This repository serves as the official code release of the paper Block Convolution: Towards Memory-Efficient Inference of Large-Scale CNNs on FPGA (pubilished at TCAD 2021).
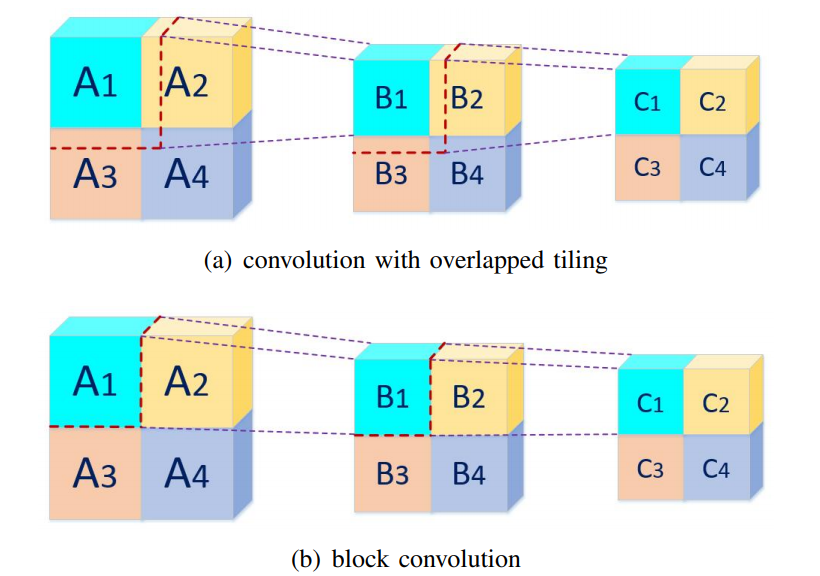
Block convolution is a hardware-friendly, simple, yet efficient convolution operation that can completely avoid the off-chip transfer of intermediate feature maps at runtime. The fundamental idea of block convolution is to eliminate the dependency of feature map tiles in the spatial dimension when spatial tiling is used, which is realized by splitting a feature map into independent blocks so that convolution can be performed separately on individual blocks.
- Python version >= 3.8
- Pytorch version >= 1.8
# create conda environment
conda create -n BlockConv
conda activate BlockConv
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2
pip install torchnet tqdm tabulate gitpython tensorboard
# install from source code
git clone https://github.com/zejiangp/BlockConv.git
cd BlockConv
--arch: block_resnet18, block_resnet50, block_vgg16, block_mobilenet--padding_mode: constant (equal to zero padding), replicate, reflect--type: 0 (Fixed blocking), 1 (hierarchical blocking)
For example, if we want to train a resnet18 with block size 28, fixed blocking mode, and zero padding from scratch, the command as below:
python classification.py \
./data/ilsvrc12 \
--dataset=imagenet \
--out_dir=logs/ \
--gpus=0,1,2,3 \
--arch=block_resnet18\
--name=resnet18_F28_constant_scratch \
--batch_size=128 \
-j=32 \
--epochs=90 \
--lr=0.1 \
--wd=1e-4 \
--momentum=0.9 \
--milestones=30,60 \
--block_size 28,28 \
--padding_mode constant \
--type 0 \
--do_train \
--do_eval
Another way to get a model using block convolution is fine-tuning from the pre-trained model:
python classification.py \
./data/ilsvrc12 \
--dataset=imagenet \
--out_dir=logs/ \
--gpus=0,1,2,3 \
--arch=block_resnet18\
--name=resnet18_F28_constant \
--batch_size=128 \
-j=32 \
--epochs=30 \
--lr=0.001 \
--wd=1e-4 \
--momentum=0.9 \
--milestones=10,20 \
--block_size 28,28 \
--padding_mode constant \
--type 0 \
--resume_from logs/resnet18_baseline.pth.tar \
--reset_optimizer \
--do_train \
--do_eval
| strategy | model | epochs | batch size | learning rate | weight decay | milestones |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training from scratch | resnet18 resnet 50 vgg16 mobilenet |
90 90 105 300 |
128 128 256 128 |
0.1 0.1 0.01 0.0001 |
1e-4 1e-4 5e-4 5e-5 |
30,60 30, 60 30, 60, 90 - |
| Fine-tuning | resnet18 resnet 50 vgg16 mobilenet |
30 30 20 50 |
128 128 256 128 |
0.001 0.001 0.001 0.0001 |
1e-4 1e-4 1e-4 5e-5 |
10, 20 10, 20 8, 16 - |
python classification.py \
./data/ilsvrc12 \
--dataset=imagenet \
--out_dir=test_logs/ \
--gpus=0 \
--arch=block_vgg16 \
--name=test_vgg \
--batch_size=128 \
-j=32 \
--block_size 28,28 \
--padding_mode constant \
--type 0 \
--do_eval \
--resume_from logs/vgg16_finetune_F28_zero.pth.tar
We provide pre-trained models for evaluations here.
- TOP-1 accuracy on ImageNet classification task.
| model | baseline | Scratch | Fine-tuning |
|---|---|---|---|
| vgg16 | 71.59% | 70.47% | 71.45% |
| resnet18 | 70.60% | 69.94% | 71.21% |
| resnet50 | 75.86% | 75.42% | 76.67% |
| mobilenetv1 | 72.29% | 72.05% | 71.76% |
- Top-1 accuracy of blocked networks with respect to blocking ratio under fixed blocking (F) and hierarchical blocking (H).
| model | H2x2 | H4x4 | H8x8 | H16x16 | F112 | F56 | F28 | F14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vgg16 | 70.14% | 70.28% | 70.76% | 71.18% | 71.81% | 71.74% | 71.45% | 70.48% |
| resnet18 | 70.06% | 70.67% | 71.12% | 70.82% | 71.60% | 71.37% | 71.21% | 70.20% |
| mobilenetv1 | 69.96% | 71.49% | 71.53% | 71.50% | 72.16% | 71.89% | 71.76% | 71.13% |
- Impact of block padding on classification accuracy.
| model | zero | replicate | reflect |
|---|---|---|---|
| vgg16 | 71.45% | 70.90% | 70.22% |
| resnet18 | 71.21% | 70.92% | 70.61% |
| resnet50 | 76.67% | 76.71% | 76.47% |
| mobilenetv1 | 71.76% | 71.92% | 71.58% |
If you found the library useful for your work, please kindly cite our work:
@article{Gangli2022BlockConv,
author={Li, Gang and Liu, Zejian and Li, Fanrong and Cheng, Jian},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems},
title={Block Convolution: Toward Memory-Efficient Inference of Large-Scale CNNs on FPGA},
year={2022},
volume={41},
number={5},
pages={1436-1447},
doi={10.1109/TCAD.2021.3082868}
}