Datastructure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used effectively.
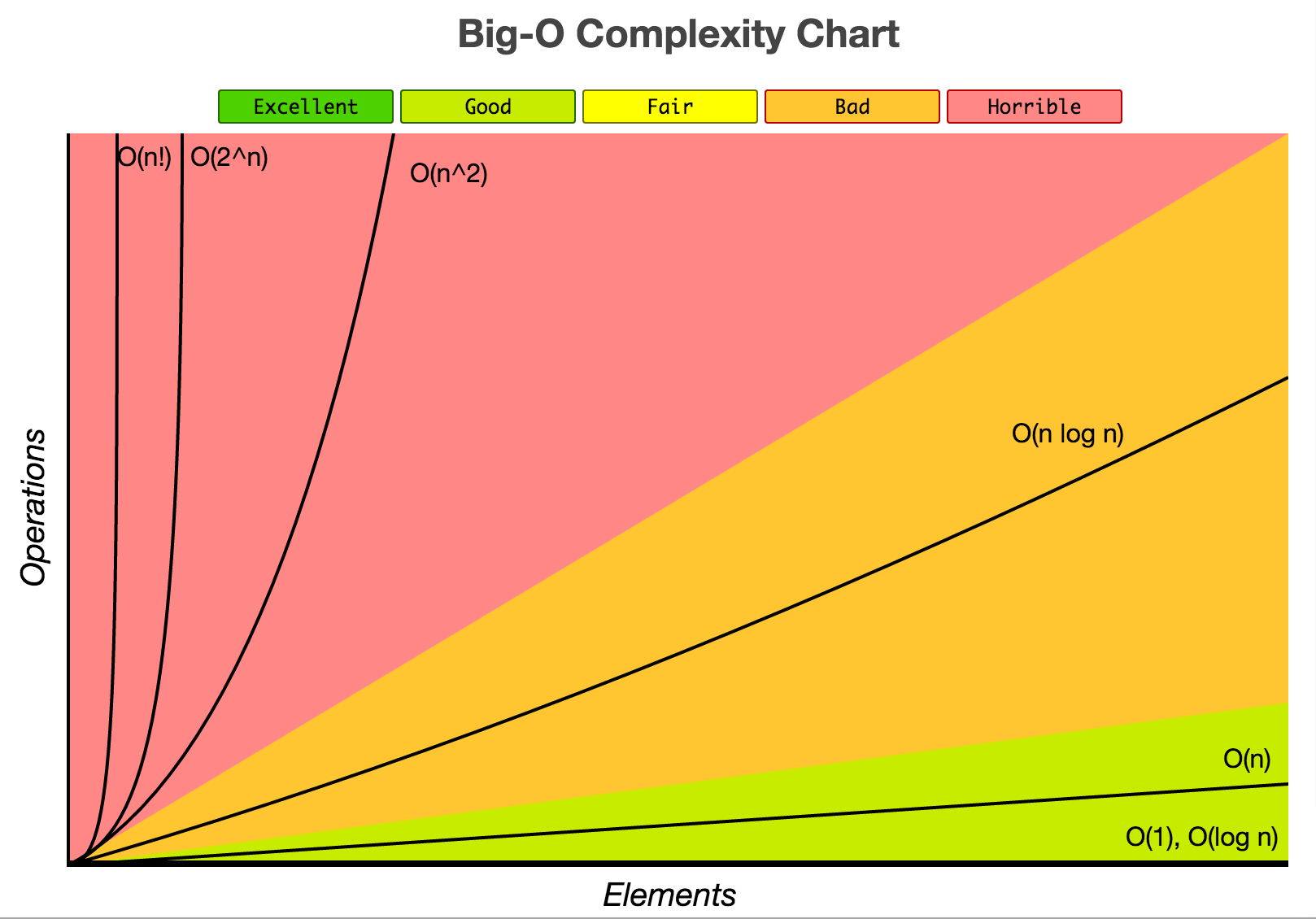
Big O Notation is a way to measure an algorithm's efficiency. It measures the time it takes to run your function as the input grows.
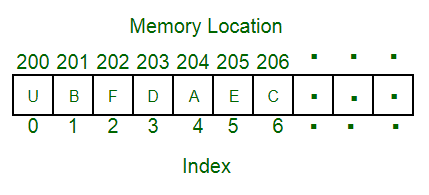
An array is a collection of items of same or different data types stored at contiguous memory locations.
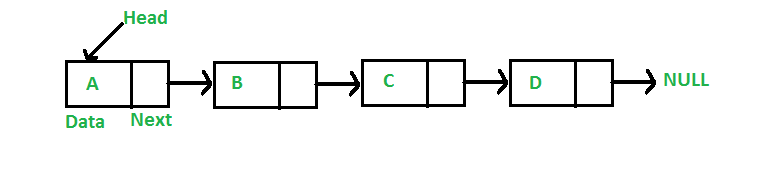
Unlike arrays, linked list elements are not stored at a contiguous location; the elements are linked using pointers. They include a series of connected nodes. Here, each node stores the data and the address of the next node.
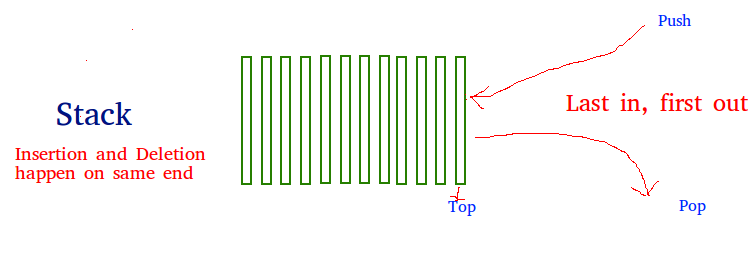
There are many real-life examples of a stack. Consider an example of plates stacked over one another in the canteen. The plate which is at the top is the first one to be removed, i.e. the plate which has been placed at the bottommost position remains in the stack for the longest period of time. So, it can be simply seen to follow LIFO(Last In First Out)/FILO(First In Last Out) order.
A queue is defined as a linear data structure that is open at both ends and the operations are performed in First In First Out (FIFO) order.
We define a queue to be a list in which all additions to the list are made at one end, and all deletions from the list are made at the other end. The element which is first pushed into the order, the operation is first performed on that.
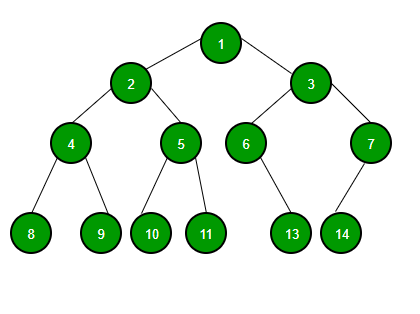
Binary Tree is defined as a Tree data structure with at most 2 children. Since each element in a binary tree can have only 2 children, we typically name them the left and right child.
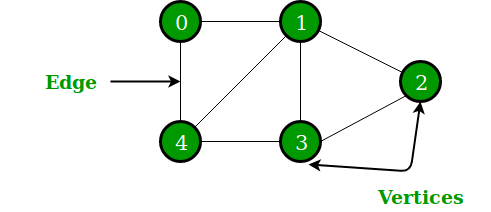
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges. The vertices are sometimes also referred to as nodes and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph. More formally a Graph is composed of a set of vertices( V ) and a set of edges( E ). The graph is denoted by G(E, V).