This is the final project of SJTU-CS337-Computer Graphics.
This doc helps you to get the general idea of the project and run the code. For more details, please refer to our code and this paper.
Although real-time rendering is emerging, high processing latency, high resource demand and specific hardware requirement hinder its further employment. To explore the possibility of rendering image with high performance but low latency and demand, Sparse sampling methods that sample the origin image into sparse grids or patches are considered.
In this project, two sampling methods are proposed and implemented, and they are defined as Sparse-Grid Sampling and Sparse-Patch Sampling, which respectively sample the origin images into sparse grids or sparse patches.
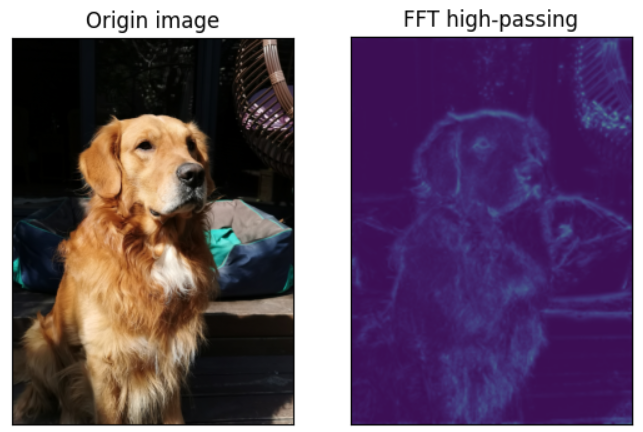
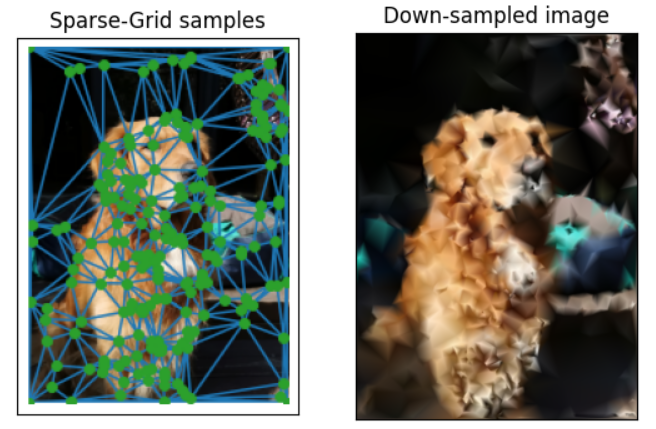
Specifically, both sampling processes are based on FFT high-pass filtering, which is shown in this project to bring excellent down-sampling effect. FFT high-pass filtering is utilized to extract the areas with higher signal frequency (which means more detailed information), and the result is shown in the following figure. (This is the photo of my dog, his name is Rainbow!)
In this process, the regions with more details are sampled with much higher sampling rate, which results in retaining relatively more information of the origin image with the same number of sampling points.
Next, the Delaunay Triangulation algorithm is performed, which generates triangles from the randomly-generated sample points. This results in each pixel’s staying in one and only one triangle, making it possible to set the color of each pixel based on the colors of the vertices of the triangle.
Specifically, the color of each pixel of the LR image is interpolated by the color of each vertex of the triangle, using the barycentric coordinate. The sampling process is shown in the following figure.
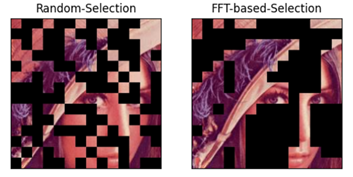
This method follows the procedure of Vision Transformer (ViT). Each image is split into fixed-size patches. In the next step, the patches that contain more detailed information are sampled. The comparison of random and FFT-based strategies is shown in the following figure (the patches that are not selected are depicted as masks).
For each sparse sampling algorithm, a method is designed and implemented in this project in order to obtain the HR origin images based on the sparse samples.
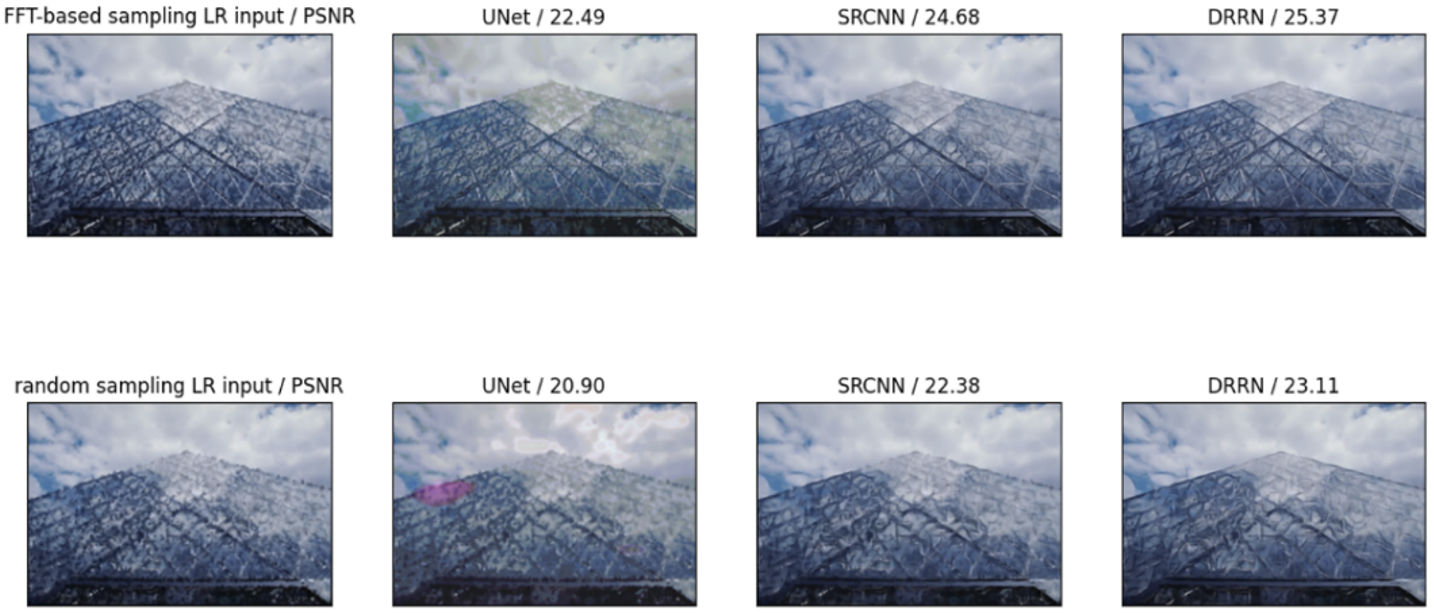
For Sparse-Grid Sampling, the Single Image Super-Resolution (SISR) is performed to obtain the HR images. Three different networks: SRCNN, DRRN and UNet are tested in this project, and DRRN largely outperforms other methods when it comes to the PSNR results.
The comparison of the super-resolution results of each network is shown in the following figures. (10X down-sampling)
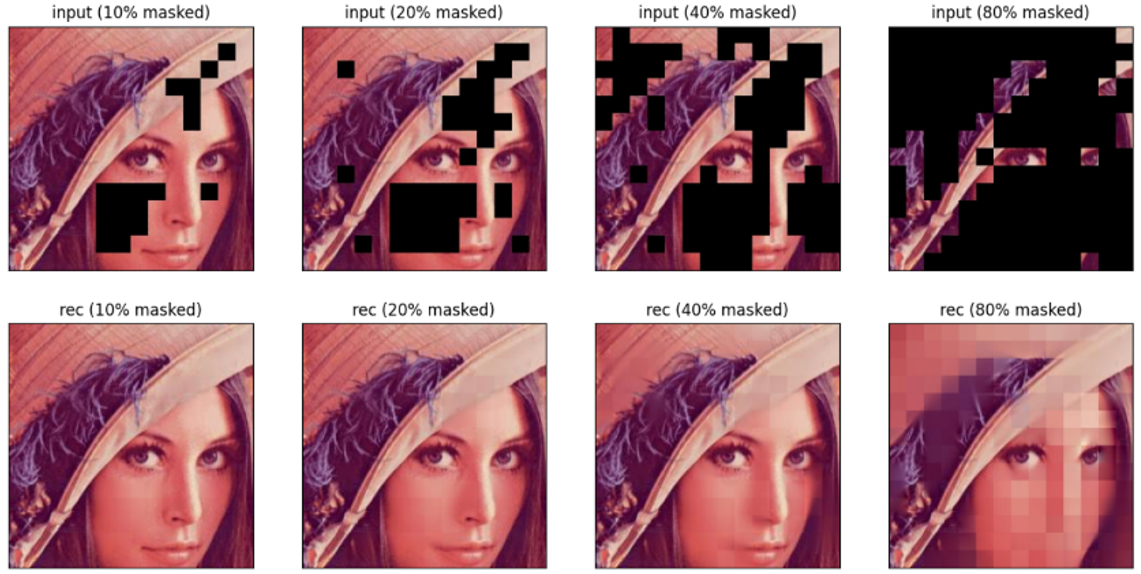
In Sparse-Patch Sampling scenario, the newly-proposed Masked Auto Encoder (MAE) is used to reconstruct the origin image from the sparse sample patches, and it also has great effect for image sparse-patch sampling reconstruction.
In order to compare the reconstruction results, the mask-ratio ranging from 0.1 to 0.9 are adopted. The results of the experiments are shown in the following figures.
pip install -r requirements.txtThe data used can be downloaded from here.
Next, extract the data into the corresponding folder:
unzip data.zip code/Sparse-Grid-Sampling/We also provide a simple way to create your own dataset from any data using the scripts in code/data/scripts.
What you need to is follow 2 simple steps:
-
Create Database
Set the dataset name and train-val-test split in generate_db.ipynb, then execute the whole script.
dataset_name = 'union' # name of the HR image folder split = [0.8, 0.1, 0.1] # train-val-test split
-
Down-sample HR images to LR images
Set method and scale of down-sampling process and direction of HR images in HR2LR.ipynb, then execute the whole script.
FFT = True # whether to use FFT-based down-sampling scale = 10 # down-sampling scale HR_dir="../Set5/" # origin image folder
cd code/Sparse-Grid-Sampling/
sh run_train.shcd code/Sparse-Grid-Sampling/
sh run_test.shcd code/Sparse-Patch-Sampling/
sh run.shSome of the code used in this project are obtained from the following resources, and their hard work are highly appreciated!
- SRCNN: https://github.com/yjn870/SRCNN-pytorch
- DRRN: https://github.com/jt827859032/DRRN-pytorch
- UNet: https://github.com/milesial/Pytorch-UNet
- MAE: https://github.com/pengzhiliang/MAE-pytorch
Group Members:
Mentor: Tianchen Xu