-
Made in Windows-10
-
Version of python used: Python 3.12.3
-
Currently there is no open-source project of sign calculator. This is first of it's kind.
-
Please enable internet access so that the images in the notebook can load properly.
-
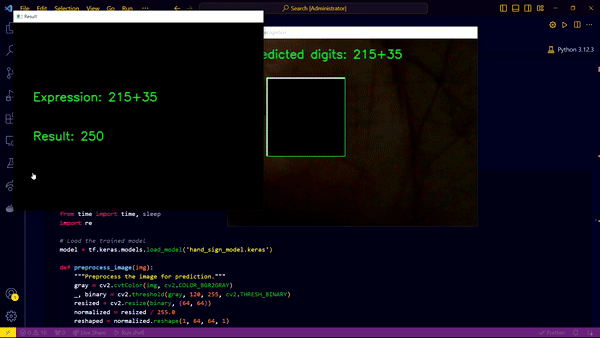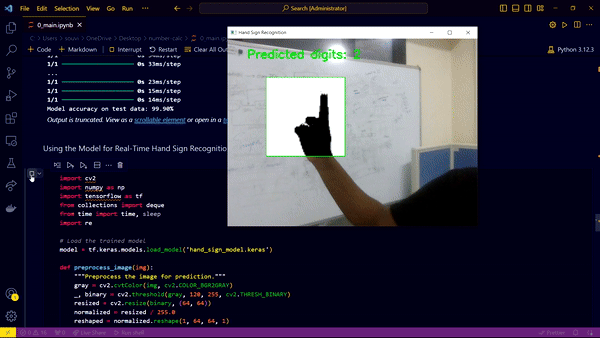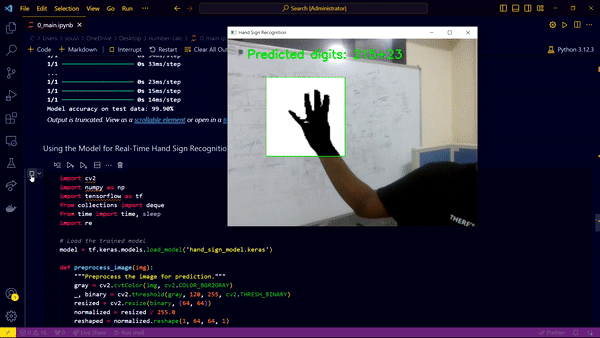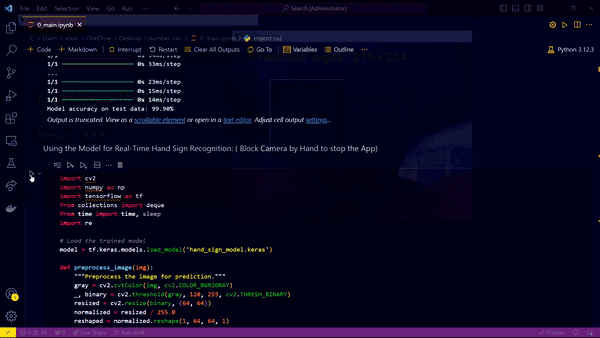
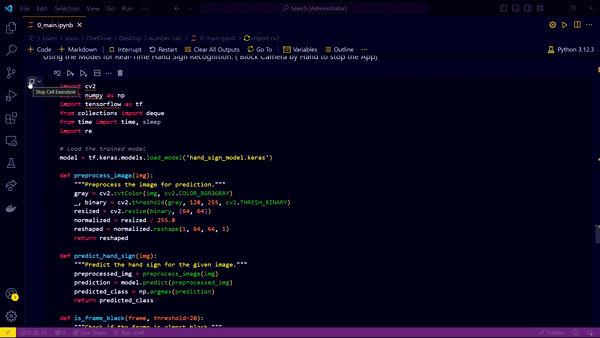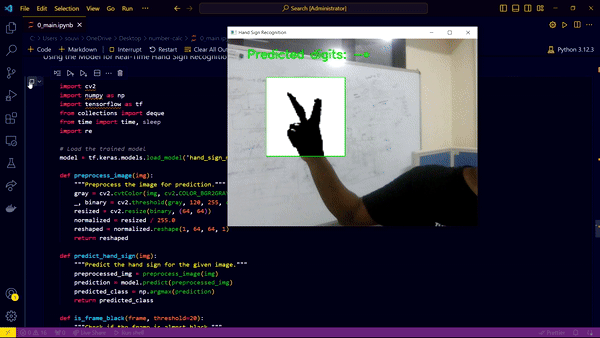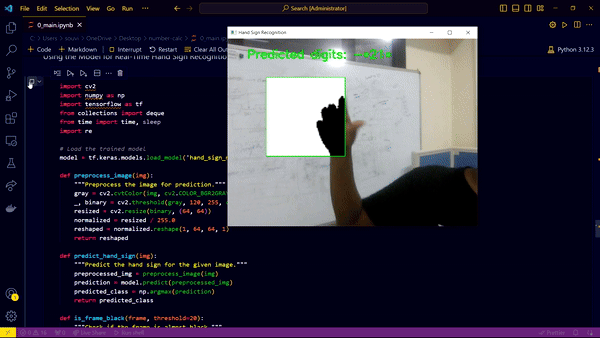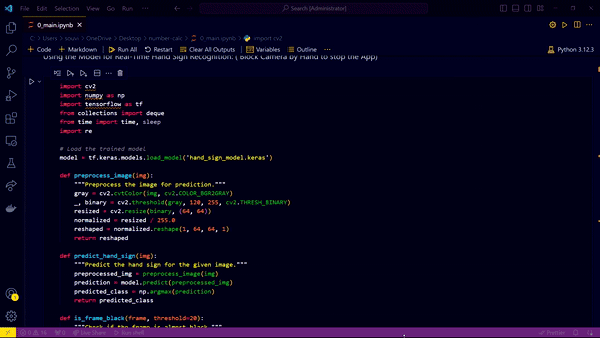
Block Camera by Hand to stop the App & Evaluate the answer on screen
-
Do not let your face come in the camera screen, otherwise auto brightness/contrast will over-brighten the fingers, giving poor accuracy
We have developed an innovative sign calculator that utilizes hand gestures to input numerical digits and arithmetic operators. The system employs a webcam to capture hand signs, processes these inputs, and evaluates the resulting mathematical expression. The final computed result is displayed on the screen when the user places their hand over the webcam, causing it to stop capturing.
In addressing the issue that not all learning materials are accessible to students with disabilities, this sign calculator project offers a promising solution. Traditional educational tools often fail to accommodate the diverse needs of students with disabilities. By incorporating an inclusive learning solution that leverages hand signs for input, this project caters to students with limited mobility or dexterity who may find using keyboards or touchscreens challenging. This sign calculator can be integrated with text-to-speech systems to provide auditory feedback, ensuring that visually impaired students can also benefit from the tool. Furthermore, the project can be expanded to include closed captions for instructional videos and alternative learning formats, making mathematical learning more accessible. This holistic approach not only facilitates better engagement and understanding for students with disabilities but also fosters an inclusive educational environment where all students have the opportunity to succeed.
This sign calculator project can significantly enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities by providing an intuitive and interactive way to perform mathematical operations. For those with limited mobility or dexterity, traditional input methods such as keyboards and touchscreens can be challenging. This project allows users to input numbers and operators through hand signs, which can be especially beneficial for individuals with motor impairments. By leveraging sign language and hand gestures, users can interact with the calculator more comfortably and efficiently, reducing the physical strain of conventional input methods. Additionally, the visual feedback and real-time evaluation of expressions ensure a seamless and user-friendly experience, making technology more inclusive and accessible for everyone.
- Hand Sign Input: The calculator takes numerical digits (0-5) and arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /) as inputs through hand signs.
- Expression Evaluation: The system evaluates the captured expression and displays the result on the screen.
- Webcam Integration: The webcam captures the hand signs, and the process halts when the user places their hand on the webcam, making the screen dark. This triggers the evaluation and display of the computed output.
- Dataset: The model is trained using a Kaggle dataset specifically designed for hand sign recognition.
- Model Scope: Currently, the model is trained to recognize digits 0 to 5 and operators "+, -, *, /".
- Usage Precaution: Users are advised to keep their face away from the webcam during prediction to prevent auto brightness/contrast adjustments that could interfere with finger visibility.
- Notebook Structure:
- Cell One: Training the dataset.
- Cell Two: Testing on the test dataset.
- Cell Three: Capturing hand signs using the webcam and displaying the evaluated answer. The camera stops capturing once the user places their hand over it, making the screen dark, and immediately evaluates and displays the expression.
The model employed is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) designed to recognize hand signs. The architecture consists of multiple layers to effectively extract and learn features from the input images.
-
Convolutional Layers: Three convolutional layers with ReLU activation are used to capture spatial hierarchies in the input images.
- First layer: 32 filters, kernel size (3, 3)
- Second layer: 64 filters, kernel size (3, 3)
- Third layer: 128 filters, kernel size (3, 3)
-
Pooling Layers: MaxPooling layers follow each convolutional layer to reduce the spatial dimensions and retain essential features.
- Pooling size: (2, 2)
-
Dropout Layers: Dropout is used after each pooling layer to prevent overfitting by randomly dropping units during training.
- Dropout rate: 0.25 after first two pooling layers, 0.5 after the third pooling layer and fully connected layer.
-
Fully Connected Layers: Flattening the output from the last pooling layer, the model includes a dense layer to learn complex features.
- Dense layer: 512 units, ReLU activation
-
Output Layer: A softmax layer for classification into 10 classes (0-5 digits and 4 operators).
The model is trained using the categorical cross-entropy loss function and the Adam optimizer, which adapts the learning rate during training. The training process includes data augmentation techniques to enhance the robustness of the model.
The trained model is evaluated on a test dataset to assess its accuracy and generalization capability. The accuracy score provides an indication of the model’s performance on unseen data.
The real-time deployment involves capturing hand signs through the webcam. The captured frames are processed and fed into the trained model to predict the corresponding digit or operator. The predictions are accumulated to form a mathematical expression, which is evaluated and displayed when the webcam capture is halted.
This sign calculator project demonstrates the practical application of CNNs in real-time hand sign recognition and expression evaluation. The integration of machine learning, computer vision, and real-time processing offers a unique and interactive approach to performing arithmetic calculations. With further enhancements and training on a more comprehensive dataset, the model can be extended to recognize a wider range of digits and operators.
- Using the Model for Real-Time Numeric Hand Sign Recognition & Real Time On-Screen Expression Evaluation:
- Block Camera by Hand to stop the App & Evaluate the answer on screen
- Do not let your face come in the camera screen, otherwise auto brightness/contrast will over-brighten the fingers, giving poor accuracy
https://nbviewer.org/github/souvikcseiitk/sign-calculator/blob/main/0_main.ipynb