Platform for running Python-based scripts on Windows with hotkeys, tray menu, HTTP server and many more.
def my_task(hotkey='ctrl+shift+t', http=True):
print('This is my code!')
Then press Ctrl+Shift+T or open in browser URL http://127.0.0.1:8275/my_task and your task will be executed.
Another example: show message box every day at 10:30 and hide this task from menu:
def my_another_task(every='day 10:30', menu=False):
dialog('Take the pills')
An example using the extension for Firefox:
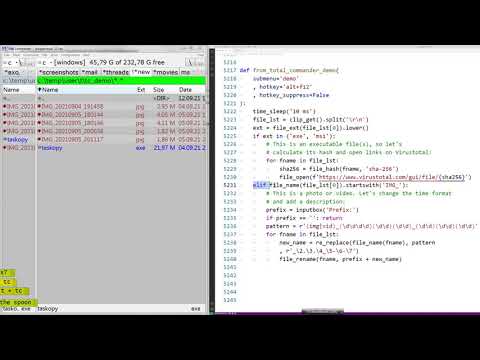
Use with Total Commander:
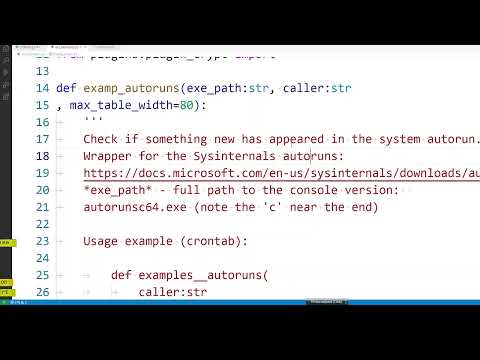
Tracking changes in the Windows startup:
Remote control:
Telegram chat: https://t.me/taskopy_g
- Installation
- Usage
- Task options
- Settings
- Keywords
- Tips and tricks
- Firefox extension
- Context menu
- Help me
- Task examples
Requirements: Windows 7 and above. You can download archive with binary release.
Requirements: Python > 3.7; Windows 7 and above.
Download project, install requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Note: wxPython requires Pillow, but Pillow > 9.5.0 no longer includes 32-bit wheels so install 9.5.0:
pip install Pillow==9.5.0
Create a shortcut taskopy.py in the user's startup folder with the built-in Add to startup task.
Open crontab.py in your favorite text editor and create your task as function with arguments:
def demo_task_3('left_click'=True, log=False):
proc_start('calc.exe')
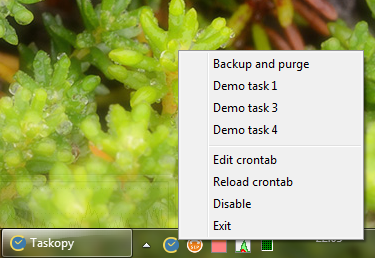
Then right click on tray icon and choose Reload crontab and your task is ready.
This is what you need to put in round brackets in task (function). It is not actual arguments for function.
Format: option name (default value) — description.
-
date (None) - date and time for the task, e.g. '2020.09.01 22:53'. You can use '*' as a placeholder.
-
event_log (None) - the name of the Windows log (System, Application, Security, Setup), i.e. run the task on new events in this log. To test you can create a new event with this command in elevated cmd:
eventcreate /ID 174 /L Application /T Information /D "Test"
If a task has a data argument, then it will be assigned information about the event in the DataEvent format. Task example:
def windows_errors( event_log = 'System' , event_xpath = '*[System[Level < 4]]' , data:DataEvent = None , menu=False, log=False ): balloon(f'Event (ID {data.EventID}): {data.Provider}\n{data.TimeCreated}') -
event_xpath ('*') - XPath to filter events. Case-sensitive. Example:
event_xpath='*[System[Level < 4]]' - only for new events with level less than 4.
-
task_name (None) — name for humans.
-
menu (True) — show in tray menu.
-
hotkey (None) — assign to global hotkey. Example: hotkey='alt+ctrl+m'
-
hotkey_suppress (True) — if set to False hotkey will not supressed so active window ill still receive it.
-
hyperactive — run task even if the Taskopy is disabled.
-
every ('') — run on schedule.
Examples:
Run task every 5 minutes:every='5 min'Every hour at 30 minutes:
every='hour :30'Every wednesday at 13:15:
every='wed 13:15'Every day at 08:30:
every='day 08:30'You can set multiple schedule at once with list:
every=('wed 18:00', 'fri 17:00') -
active (True) — to enable-disable task.
-
startup (False) — run at taskopy startup.
-
sys_startup (False) — run at Windows startup (uptime is less than 3 min).
-
left_click (False) — assign to mouse left button click on tray icon.
-
log (True) — log to console and file.
-
rule (None) — function or a tuple of functions. If the function returns
False, the task is not executed. This check is not performed if the task is launched from the system tray menu. -
single (True) — allow only one instance of running task.
-
submenu (None) — place task in this sub menu.
-
result (False) — task should return some value. Use together with http option to get page with task results.
-
http (False) — run task by HTTP request. HTTP request syntax: http://127.0.0.1:8275/your_task_name where «your_task_name» is the name of function from crontab, 8275 - default port.
This parameter can also accept a string with a regular expression pattern or a tuple of such strings. Example:
http=(r'task_\w+', r'task_\d+')So the task of displaying the text when you go to the root of the site will be as follows:
def http_root(http='^$', result=True): return 'It is a root'If option result also enabled then HTTP request will show what task will return or 'OK' if there is no value returned. Example:
def demo_task_4(http=True, result=True): # Get list of files and folders in Taskopy folder: listing = dir_list('*') # return this list as string divided by html br tag: return '<br>'.join(listing)Result in browser:
backup crontab.py log resources settings.ini taskopy.exeIf a task has a data argument, it will be assigned query information as DataHTTPReq object.
See also settings section for IP and port bindings.
-
http_dir — folder where to save files sent via HTTP POST request. If not set then use system temporary folder.
-
http_white_list — white list of IP addresses for this task only. Example:
http_white_list=['127.0.0.1', '192.168.0.*'] -
on_dir_change — run the task when changes are made in the folder.
def demo__on_dir_change(on_dir_change=temp_dir() , data:tuple=None, active=True): fpath, action = data tprint(f'{action}: {fpath}') -
on_exit — start the task when you exit Taskopy. Notice that Taskopy will not be closed until these tasks are completed.
-
on_file_change — run task when the file changes.
-
caller — place this option before other options and in task body you will know who actually launched task this time. Possible values: http, menu, scheduler, hotkey. See def check_free_space in Task Examples.
-
data — to pass any data to the task, e.g. DataEvent or DataHTTPReq.
-
idle — Perform the task when the user is idle for the specified time. For example, idle='5 min' - run when the user is idle for 5 minutes. The task is executed only once during the inactivity.
-
err_threshold — do not report any errors in the task until this threshold is exceeded.
Global settings are stored in settiings.ini file.
Format: setting (default value) — description.
- language (en) — language for menus and messages. Variants: en, ru.
- editor (notepad) — text editor for «Edit crontab» menu command.
- hide_console — hide the console window.
- server_ip (127.0.0.1) — bind HTTP server to this local IP. For access from any address set to 0.0.0.0. IT IS DANGEROUS TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM ANY IP! Do not use 0.0.0.0 in public networks or limit access with firewall.
- white_list (127.0.0.1) — a list of IP addresses separated by commas from which requests are received.
- server_port (8275) — HTTP server port.
-
app_enable() — enabling the application.
-
app_disable() — disabling the application. You can still start a task via the icon menu.
-
balloon(msg:str, title:str=APP_NAME,timeout:int=None, icon:str=None) — shows baloon message from tray icon.
title- 63 symbols max,msg- 255 symbols.icon- 'info', 'warning' or 'error'. -
benchmark(func, b_iter:int=1000, a:tuple=(), ka:dict={})->datetime.timedelta — run function
funcb_itertimes and print time. Returns the total time as a datetime.timedelta object. Example:benchmark(dir_size, b_iter=100, a=('logs',) ) -
crontab_reload() — reloads the crontab.
-
dialog(msg:str=None, buttons:list=None, title:str=None, content:str=None, default_button:int=0, timeout:int=None, return_button:bool=False)->int — shows a dialog with many buttons. Returns ID of selected buttons starting with 1000. buttons - a list with text on the buttons. Number of strings = number of buttons. title - dialog title. content - supplementary text. default_button - button number starting with 0, which is selected by default. timeout - timeout after which the message will be closed automatically. Example:
dialog('File is downloaded', ['Run', 'Copy full path', 'Cancel'], content='File source: GitHub', timeout=60, default_button=2) -
exc_name()->str — returns exception name only:
try: 0 / 0 except: asrt(exc_name(), 'ZeroDivisionError') asrt( benchmark(exc_name), 521, "<" ) -
hint(text:str, position:tuple=None)->int — shows a small window with the specified text. Only for the Python version. position - a tuple with coordinates. If no coordinates are specified, it appears in the center of the screen. Returns the PID of the hint process.
-
HTTPFile — Use this class if your HTTP task returns a file:
def http_file_demo(http=True, result=True , submenu='demo'): # http://127.0.0.1:8275/http_file_demo return HTTPFile( fullpath=r'resources\icon.png' , use_save_to=True ) -
is_often(ident, interval)->bool — is some event happening too often?
The purpose is not to bother the user too often with event alerts.
ident - unique identifier of an event.
interval - interval for measurement , not less than 1 ms.is_often('_', '1 ms') asrt( is_often('_', '1 ms'), True) time_sleep('1 ms') asrt( is_often('_', '1 ms'), False) asrt( benchmark(is_often, ('_', '1 ms')), 5000, "<" ) -
Job(func, args, job_name:str='', kwargs) — class for concurrent function execution in job_batch and job_pool. Properties:
- result - functional result
- time - time in seconds
- error - there was an error
-
job_batch(jobs:list, timeout:int)->list: — starts functions (they do not necessarily have to be the same) in parallel and waits for them to be executed or timeout. jobs - list of Job class instances. Use job_batch when you don't want to wait because of one hung function.
Example - create jobs list out of dialog function with different parameters:
jobs = [] jobs.append( Job(dialog, 'Test job 1', timeout=10) ) jobs.append( Job(dialog, ['Button 1', 'Button 2']) ) for job in job_batch(jobs, timeout=5): print(job.error, job.result, job.time) -
job_pool(jobs:list, pool_size:int, args:tuple)->list — Launches 'pool_size' functions at a time for all the 'args'. 'args' may be a tuple of tuples or tuple of values. If 'pool_size' not specified, then pool_size = number of CPU.
Example:
jobs = [] jobs.append( Job(dialog, 'Test job 1', timeout=10) ) jobs.append( Job(dialog, ['Button 1', 'Button 2']) ) jobs.append( Job(dialog, 'Third job') ) for job in job_pool(jobs, pool_size=2): print(job.error, job.result, job.time)Difference between
job_batchandjob_pool:job_batch- all jobs are started simultaneously. If some job is not finished during specified timeout, it returns error (job.error = True, job.result = 'timeout').job_pool- only the specified number of jobs is executed simultaneously.
-
msgbox(msg:str, title:str=APP_NAME, ui:int=None, wait:bool=True, timeout=None)->int — show messagebox and return user choice. Arguments: msg — text title — messagebox title ui — interface flags. Example: ui = MB_ICONINFORMATION + MB_YESNO wait — if set to False — continue task execution without waiting for user responce. timeout (number of seconds or string with interval like '1 hour' or '5 min') — automatically close messagebox. If messagebox is closed by timeout (no button is pressed by user) and ui contains more than one button (MB_YESNO for example) then it will return 32000. dis_timeout (in seconds) — hide the buttons for a specified number of seconds. Example:
def test_msgbox(): if msgbox('Can I have a cheeseburger?') == IDYES: print('Yes!') else: print('No :-(')If you need a message with many buttons see dialog.
-
safe — function wrapper for safe execution. Example:
func(arg) -> resultWith safe:
safe(func)(arg) -> True, result OR safe(func)(arg) -> False, Exception -
sound_play (fullpath:str, wait:bool)->str — play .wav file. wait — do not pause task execution. If fullpath is a folder then pick random file.
-
str_diff(text1:str, text2:str)->tuple[tuple[str]] — returns the different lines between two texts (strings with line breaks) as a tuple of tuples.
tass( tuple(str_diff('foo\nbar', 'fooo\nbar')) , (('foo', 'fooo'),) ) # Different new line symbols are ok: tass( tuple(str_diff('same\r\nlines', 'same\nlines') ), () ) # Note no difference here: tass( tuple(**str_diff**('same\nlines', 'lines\nsame') ), () ) -
str_short(text:str, width:int=0, placeholder:str='...')->str — collapse and truncate the given text to fit in the given width.
Non-printing characters are removed first. If after that the line fits in the specified width, it is returned. Otherwise, as many words as possible are joined and then the placeholder is appended.
If width is not specified, the current terminal width is used.tass( str_short('Hello, world! ', 13), 'Hello, world!' ) tass( str_short('Hello, world! ', 12), 'Hello,...' ) tass( str_short('Hello\nworld! ', 12), 'Hello world!' ) tass( str_short('Hello\nworld! ', 11), 'Hello...' ) tass( benchmark(str_short, ('Hello, world! ',)), 60_000, '<') -
time_diff(start, end, unit:str='sec')->int — returns difference between dates in units. start and end should be in datetime format.
-
time_diff_str(start, end)->str — returns difference between dates in string like that: '3:01:35'. start and end should be in datetime format.
-
time_now(**delta)->datetime.datetime — returns datetime object. Use
datetime.timedeltakeywords to get different time. Yesterday:time_now(days=-1) -
time_now_str(template:str='%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S')->str — string with current time.
-
toast(msg:str|tuple|list, dur:str='default', img:str='', often_ident:str='', often_inter:str='30 sec', on_click:Callable=None, appid:str=APP_NAME) — windows toast notification.
img - full path to a picture.
duration - 'short'|'long'|'default'. 'default' and 'short' the same? 'long' is about 30 sec.
on_click - an action to perform on click. It is passed an argument with the click properties. If the notification has already disappeared from the screen and is in the Action Center , the action will be performed only if an valid appid is specified
appid - custom AppID. If you want toast to have the Taskopy icon, run theemb_appid_addtask from ext_embedded. -
pause(sec:float) — pause the execution of the task for the specified number of seconds. interval - time in seconds or a string specifying a unit like '5 ms' or '6 sec' or '7 min'.
-
var_lst_get(var:str, default=[], encoding:str='utf-8', com_str:str='#')->list — returns list with the text lines. Excludes empty lines and lines that begin with com_str
var_lst_set('test', ['a', 'b']) assert var_lst_get('test') == ['a', 'b'] var_lst_set('test', map(str, (1, 2))) assert var_lst_get('test') == ['1', '2'] assert var_del('test') == True -
var_lst_set(var, value, encoding:str='utf-8') — sets the disk list variable.
# Note that the number has become a string: var_lst_set('test', ['a', 'b', 1]) assert var_lst_get('test') == ['a', 'b', '1'] assert var_del('test') -
var_set(var_name:str, value:str) — save value of variable var_name to disk so it will persist between program starts.
var_set('test', 5) assert var_get('test') == '5' assert var_del('test') == True # Composite variable name. Intermediate folders # will be created: var = ('file', 'c:\\pagefile.sys') var_set(var, 1) assert var_get(var, 1) == '1' assert var_del(var) == True -
var_get(var_name:str)->str — retrieve disk variable value.
as_literal - converts to a literal (dict, list, tuple etc). Dangerous! - it's just eval and not ast.literal_eval
var_set('test', 1) assert var_get('test') == '1' assert var_get('test', as_literal=True) == 1 assert var_del('test') == True -
clip_set(txt:str)-> — copy text to clipboard.
-
clip_get()->str-> — get text from clipboard.
-
re_find(source:str, re_pattern:str, sort:bool=True)->list — search in source with regular expression.
-
re_match(source:str, re_pattern:str, re_flags:int=re.IGNORECASE)->bool — regexp match.
-
re_replace(source:str, re_pattern:str, repl:str='') — replace in source all matches with repl string.
-
re_split(source:str, re_pattern:str, maxsplit:int=0, re_flags:int=re.IGNORECASE)->List[str] — regexp split:
tass( re_split('abc', 'b'), ['a', 'c'] ) -
inputbox(message:str, title:str, is_pwd:bool=False)->str — show a message with an input request. Returns the entered line or empty string if user pressed cancel. is_pwd — hide the typed text.
-
random_num(a, b)->int — return a random integer in the range from a to b, including a and b.
-
random_str(string_len:int=10, string_source:str=None)->str — generate a string of random characters with a given length.
- key_pressed(hotkey:str)->bool — is the key pressed?
- key_send(hotkey:str) — press the key combination.
- key_write(text:str) — write a text.
fullpath means full name of file, for example 'c:\\Windows\\System32\\calc.exe'
IMPORTANT: always use double backslash "\\" in paths!
-
csv_read(fullpath:str, encoding:str='utf-8', fieldnames=None, delimiter:str=';', quotechar:str='"')->list — read a CSV file and return the contents as a list of dictionaries.
-
csv_write(fullpath:str, content:list, fieldnames:tuple=None, encoding:str='utf-8', delimiter:str=';', quotechar:str='"', quoting:int=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)->str — writes the list of dictionaries as a CSV file. If fieldnames is not specified - it takes the keys of the first dictionary as headers. Returns the full path to the file. content example:
[ {'name': 'some name', 'number': 1} , {'name': 'another name', 'number': 2} ... ] -
dir_copy(fullpath:str, destination:str)->int — copy the folder and all its contents. Returns the number of errors.
-
dir_delete(fullpath:str) — delete directory.
-
dir_dialog(title:str=None, default_dir:str='', on_top:bool=True, must_exist:bool=True)->str — directory selection dialog.
-
dir_dirs(fullpath, subdirs:bool=True)->list — returns list of full paths of all directories in this directory and its subdirectories.
-
dir_exists(fullpath:str)->bool — directory exists?
-
dir_files(fullpath, subdirs:bool=True, **rules)->Iterator[str] — returns list of full filenames of all files in the given directory and its subdirectories.
subdirs - including files from subfolders.
rules - rules for thepath_rulefunctiontass( tuple(dir_files('plugins', in_ext='jpg') ), tuple() ) tass( tuple(dir_files('plugins', in_ext='py'))[0] , 'plugins\\constants.py' ) tass( tuple( dir_files('plugins', ex_ext='pyc') ) , tuple( dir_files('plugins', in_ext='py') ) ) -
dir_find(fullpath, only_files:bool=False)->list — returns list of paths in specified folder.
fullpath passed to the glob.glob
only_files - return only files and not files and directories.
Examples:
# Only files in current directory: dir_find('d:\\folder\\*.jpg') # with subdirectories: dir_find('d:\\folder\\**\\*.jpg') -
dir_junc(src_path, dst_path) — creates a junction link to a directory.
Only for local paths.td = dir_test() tdj = file_name_add(td, ' junc') dir_junc(td, tdj) asrt( dir_exists(tdj), True ) # Delete source dir: dir_delete(td) # Now the link doesn't work: asrt( dir_exists(tdj), False ) dir_delete(tdj) -
dir_list(fullpath, **rules)->Iterator[str] — returns all directory content (dirs and files).
rules - rules for thepath_rulefunction.tass( 'resources\\icon.png' in dir_list('resources'), True) tass( 'resources\\icon.png' in dir_list('resources', ex_ext='png'), False) tass( benchmark(lambda d: tuple(dir_list(d)), 'log', b_iter=5) , 500_000 , '<' ) -
dir_purge(fullpath, days:int=0, subdirs:bool=False, creation:bool=False, test:bool=False, print_del:bool=False, **rules)->int — deletes files older than x days.
Returns number of deleted files and folders.days=0 - delete everything
creation - use date of creation, otherwise use last modification date.
subdirs - delete in subfolders too. Empty subfolders will be deleted.
test - only display the files and folders that should be deleted, without actually deleting them.
print_del - print path when deleting.
rules - rules for thepath_rulefunction -
dir_rnd_dirs(fullpath, attempts:int=5, filter_func=None)->str — same as
dir_rnd_file, but returns the subdirectories. -
dir_rnd_files(fullpath, file_num:int=1, attempts:int=5, **rules)->Iterator[str] — gets random files from a directory or None if nothing is found.
file_num - how many files to return.
rules - a tuple of rules from thepath_rule.Designed for large directories that take a significant amount of time to list.
The function will not return the same file twice.
Example:dir_rnd_files('.') tuple(dir_rnd_files('.', ex_ext='py'))Compared to
dir_fileswithrandom.choice:> benchmark(lambda: random.choice( list(dir_files(temp_dir() ) ) ), b_iter=10) benchmark: 113 367 113 ns/loop > benchmark(dir_rnd_files, a=(temp_dir(), ), b_iter=10) 620 > len( tuple( dir_files( temp_dir() ) ) ) 1914 -
dir_size(fullpath:str, unit:str='b')->int — folder size in specified units.
-
dir_sync(src_dir, dst_dir, report:bool=False, **rules)->dict — syncrhonize two directories.
For rules see thepath_rule.
Returns dict with errors:{'path\\file.exe': 'copy error', ...} -
dir_zip(source:str, destination:str)->str — zip the folder return the path to the archive.
-
dir_user_desktop()->str — current user's desktop folder.
-
dir_user_startup()->str — startup folder of the current user*.
-
drive_io(drive_num:int=None)->dict — returns physical drive (not partition!) i/o generator that returns a named tuples with counters. example:
dio = drive_io() print(next(dio)[0].read_bytes) time_sleep('1 sec') print( file_size_str(next(dio)[0].total_bytes_delta) ) -
drive_list(exclude:str='')->str — string of logical drives letters.
-
file_append(fullpath:str, content:str)->str — appends content to a file. Creates fullpath if not specified. Returns fullpath.
-
file_attr_set(fullpath, attribute:int=win32con.FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL) — sets file attribute.
-
file_backup(fullpath:str, dest_dir:str='', suffix_format:str='%y-%m-%d%H-%M-%S')->str — copy 'somefile.txt' to 'somefile_2019-05-19_21-23-02.txt'. dest_dir - destination directory. If not specified - current folder. Returns full path of new file.
-
file_basename(fullpath:str)->str — returns basename: file name without parent folder and extension.
-
file_backup(fullpath, folder:str=None) — make copy of file with added timestamp. folder — place copy to this folder. If omitted — place in original folder.
-
file_copy(fullpath, destination:str, copy_metadata:bool=False) — copy file to destination (fullpath or just folder).
-
file_date_a(fullpath) — file access date .
-
file_date_c(fullpath) — file creation date.
-
file_date_m(fullpath) — file modification date.
-
file_date_set(fullpath, datec=None, datea=None, datem=None) — sets a file date.
fp = temp_file(content=' ') asrt( benchmark(file_date_set, ka={'fullpath': fp, 'datec': time_now()}, b_iter=3) , 220000 , "<" ) file_delete(fp) -
file_delete(fullpath:str) — delete file. See also file_recycle.
-
file_dialog(title:str=None, multiple:bool=False, default_dir:str='', default_file:str='', wildcard:str='', on_top:bool=True) — Shows standard file dialog and returns fullpath or list of fullpaths if multiple == True.
-
file_dir(fullpath:str)->str: — get parent directory name of file.
-
file_dir_repl(fullpath, new_dir:str)->str — changes the directory of the file (in full path)
-
file_drive(fullpath)->str — returns a drive letter in lowercase from a file name:
assert file_drive(r'c:\\pagefile.sys') == 'c' -
file_exists(fullpath:str)->bool — file exists?
-
file_ext(fullpath:str)->str — file extension in lower case without dot.
-
file_hash(fullpath:str, algorithm:str='crc32')->str — returns hash of file. algorithm - 'crc32' or any algorithm from hashlib ('md5', 'sha512' etc)
-
file_lock_wait(fullpath, wait_interval:str='100 ms')->bool — blocks execution until the file is available. Usage - wait for another process to stop writing to the file.
-
file_log(fullpath:str, message:str, encoding:str='utf-8', time_format:str='%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S') — log message to fullpath file.
-
file_move(fullpath:str, destination:str) — move file to destination folder or file.
-
file_name(fullpath:str)->str — get file name without directory.
-
file_name_add(fullpath, suffix:str='', prefix:str='')->str — adds a string (prefix or suffix) to the file name before the extension (or from beginning). Example:
file_name_add('my_file.txt', suffix='_1') 'my_file_1.txt' -
file_name_fix(filename:str, repl_char:str='_')->str — replaces forbidden characters with repl_char. Removes leading and trailing spaces. Adds '\\?\' for long paths.
-
file_name_rem(fullpath, suffix:str='', prefix:str='')->str — removes a suffix or prefix from a filename.
-
file_print(fullpath, printer:str=None, use_alternative:bool=False)->bool — prints the file on the specified printer.
-
file_read(fullpath:str)->str: — get content of file.
-
file_recycle(fullpath:str, silent:bool=True)->bool — move file to the recycle bin. silent - do not show standard windows dialog to confirm deletion. Returns True on successful operation.
-
file_relpath(fullpath, start)->str — relative file name.
-
file_rename(fullpath:str, dest:str)->str — rename the file. dest is the full path or just a new file name without a folder.
-
file_size(fullpath:str, unit:str='b')->bool: — get size of file in units (gb, mb, kb, b).
-
file_write(fullpath:str, content=str, encoding:str='utf-8')->str — saves content to a file. Creates file if the fullpath doesn't exist. If fullpath is '' or None - uses temp_file(). Returns fullpath.
-
file_zip(fullpath, destination:str)->str — compress a file or files into an archive. fullpath — a string with a full file name or a list of files. destiniation — full path to the archive.
-
drive_free(letter:str, unit:str='GB')->int: — get drive free space in units (gb, mb, kb, b).
-
is_directory(fullpath:str)->bool: — fullpath is directory?
-
path_exists(fullpath:str)->bool: — fullpath exists (no matter is it folder or file)?
-
path_short(fullpath, max_len:int=100)->str — shortens a long file name to display.
path = r'c:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe' tass(path_short(path, 22), 'c:\Windo...msiexec.exe') tass(path_short(path, 23), 'c:\Window...msiexec.exe') -
rec_bin_purge(drive:str=None, progress:bool=False, sound:bool=True) — clears the recycle bin.
# One drive: rec_bin_purge('c') # All drives: rec_bin_purge() -
rec_bin_size(drive:str|None=None)->tuple — retrieves the total size and number of items in the Recycle Bin for a specified drive.
-
shortcut_create(fullpath, dest:str=None, descr:str=None, icon_fullpath:str=None, icon_index:int=None, win_style:int=win32con.SW_SHOWNORMAL, cwd:str=None)->str — creates a shortcut for a file. Returns full path of shortcut.
- dest - full name of the shortcut file. If not specified, the desktop folder of the current user is used.
- descr - shortcut description.
- icon_fullpath - source file for icon.
- icon_index - icon index. If icon_fullpath not specified then uses fullpath as source.
-
temp_dir(new_dir:str=None)->str — returns the path to the temporary folder. If new_dir is specified, it creates a subfolder in the temporary folder and returns its path.
-
temp_file(prefix:str='', suffix:str='')->str — returns the name for the temporary file.
-
domain_ip(domain:str)->list — get a list of IP-addresses by domain name.
-
file_download(url:str, destination:str=None)->str: — download file and return fullpath. destination — it may be None, fullpath or folder. If None then download to temporary folder with random name.
-
ftp_upload(fullpath, server:str, user:str, pwd:str, dst_dir:str='/', port:int=21, active:bool=True, debug_lvl:int=0, attempts:int=3, timeout:int=10, secure:bool=False, encoding:str='utf-8')->tuple — uploads file(s) to an FTP server. Returns (True, None) or (False, ('error1', 'error2'...))
debug_lvl - set to 1 to see the commands.
-
html_element(url:str, element, element_num:int=0)->str: — download page and retrieve value of html element. element — dictionary that contain element information such as name or attributes, or list with such dictionaries or string with xpath. element_num - item number, if there are several of them found. Example:
# Get the internal text of span element which has # the attribute itemprop="softwareVersion" element={ 'name': 'span' , 'attrs': {'itemprop':'softwareVersion'} }See get_current_ip in task examples
-
html_clean(html_str:str, separator=' ')->str — removes HTML tags from string.
-
is_online(*sites, timeout:float=2.0)->int — checks if there is an internet connection using HEAD requests to the specified web sites.
The function will not raise an exception.
timeout - timeout in seconds.tass( is_online(), 2 ) tass( is_online('https://non.existent.domain'), 0 ) -
json_element(url:str, element:list) — same as html_element but for JSON. element — a list with a map to desired item. Example: element=['usd', 2, 'value']
-
http_req(url:str, encoding:str='utf-8', post_file:str=None, post_hash:bool=False)->str: — download page by url and return it's html as a string. post_file - send this file with POST request. post_hash - add the checksum of the file to request headers to check the integrity (see Task Options).
-
http_req_status(url:str, method='HEAD')->int — returns just a status of HTTP request:
assert http_req_status('https://github.com') == 200 -
net_html_unescape(html_str:str)->str — decodes HTML escaped symbols:
"That's an example" -> "That's an example" -
net_pc_ip()->str — returns the IP address of the computer.
-
net_url_decode(url:str, encoding:str='utf-8')->str — decodes URL.
-
net_url_encode(url:str, encoding:str='utf-8')->str — encodes URL.
-
pc_name()->str — computer name.
-
ping_icmp(host:str, count:int=3, timeout:int=500, encoding:str='cp866')->tuple — Returns (True, (loss %, aver. time) ) or (False, 'cause of failure'). Examples:
ping_icmp('8.8.8.8') > (True, (0, 47)) ping_icmp('domain.does.not.exist') > (False, 'host unreachable (1)') -
ping_tcp(host:str, port:int, count:int=1, pause:int=100, timeout:int=500)->tuple — measure loss and response time with a tcp connection. Returns (True, (loss percentage, time in ms) ) or (False, 'error text').
pause - pause in milliseconds between attempts
timeout - the waiting time for a response in milliseconds.
Examples:
ping_tcp('8.8.8.8', 443) > (true, (0, 49)) ping_tcp('domain.does.not.exist', 80) > (false, '[errno 11004] getaddrinfo failed') -
table_html(table:list, headers:bool=True , empty_str:str='-', consider_empty:tuple=(None, '') , table_class:str='')->str — converts list of tuples/lists to a html table.List example:
[ ('name', 'age'), ('john', '27'), ('jane', '24'), ] -
url_hostname(url:str, , sld:bool=True)->str — extract the domain name from the URL.
sld - if True then return the second level domain otherwise return the full domain.
assert url_hostname('https://www.example.gov.uk') == 'example.gov.uk' assert url_hostname('https://www.example.gov.uk', sld=False) \ == 'www.example.gov.uk' assert url_hostname('http://user:pwd@abc.example.com:443/api') \ == 'example.com' assert url_hostname('http://user:pwd@abc.example.com:443/api' , sld=False) == 'abc.example.com' assert url_hostname('http://user:pwd@192.168.0.1:80/api') \ == '192.168.0.1' -
xml_element(url:str, element:str, element_num:int=0, encoding:str='utf-8', **kwargs) — downloads the document from URL and returns the value by the specified XPath e.g:
element='/result/array/msgContact[1]/msgCtnt'
In the functions for working with windows, the window argument can be either a string with the window title or a number representing the window handle.
-
free_ram(unit:str='percent') — amount of free memory. unit — 'kb', 'mb'... or 'percent'.
-
idle_duration(unit:str='msec')->int — how much time has passed since user's last activity.
-
monitor_off() — turn off the monitor.
-
monitor_on() — turns on the monitor.
-
registry_get(fullpath:str) — get value from Windows Registry. fullpath — string like 'HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Calc\layout'
-
win_activate(window=None)->int — bring window to front. window may be a string with title or integer with window handle.
Note: it is not always possible to activate the window. It will just blink on the taskbar. -
win_by_pid(process)->tuple — returns top window of a process as a tuple
(hwnd:int, title:str). -
win_close(window=None, wait:bool=True)->bool — closes window and returns True on success.
-
win_find(title:str)->list — find window by title. Returns list of all found windows.
-
win_hide(window=None)->int — hide window.
-
win_is_min(window)->bool|None — returns
Trueif the window is minimized.asrt( win_is_min(win_get(class_name=WIN_TASKBAR_CLS)), False ) -
win_list(title_filter:str=None, class_filter:str=None, case_sensitive:bool=False)->list — list of titles of all windows. title_filter - optional filter for titles. - win_on_top(window=None, on_top:bool=True)->int — makes the window to stay always on top.
-
win_show(window=None)->int — show window.
-
win_title_set(window=None, new_title:str='')->int — change window title from cur_title to new_title
-
mail_check(server:str, login:str, password:str, folders:list=['inbox'], msg_status:str='UNSEEN', headers:tuple=('subject', 'from', 'to', 'date'), silent:bool=True)->Tuple[ List[MailMsg], List[str] ] — returns list of MailMsg and list of errors.
headers - message headers to fetch. You can access them later in MailMsg attributes. -
mail_download(server:str, login:str, password:str, output_dir:str, folders:list=['inbox'], trash_folder:str='Trash')->tuple — downloads all messages to the specified folder. Successfully downloaded messages are moved to the IMAP trash_folder folder on the server. Returns a tuple of two lists: a list with decoded mail subjects and a list with errors.
-
mail_send(recipient:str, subject:str, message:str, smtp_server:str, smtp_port:int, smtp_user:str, smtp_password:str) — send email.
-
proc_start(proc_path:str, args:str='', wait:bool=False) — start application. If wait=True — returns process return code, if False — returns PID of created process. proc_path — path to executable file. args — command-line arguments. wait — wait until application will be closed.
-
file_open(fullpath:str) — open file or URL in default application.
-
proc_close(process, timeout:int=10, cmd_filter:str=None) — soft completion of the process: first all windows belonging to the specified process are closed, and after the timeout (in seconds) the process itself is killed, if still exists. cmd_filter - kill only processes with that string in command line.
-
proc_exists(process, cmd_filter:str=None, user_filter:str=None)->int — returns PID if the process with the specified name exists.
process - image name or PID.
cmd_filter - optional string to search in the command line of the process.
user_filter - only search within processes of specified user. Format: pc\username -
proc_list(name:str='', cmd_filter:str=None)->list — get list of processes with that name. Item in list is a DictToObj object with this attributes: pid — PID of found process. name — short name of executable. username — username. exe — full path to executable. cmdline — command-line as list.
cmd_filter - filter by the presence of this substring on the command line.
Example — print PIDs of all Firefox processes:
for proc in proc_list('firefox.exe'): print(proc.pid) -
proc_cpu(process, interval:float=1.0)->float — returns CPU usage of specified PID for specified interval of time in seconds.
If a process not found then returns -1:tass(proc_cpu('not existing process'), -1) tass(proc_cpu(0), 1, '>') -
proc_kill(process, cmd_filter:str=None) — kill process or processes. process may be an integer so only process with this PID will be terminated. If process is a string then kill every process with that name. cmd_filter - kill only processes with that string in command line.
-
proc_uptime(process)->float — returns process running time in seconds or -1.0 f no process is found.
-
screen_width()->int — width of screen.
-
screen_height()->int — height of screen.
-
service_start(service:str, args:tuple=None) — starts the service.
-
service_stop(service:str)->tuple — stops the service.
-
service_running(service:str)->bool — the service is up and running?
-
wts_message(sessionid:int, msg:str, title:str, style:int=0, timeout:int=0, wait:bool=False) — sends message to WTS session. style - styles like in msgbox (0 - MB_OK). timeout - timeout in seconds (0 - no timeout). Returns same values as msgbox.
-
wts_cur_sessionid()->int — returns SessionID of current process
-
wts_logoff(sessionid:int, wait:bool=False)->int — logoffs session. wait - wait for completion.
-
wts_proc_list(process:str=None)->list — returns list of DictToObj objects with properties: .sessionid:int, .pid:int, .process:str (name of exe file), .pysid:obj, .username:str, .cmdline:list. process - filter by process name.
-
wts_user_sessionid(users, only_active:bool=True)->list — converts list of users to a list of session ID's. only_active - return only WTSActive sessions.
- file_enc_write(fullpath:str, content:str, password:str, encoding:str='utf-8')->tuple: — encrypts content with password and writes to a file. Adds salt as file extension. Returns status, fullpath/error.
- file_enc_read(fullpath:str, password:str, encoding:str='utf-8')->tuple — decrypts the contents of the file and returns status, content/error
- file_encrypt(fullpath:str, password:str)->tuple — encrypts file with password. Returns status, fullpath/error. Adds salt as file extension.
- file_decrypt(fullpath:str, password:str)->tuple — decrypts file with password. Returns status, fullpath/or error.
-
routeros_query(query:list, device_ip:str=None, device_port:str='8728', device_user:str='admin', device_pwd:str='') — send query to router and get status and data. Please read wiki wiki about query syntax. Example — get information about interface 'bridge1':
status, data = routeros_query( [ '/interface/print' , '?name=bridge1' ] , '192.168.0.1' , '8728' , 'admin' , 'pAsSworD' )Contents of data:
[{'=.id': '*2', '=name': 'bridge1', '=type': 'bridge', '=mtu': 'auto', '=actual-mtu': '1500', '=l2mtu': '1596', '=mac-address': '6b:34:1B:2F:AA:21', '=last-link-up-time': 'jun/10/2019 10:33:35', '=link-downs': '0', '=rx-byte': '1325381950539', '=tx-byte': '2786508773388', '=rx-packet': '2216725736', '=tx-packet': '2703349720', '=rx-drop': '0', '=tx-drop': '0', '=tx-queue-drop': '0', '=rx-error': '0', '=tx-error': '0', '=fp-rx-byte': '1325315798948', '=fp-tx-byte': '0', '=fp-rx-packet': '2216034870', '=fp-tx-packet': '0', '=running': 'true', '=disabled': 'false', '=comment': 'lan'}] -
routeros_send(cmd:str, device_ip:str=None, device_port:str='8728', device_user:str='admin', device_pwd:str='') — send command to router and get status and error. Example: get list of static items from specified address-list then delete them all:
status, data = routeros_query( [ '/ip/firewall/address-list/print' , '?list=my_list' , '?dynamic=false' ] , device_ip='192.168.0.1' , device_user='admin' , device_pwd='PaSsWorD' ) # check status and exit if there is error: if not status: print(f'Error: {data}') return # get list items from data: items = [i['=.id'] for i in data] # Now send commands for removing items from list. # Notice: cmd is list of lists routeros_send( [ [ '/ip/firewall/address-list/remove' , f'=.id={i}' ] for i in items ] , device_ip='192.168.0.1' , device_user='admin' , device_pwd='PaSsWorD' ) -
routeros_find_send(cmd_find:list, cmd_send:list, device_ip:str=None, device_port:str='8728', device_user:str='admin', device_pwd:str='') — find all id's and perform some action on them. cmd_find — list with API print command to find what we need. cmd_send — list with action to perform. Example — remove all static entries from address-list my_list:
routeros_find_send( cmd_find=[ '/ip/firewall/address-list/print' , '?list=my_list' , '?dynamic=false' ] , cmd_send=['/ip/firewall/address-list/remove'] , device_ip='192.168.88.1' , device_user='admin' , device_pwd='PaSsW0rd' )
If you want to save something so that it survives a crontab reload, use the global dictionary gdic:
def demo__gdic():
if not gdic.get('test var'):
gdic['test var'] = 0
gdic['test var'] += 1
dialog(f'Try to reload crontab: {gdic["test var"]}')
If you want to save something so that it survives a Taskopy restart, use the file variables: var_get, var_set, etc.
How to update the task code on multiple computers.
You can define a task not only in a crontab, but also in an extension, using the task_add decorator. So, on the client computer, you can import from an extension once into crontab, and then update only the file with the extension that contains the task.
You can programmatically reload the crontab with crontab_reload. This is safe, since the crontab is actually loaded in test mode first. Even if there are gross errors in the crontab, the updated crontab will not load and the old tasks will still run.
https://addons.mozilla.org/ru/firefox/addon/send-to-taskopy/
Extension adds item to context menu. With it you can run task in Taskopy.
In extension settings specify the URL of your task that will process data, for example:
http://127.0.0.1:8275/get_data_from_browser
This task should have data and http=True properties. The data argument will be passed information about the request in DataBrowserExt format.
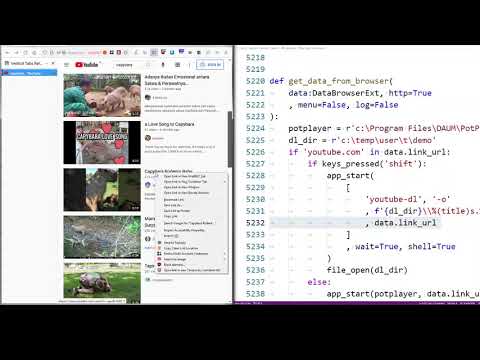
Example - play Youtube video in PotPlayer:
def get_data_from_browser(data:DataBrowserExt, http=True, menu=False, log=False):
if ('youtube.com' in data.link_url
or 'youtu.be' in data.link_url):
proc_start(
r'c:\Program Files\DAUM\PotPlayer\PotPlayerMini64.exe'
, data.link_url
)
You can add Taskopy to the Send to submenu of context menu.
There is a simple powershell script Taskopy.ps1 in resources directory. You need to create a shortcut to this script in user directory:
%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo\
Task name is send_to by default. This task must have properties data and http so inside task you can access the full path of file via data.fullpath
Example - pass the file name to the task virustotal_demo from Task examples:
def send_to(data, http, menu=False, log=False):
if file_ext(data.fullpath) in ['exe', 'msi']:
virustotal_demo(data.fullpath)
Inside virustotal_demo you can see another way to pass a file name to a task - via file_dialog
- I've been in need of a tester for a long time :)
- Donate via PayPal
- Disk free space
- Current IP address
- Add IP-address to MikroTik router
- Virustotal check
Check the free space on all local discs every 30 minutes:
def check_free_space_demo(submenu='demo'
, every='30 minutes'):
for d in drive_list():
if drive_free(d) < 10:
dialog(f'low disk space: {d}')
Show message with current IP-address using dyndns.org:
def get_current_ip():
# Get the text of the HTML-tag 'body' from the checkip.dyndns.org page
# html_element should return a string like 'Current IP Address: 11.22.33.44'
ip = html_element(
'http://checkip.dyndns.org/'
, {'name':'body'}
).split(': ')[1]
tprint(f'Current IP: {ip}')
dialog(f'Current IP: {ip}', timeout=10)
Add the IP-address from the clipboard to the address-list of Mikrotik router:
def add_ip_to_list():
routeros_send(
[
'/ip/firewall/address-list/add'
, '=list=my_list'
, '=address=' + clip_get()
]
, device_ip='192.168.88.1'
, device_user='admin'
, device_pwd='PaSsWoRd'
)
dialog('Done!', timeout=3)
Check MD5 hash of file in the Virustotal. You need to register to obtain free API key:
def virustotal_demo(fullpath:str=None, submenu='demo'):
APIKEY = 'your API key'
if not fullpath:
fullpath = file_dialog('Virustotal', wildcard='*.exe;*.msi')
if not fullpath:
return
md5 = file_hash(fullpath, 'md5')
scan_result = json_element(f'https://www.virustotal.com/vtapi/v2/file/report?apikey={APIKEY}&resource={md5}')
if isinstance(scan_result, Exception):
tprint(scan_result)
dialog('HTTP request exception')
return
if scan_result['response_code'] == 0:
dialog('Unknown file', timeout=3)
return
res = DictToObj(scan_result)
for av in res.scans.keys():
if res.scans[av]['detected']:
print(f'{av}: ' + res.scans[av]['result'])
dialog(f'Result: {res.positives} of {res.total}', timeout=5)
Receive a file via HTTP POST request and show a message with a comment and the full name of the file:
def http_post_demo(data, http=True, log=False, menu=False):
dialog(f'{data.filecomment}\n\n{data.post_file}')
Example of sending a request to a task:
curl -F "filecomment=Take this!" -F "file=@d:\my_picture.jpg" http://127.0.0.1:8275/http_post_demo