Tweet-nifi provides the capability to receive tweets from the Twitter public feed with NiFi and injest them into Elasticsearch.
- Download and install NiFi
- Download and install Elasticsearch
- Start your Elasticsearch instance.
- Run the tweets_template.sh script to create the mapping for the tweet indices.
- Start your NiFi instance.
- Navigate to the NiFi console in your browser, which will be http://localhost:8080/nifi.
- Click on the Upload Template button in the Operate pane.
- Click on the maginfying glass icon next to the text Select Template in the Upload Template pane.
- Navigate to the directory where you unpacked the tweet-nifi tarball.
- Select the tweet-nifi.xml file.
- Click Open.
- Click on the UPLOAD button in the Upload Template pane.
- Click on the Template button on the top of the NiFi window, then drag it to the open canvas.
- Double click on the Ingest Tweets from Public Feed processor.
- Enter the Consumer Key, Consumer Secret, Access Token, and Access Token Secret field values. Note the Consumer Key and Consumer Secret fields correspond to the Twitter API key and API key secret fields, respectively.
- Click on the APPLY button.
- Double lick on the Index Tweets in Elasticsearch processor.
- Click on the the Elasticsearch URL field.
- Enter the URL to your Elasticsearch instance.
- Click on OK.
- Click on the Index field.
- Enter the index naming pattern you want to use for your time series indices. The default is
tweets-${now():format('yyyy.MM.dd')}. - Click on OK.
- Click on the APPLY button.
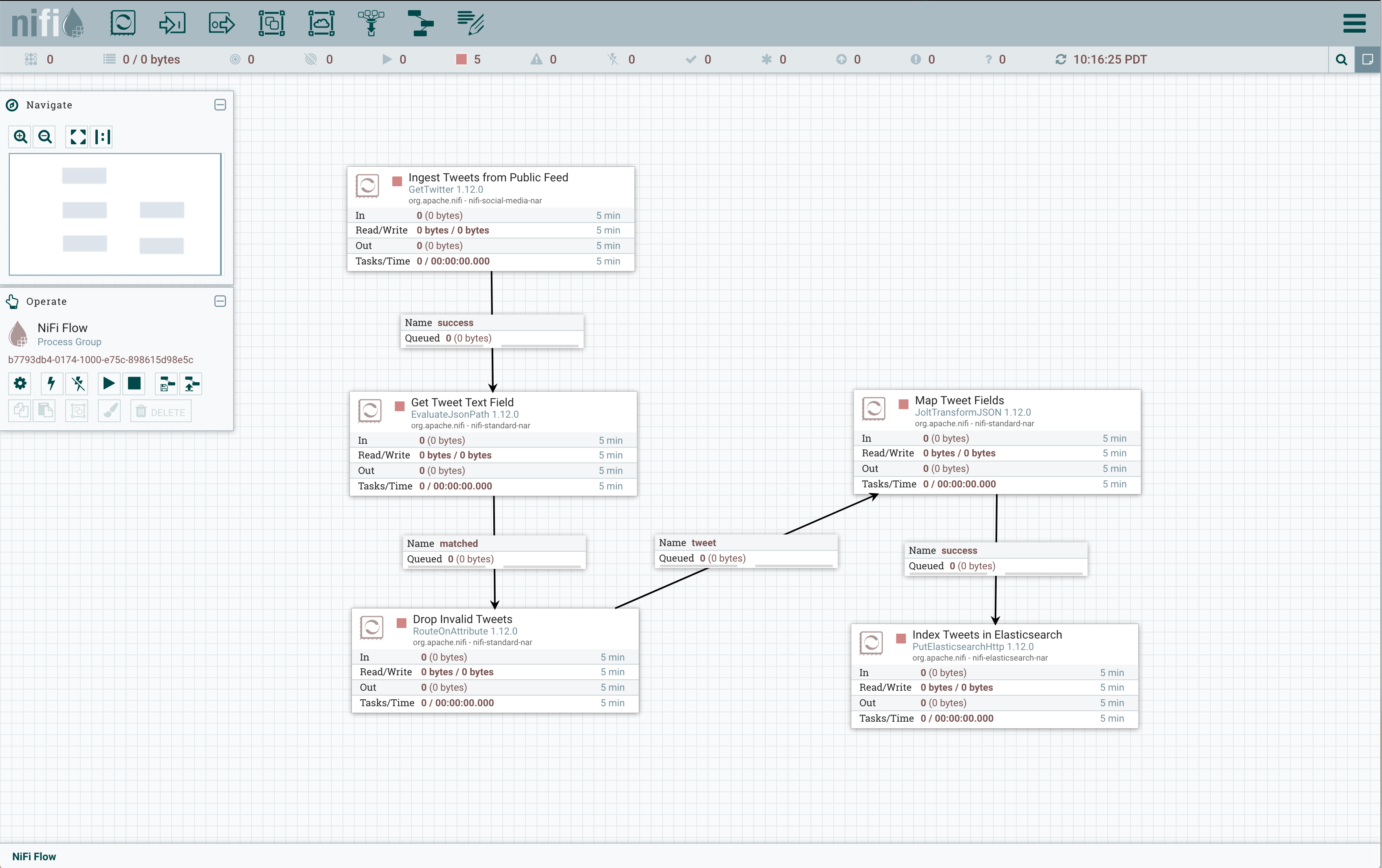
The Nifi canvas should look like this when you are done:
Click on the Start button in the Operate pane in the NiFi Console, which should be labelled NiFi Flow. After several seconds you should see the In, Read/Write, Out, and Tasks/Time field totals increasing. Verify that your tweet stream is being indexed but running a query like this in Kibana:
GET tweets-2020.09.22/_search
Here we are assuming the tweets were ingested on Sep 27, 2020. The output should look like this:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 9551,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tweets-2020.09.27",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4Fzx0XQBAxCM3ol7ftQk",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"created_at" : "Sun Sep 27 22:17:11 +0000 2020",
"timestamp_ms" : "1601245031657",
"id_str" : "1310342751716880386",
"text" : "RT @robbystarbuck: Breaking news: You guys are gonna want to sit down for this. It turns out rich people and their companies have entire te…",
"source" : """<a href="http://twitter.com/download/iphone" rel="nofollow">Twitter for iPhone</a>""",
"favorited" : false,
"retweeted" : false,
"lang" : "en",
"user_id_str" : "868768568283975680",
"user_name" : "Sahidkapadia",
"user_screen_name" : "Sahidkapadia3",
"user_description" : null,
"user_verified" : false,
"user_followers_count" : 91,
"user_friends_count" : 526,
"user_listed_count" : 0,
"user_favourites_count" : 127917,
"user_created_at" : "Sun May 28 09:59:02 +0000 2017",
"user_lang" : null
}
},
...
}
Tweets fields are mapped to output fields in Jolt Specification field the Map Tweet Fields processor. The default mapping is:
[
{
"operation": "shift",
"spec": {
"created_at": "created_at",
"time_zone": "time_zone",
"utc_offset": "utc_offset",
"timestamp_ms": "timestamp_ms",
"id_str": "id_str",
"text": "text",
"source": "source",
"favorited": "favorited",
"retweeted": "retweeted",
"possibly_sensitive": "possibly_sensitive",
"lang": "lang",
"user": {
"id_str": "user_id_str",
"name": "user_name",
"screen_name": "user_screen_name",
"description": "user_description",
"verified": "user_verified",
"followers_count": "user_followers_count",
"friends_count": "user_friends_count",
"listed_count": "user_listed_count",
"favourites_count": "user_favourites_count",
"created_at": "user_created_at",
"lang": "user_lang"
},
"entities": {
"urls": {
"*": {
"url": "url_&1",
"expanded_url": "url_expanded_&1",
"display_url": "url_display_&1"
}
}
}
}
}
]
Note that this mapping allows for 3 URLs in the tweet that are flattened out at the top level of the JSON. When a tweet lacks URLs, like the earlier example tqweet, the URL fields are simply omitted.
If you want to map more or fewer fields, or use different Elasticsearch field names, you can change this specification as needed. If and when you update the field mapping, you must restart Nifi.