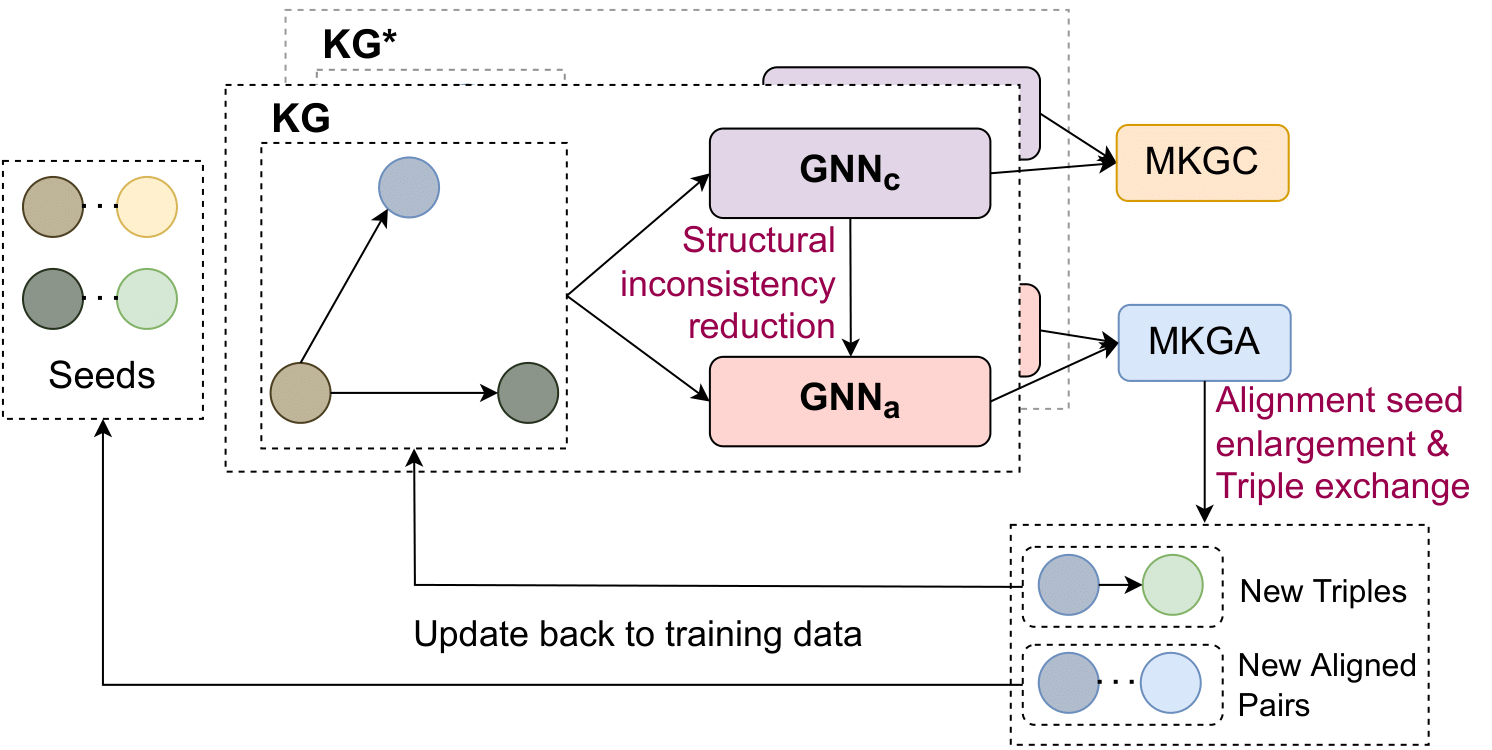
Knowledge graph (KG) alignment and completion are usually treated as two independent tasks. While recent work has leveraged entity and relation alignments from multiple KGs, such as alignments between multilingual KGs with common entities and relations, a deeper understanding of the ways in which multilingual KG completion (MKGC) can aid the creation of multilingual KG alignments (MKGA) is still limited. Motivated by the observation that structural inconsistencies -- the main challenge for MKGA models -- can be mitigated through KG completion methods, we propose a novel model for jointly completing and aligning knowledge graphs. The proposed model combines two components that jointly accomplish KG completion and alignment. These two components employ relation-aware graph neural networks that we propose to encode multi-hop neighborhood structures into entity and relation representations. Moreover, we also propose (i) a structural inconsistency reduction mechanism to incorporate information from the completion into the alignment component, and (ii) an alignment seed enlargement and triple transferring mechanism to enlarge alignment seeds and transfer triples during KGs alignment. Extensive experiments on a public multilingual benchmark show that our proposed model outperforms existing competitive baselines, obtaining new state-of-the-art results on both MKGC and MKGA tasks.
We use Python and Pytorch to implement a joint KG alignment and completion model named JMAC. The model architecture is illustrated as follows:
Details of the model architecture and experimental results can be found in our EMNLP 2022 Findings paper:
@inproceedings{tong2022jmac,
title = {{Joint Multilingual Knowledge Graph Completion and Alignment}},
author = {Tong, Vinh and Nguyen, Dat Quoc and Trung, Huynh Thanh and Nguyen, Thanh Tam and Nguyen, Quoc Viet Hung and Mathias, Niepert},
booktitle = {Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022},
year = {2022}
}
Please CITE our paper whenever our JMAC is used to help produce published results or incorporated into other software.
We use DBP-5L. The structure of the dataset is listed as follows:
datasetdbp5l/:
├── entities/
│ ├── el.tsv: entity names for language 'el'
├── kg/
│ ├── el-train.tsv: the train dataset for the completion task
│ ├── el-val.tsv: the train dataset for the completion task
│ ├── el-test.tsv: the train dataset for the completion task
├── seed_train_pairs/
│ ├── el-en.tsv: alignment training seeds
├── seed_train_pairs/
│ ├── el-en.tsv: alignment test seeds
├── relation.txt: set of relations
Before running the code, please download the pre-trained word embedder wiki-news-300d-1M.vec.zip and extract it to 'JMAC/.'
We also develop a version for running KG alignment on the DBPv1 (OpenEAv1) dataset. Please try JMAC_DBPv1 to reproduce our alignment results on the DPBv1 dataset.
# clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/vinhsuhi/JMAC.git
cd JMAC
# install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
To reproduce our experiments, please use the following script:
# w/ SI
python train.py --data_path datasetdbp5l/ --target_language ja
# w/o SI
python train.py --data_path datasetdbp5l/ --target_language ja --no_name_info --dropout 0.1