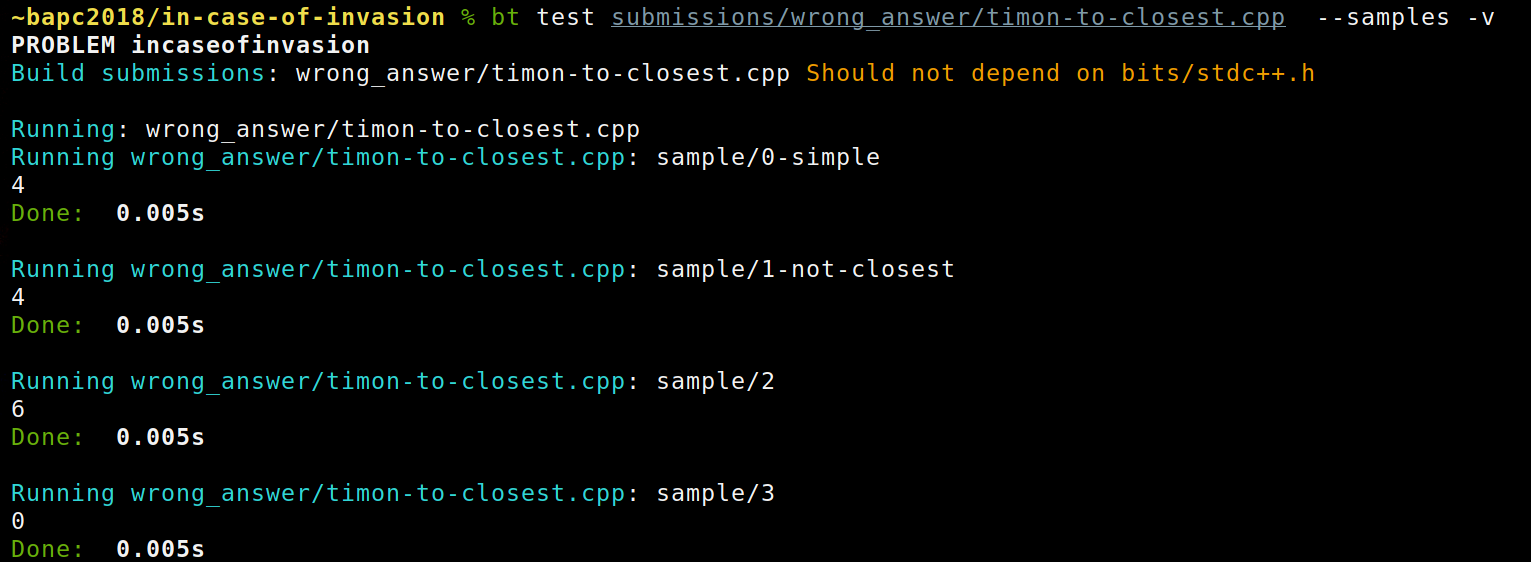
bt test <submission> [--samples | [testcases [testcases ...]]]
Use the test command to run a single submission on some testcases. The submission stdout and stderr are printed to the terminal instead of verified as an answer file.
Use --samples to run on the samples, or pass a list of testcases or directories containing testcases. Use --interactive/-i to run in interactive mode, where console input is forwarded to the submission.
This rebuilds and reruns the program until either control-C or control-D is pressed. It's also possible to supply the test case on the command line directly using e.g. < /path/to/file.in or <<< "10 20".
bt generate [-v] [--jobs JOBS]
Use the generate command to generate the testcases specified in generators/generators.yaml. See doc/generators.md for the specification of generators.yaml and see doc/commands.md#generate for the full list of arguents.
Use -j 0 to disable running multiple jobs in parallel (the default is 4).
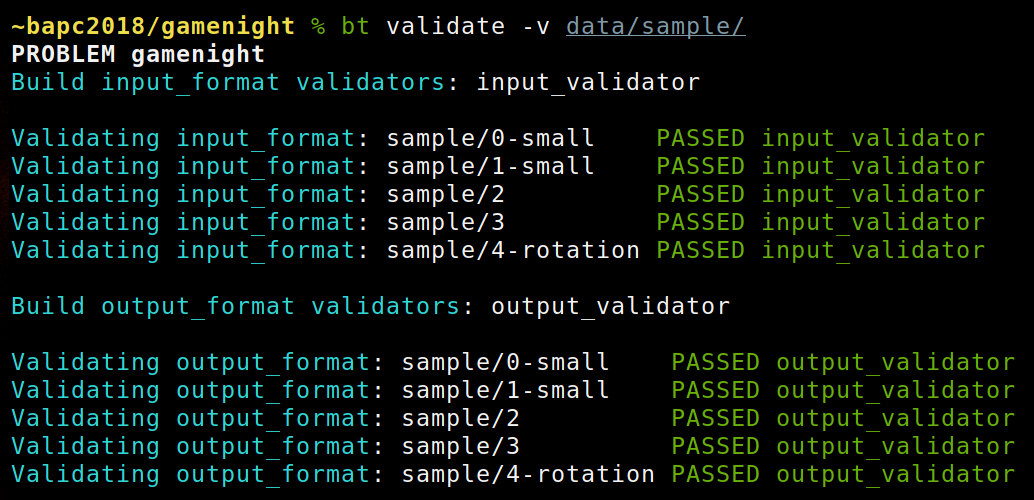
bt validate [-v] [--input | --answer] [--remove | --move-to DIR] [testcases [testcases ...]]
Validate all the .in and .ans for all (given) testcases. It runs all validators from input_validators, answer_validators, and output_validators.
Validators can be one of
- a single-file program.
- a multi-file program with all files in a common directory.
- a .ctd CheckTestData file (this needs the
checktestdataexecutable in your$PATH). - a .viva file.
You can use --remove to delete all failing testcases or --move <dir> to move
them to a separate directory.
bt pdf [-v]
Use this command to compile the problem.en.pdf from the problem_statement/problem.en.tex LaTeX statement.
problem.en.pdf is written to the problem directory itself.
This can also be used to create the contest pdf by running it from the contest directory.
For some command-line flags, it is convenient if they are always set to the same value, which differs per user
(e.g., --username or --password for commands that access a CCS like DOMjudge,
or --jobs to limit parallel execution) or per contest (e.g., which statement languages are used).
For this, you can create a configuration YAML file containing key-value pairs
in one of the following locations, from low to high priority:
$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/bapctools/config.yaml(Unix-ish systems, where$XDG_CONFIG_HOMEusually is~/.config)%AppData%/bapctools/config.yaml(Windows systems)<contest directory>/.bapctools.yaml
The keys in this config file can be any option that can be passed on the command-line.
Note that the keys should be written out in full (e.g., username: jury rather than u: jury)
and any hyphens should be replaced with an underscore (e.g., no_bar: True rather than no-bar: True).
-
The python code in the repository is formatted using black. To enable the pre-commit hook, install pre-commit with
pipor your package manager (Arch:python-pre-commit) and runpre-commit installfrom the repository root. All python code will now automatically be formatted on each commit. -
Imports are usually ordered with system libraries first, followed by a newline, followed by local includes. Both groups are sorted alphabetically, and
importcomes beforefrom ... import.