A little Search Engine implementation using Trie Data Structure.
makeCompiles and runs the project.make cmpCompiles the code.- make run Runs the already build code without compiling.
./trie-search./trie-search [path_to_file]./trie-search [path_to_file] [pattern_to_search]
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a kind of search tree—an ordered tree data structure used to store a dynamic set or associative array where the keys are usually strings.
Unlike a binary search tree, no node in the tree stores the key associated with that node; instead, its position in the tree defines the key with which it is associated; i.e., the value of the key is distributed across the structure. All the descendants of a node have a common prefix of the string associated with that node, and the root is associated with the empty string. Keys tend to be associated with leaves, though some inner nodes may correspond to keys of interest. Hence, keys are not necessarily associated with every node. For the space-optimized presentation of prefix tree, see compact prefix tree.
- Looking up data in a trie is faster in the worst case, O(m) time (where m is the length of a search string), compared to an imperfect hash table. An imperfect hash table can have key collisions. A key collision is the hash function mapping of different keys to the same position in a hash table. The worst-case lookup speed in an imperfect hash table is O(N) time, but far more typically is O(1), with O(m) time spent evaluating the hash.
- There are no collisions of different keys in a trie.
- There is no need to provide a hash function or to change hash functions as more keys are added to a trie.
- A trie can provide an alphabetical ordering of the entries by key.
Complexities
Insert : O(m) : m is the length of string.
Delete : O(m) : m is the length of string.
Search : O(m) : m is the length of string.Space Complexity : O(n*m) : n = number of string , m = avg length of strings
- in the root directory of the project run
make: it will compile the project and produce the executable inbuild/Trie_Search- data files are stored in
data/directory which consist of string units each in different line.- you can store custom strings in words.txt or add a custom file in data/ directory.
- execute the executable directly. OR
make runin the root directory.- choose the file to load in trie data structure.
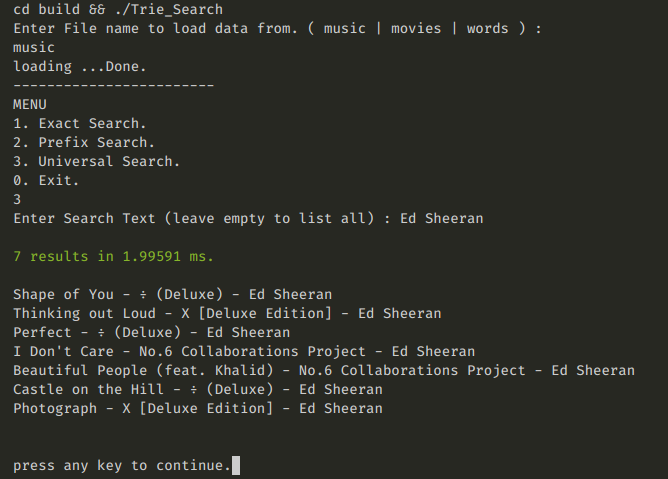
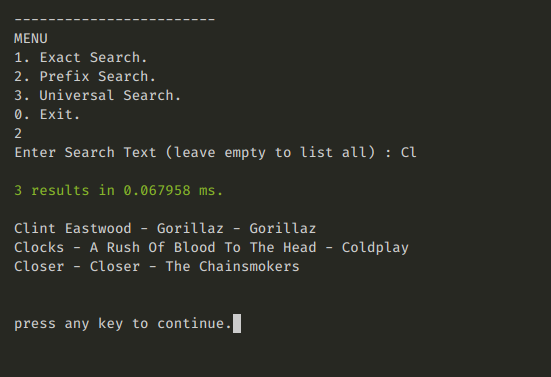
- search for keywords.
- Compile the file
src/main.cppin windows to produce the executable and then run the executable.