Note: you need to install at least ZEsarUX version 8.0
DeZog lets you use Visual Studio Code (vscode) as IDE for ZEsarUX (a ZX Spectrum emulator). With this extension it is possible to debug assembler programs built for the ZX Spectrum. It's primary intention is to support building new programs, i.e. programs with existing assembler source code. (It may also be used without source code to debug binaries but in that case the support is very limited and you could probably better directly debug at ZEsarUX.) The biggest help it offers is that you are able to step through your sources and that DeZog is aware of all labels and can give hints to what label a number resolves.
DeZog connects to ZEsarUX via a socket connection. ZEsarUX offers quite a few commands accessible via socket according to the so-called zrcp (ZEsarUX Remote Control Protocol). See ZEsarUX for more information.
Note: DeZog does not include any support for building from assembler sources. For this you need to create a build task yourself. For an example look here: https://github.com/maziac/z80-sample-program
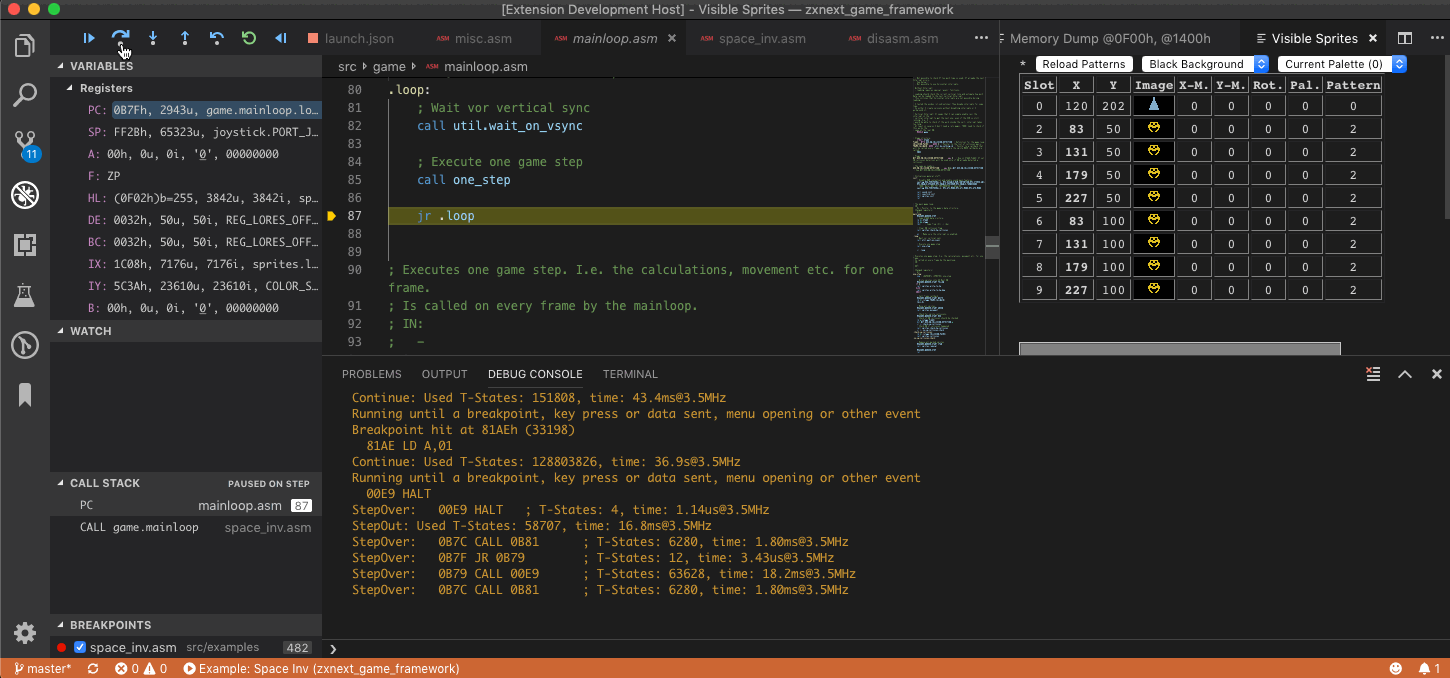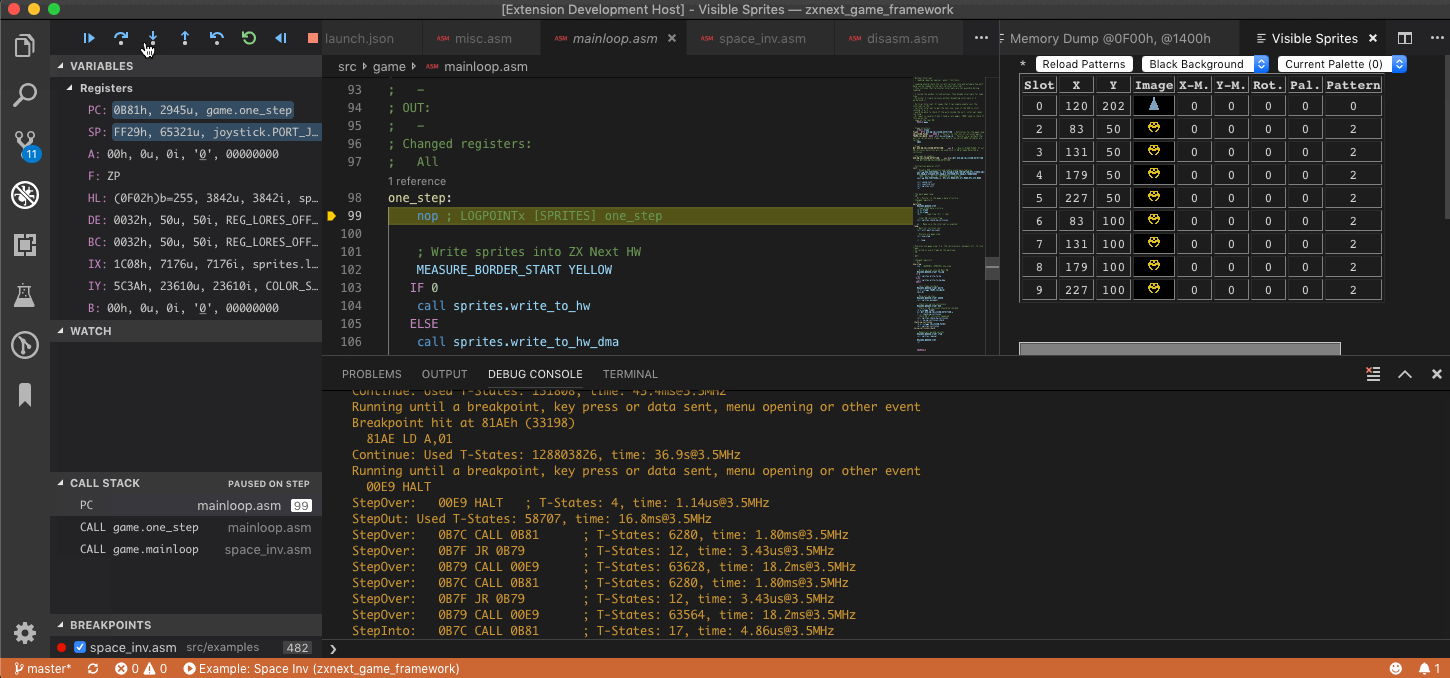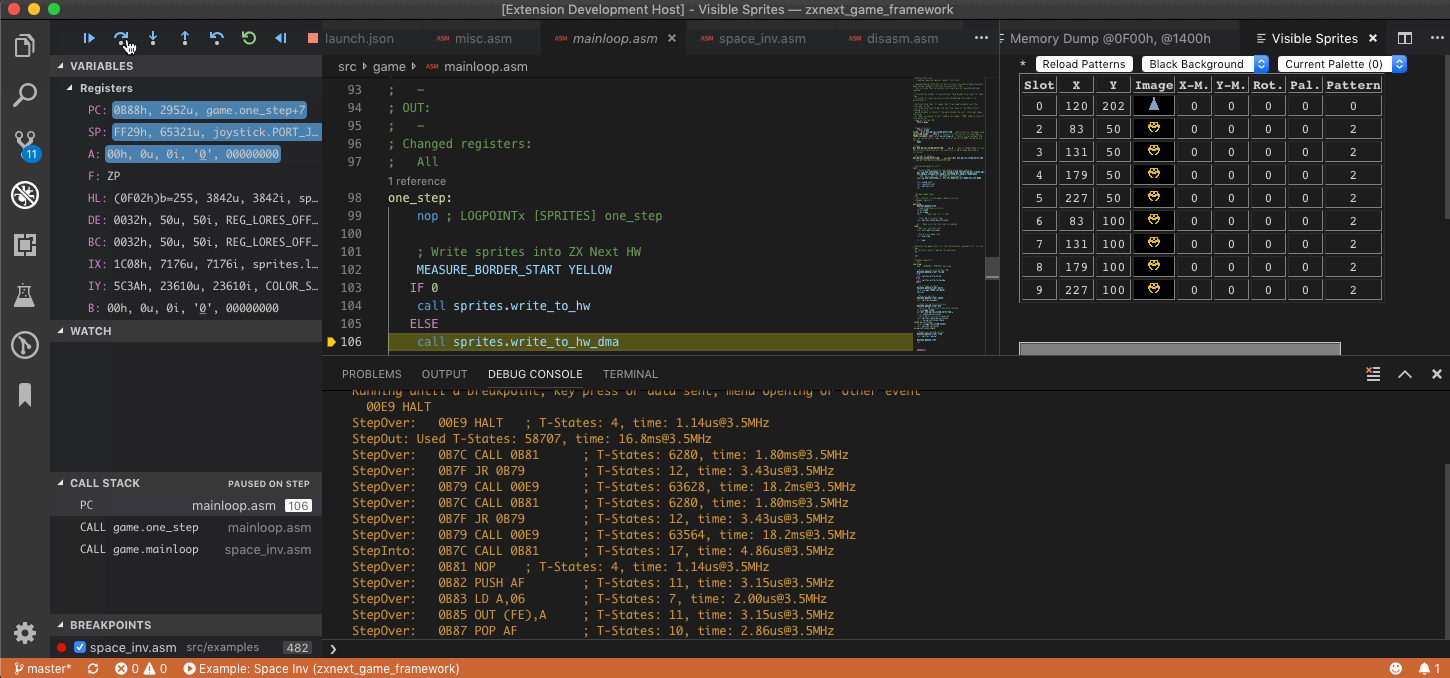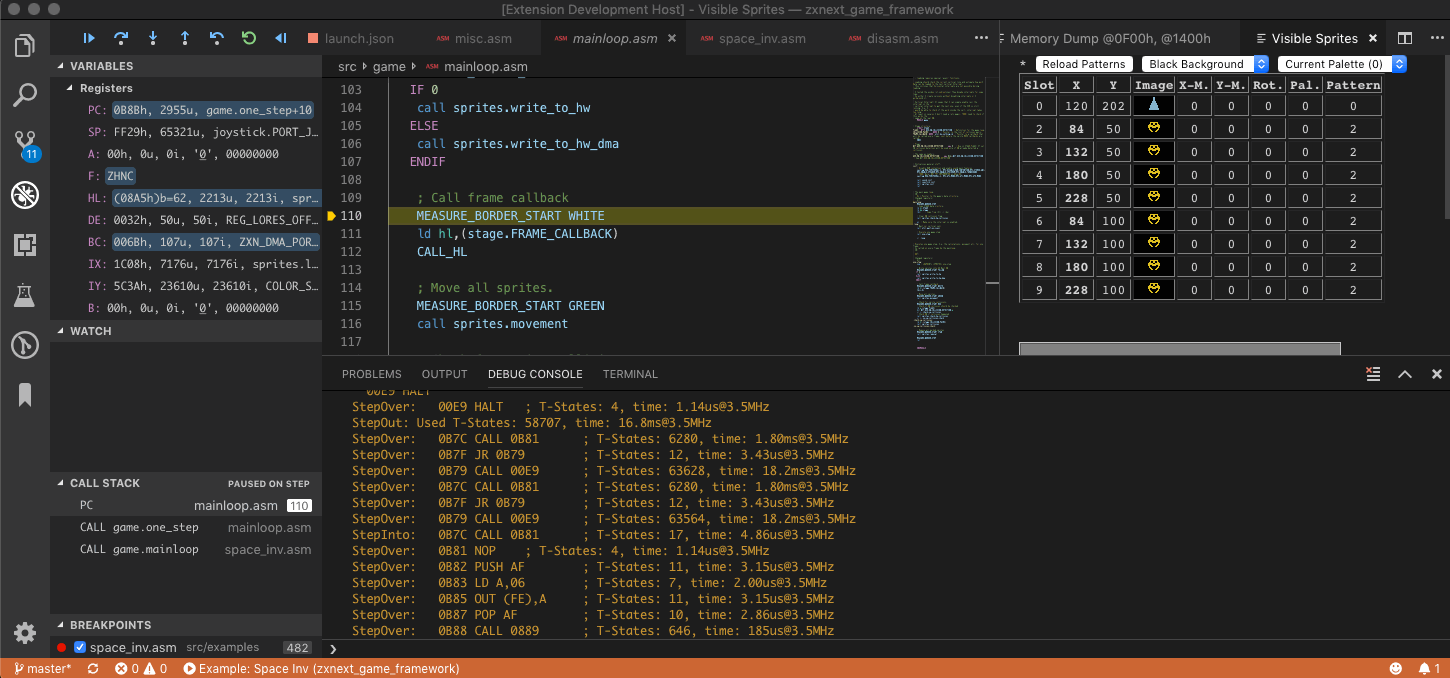
- Display of sprites with register indices and position
- Display of all patterns with indices
- supports ZEsarUX emulator (>= v8.0)
- reads .list files
- supports stepping through source code
- either in .list file or in .asm files
- step-over, step-in, step-out, continue, pause
- reverse debugging via step back and reverse continue
- code coverage visualization
- breakpoints (and breakpoints with conditions)
- display of
- disassembly
- Z80 registers
- stack
- callstack
- tbblue sprites and patterns
- changing of Z80 registers from vscode
- labels
- number-label resolution, i.e. along with numbers also the corresponding label is displayed
- hovering
- registers: reveals its contents and associated label
- labels: reveals their value
- watches of labels
- formatting registers
- customizable formatting for registers, e.g. format as hex and/or decimal and/or label etc.
- different formatting for registers while hovering
- memory viewer / editor
- automatic display of memory that is pointed to by HL, DE, etc.
- change of program counter through menu
- support for assembler unit tests
- supports only ZEsarUX emulator
- build output must
- create a .list file (support for sjasmplus, Savannah's z80asm, z88dk).
- alternatively you can use other list files with limited functionality, please consult the documentation. You can also simply fetch a disassembly of your code from ZEsarUX. Please see the "List file" section in the documentation.
- create a .sna file containing the binary
In order to use DeZog you need
- vscode (of course)
- the ZEsarUX ZX Spectrum emulator (https://github.com/chernandezba/zesarux). At least version 8.0 is required.
In Visual Studio Code simply install "DeZog" (maziac.dezog) from the Marketplace.
There are 2 other extensions that are not required to work with DeZog but may help:
- asm-code-lens:
- Z80 assembler syntax highlighting
- completions, references, jump to label, renaming
- z80-unit-tests:
- an extension to start/debug unit tests from a graphical UI
Both can be installed from the market place.
Please look at the documentation 'Usage of the VS Code Z80 Debug Adapter'.
dezog is licensed under the MIT license.
The source code is available on github.
Here is also a great tutorial from Cesar Wagener Moriana (not to confuse with Cesar Hernandez bano, the autor of ZEsarUX). He documented how he put all things together. If you are new to DeZog this is probably what you want to read to get an integrated development environment for the ZX Spectrum (Next). It deals with setting up
- sjasmplus
- ZEsarUX and the
- DeZog vscode extension
and is available in English, Spain and German here.
Please note: The tutorial uses the bleeding edge sources and therefore shows how to build ZEsarUX. It also uses a previous beta release of z80-debug. As a rule of thumb: if you use the latest ZEsarUX sources or beta releases you should also use the latest z80-debug release from github.
If you instead use the stable release for z80-debug from the market place then you can also use latest stable release for ZEsarUX.
Nevertheless Cesar (W. M.) also shows how to setup the system under Windows and explains a few features of z80-debug so that it is a great advice to get you started.