📃 Paper • 🤗 Data (CodeActInstruct) • 🤗 Model (CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1) • 🤖 Chat with CodeActAgent!
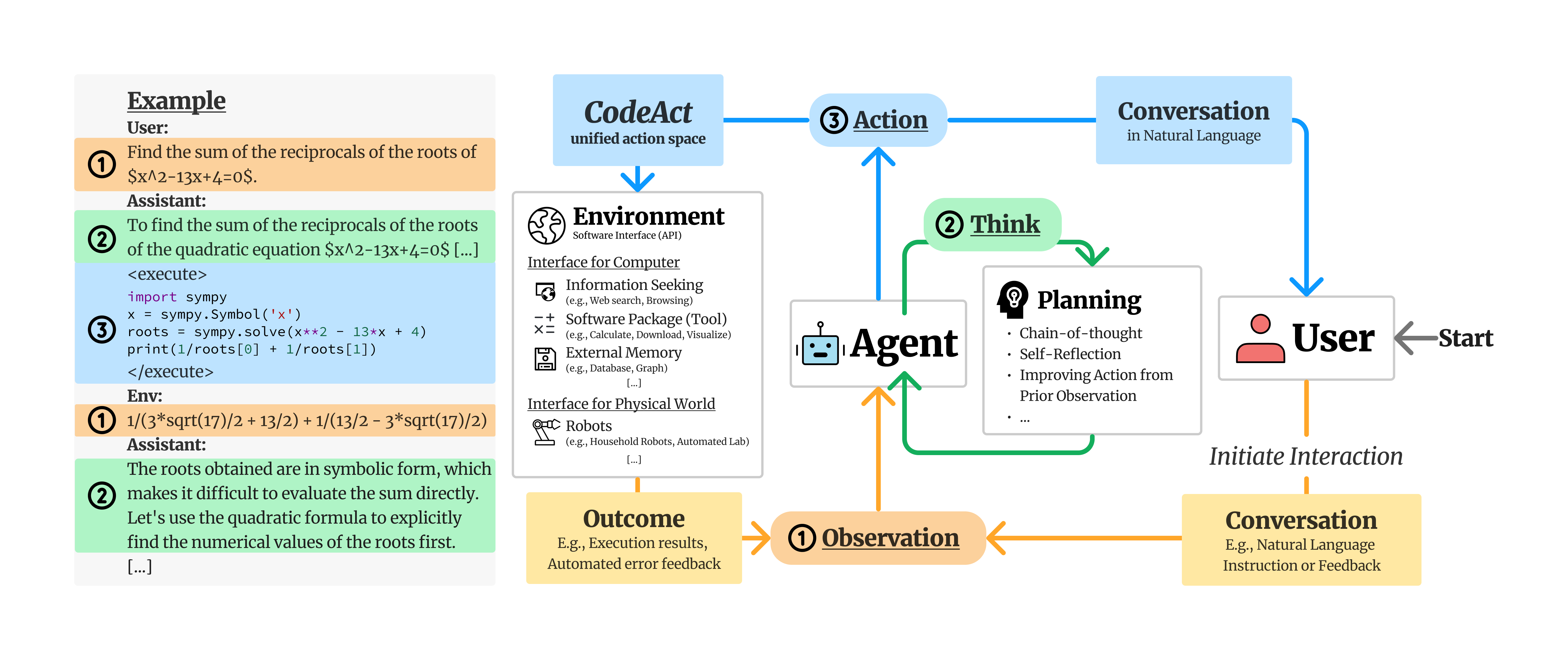
We propose to use executable code to consolidate LLM agents’ actions into a unified action space (CodeAct). Integrated with a Python interpreter, CodeAct can execute code actions and dynamically revise prior actions or emit new actions upon new observations (e.g., code execution results) through multi-turn interactions (check out this example!).
Apr 10, 2024: CodeActAgent Mistral is officially available at ollama!
Mar 11, 2024: We also add llama.cpp support for inferencing CodeActAgent on laptop (tested on MacOS), check out instructions here!
Mar 11, 2024: We now support serving all CodeActAgent's components (LLM serving, code executor, MongoDB, Chat-UI) via Kubernetes ⎈! Check out this guide!
Feb 2, 2024: CodeAct is released!
Our extensive analysis of 17 LLMs on API-Bank and a newly curated benchmark M3ToolEval shows that CodeAct outperforms widely used alternatives like Text and JSON (up to 20% higher success rate). Please check our paper for more detailed analysis!
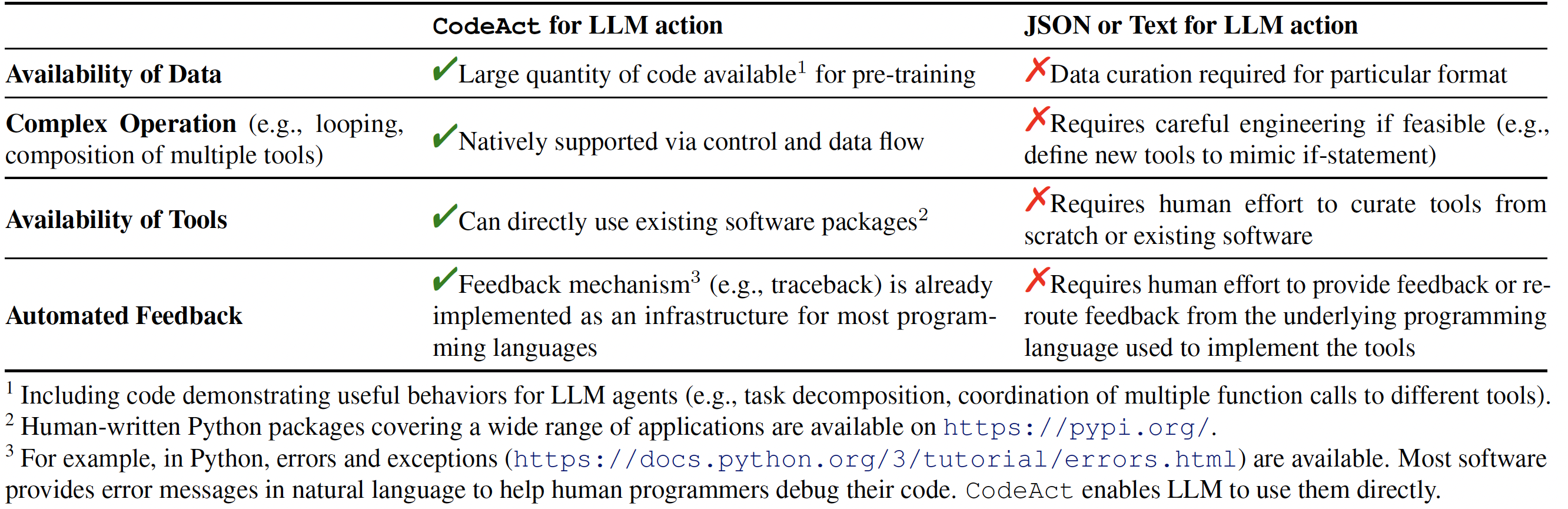 Comparison between CodeAct and Text / JSON as action.
Comparison between CodeAct and Text / JSON as action.
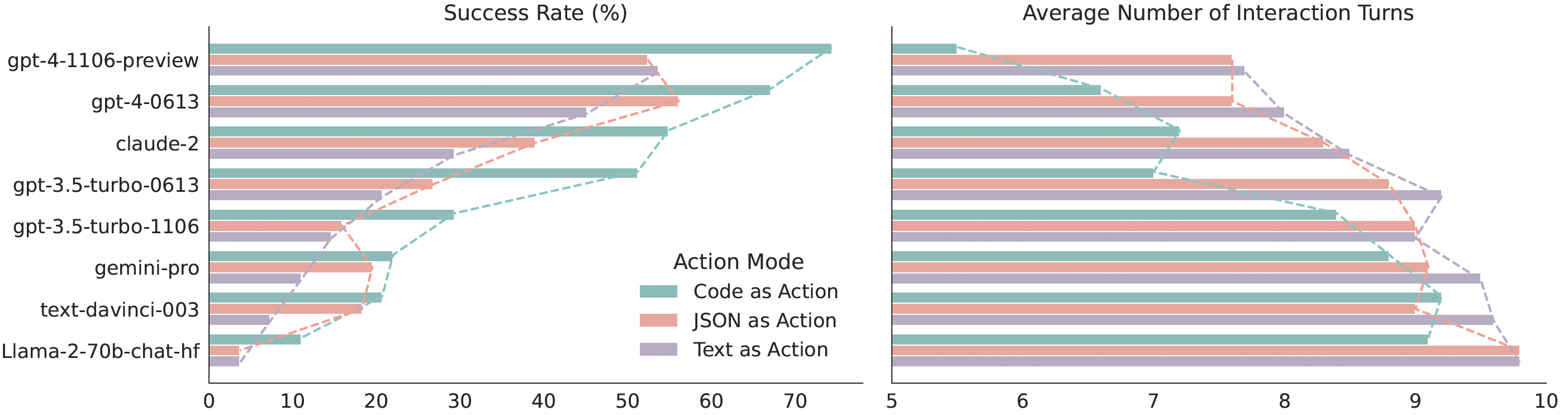 Quantitative results comparing CodeAct and {Text, JSON} on M3ToolEval.
Quantitative results comparing CodeAct and {Text, JSON} on M3ToolEval.
We collect an instruction-tuning dataset, CodeActInstruct, consists of 7k multi-turn interactions using CodeAct. Dataset is release at huggingface dataset 🤗. Please refer to the paper and this section for details of data collection.
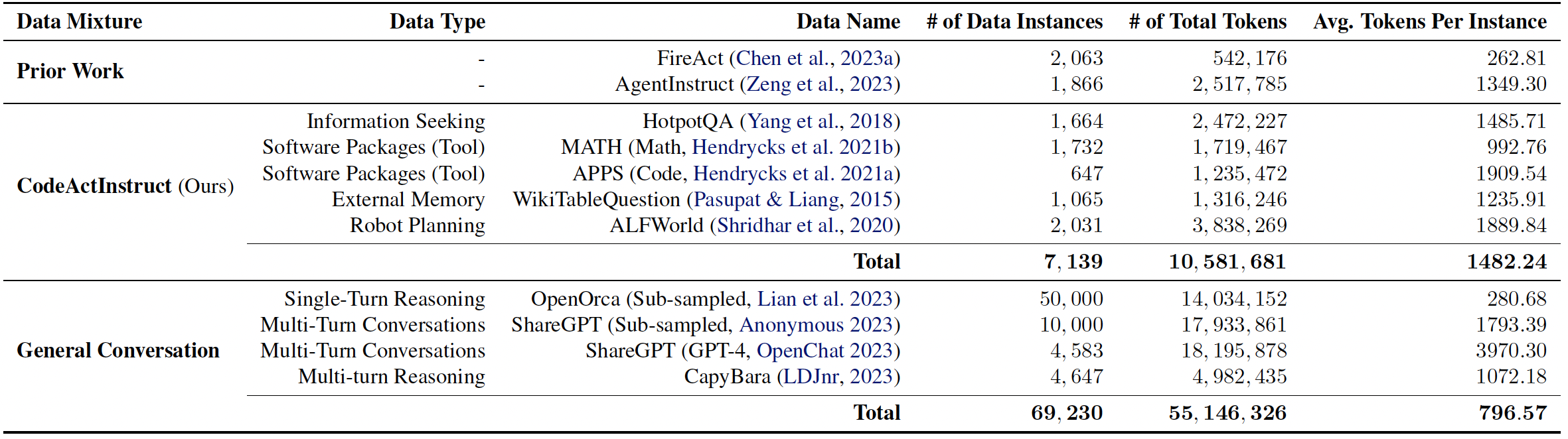 Dataset Statistics. Token statistics are computed using Llama-2 tokenizer.
Dataset Statistics. Token statistics are computed using Llama-2 tokenizer.
Trained on CodeActInstruct and general conversations, CodeActAgent excels at out-of-domain agent tasks compared to open-source models of the same size, while not sacrificing generic performance (e.g., knowledge, dialog). We release two variants of CodeActAgent:
- CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1 (recommended, model link): using Mistral-7b-v0.1 as the base model with 32k context window.
- CodeActAgent-Llama-7b (model link): using Llama-2-7b as the base model with 4k context window.
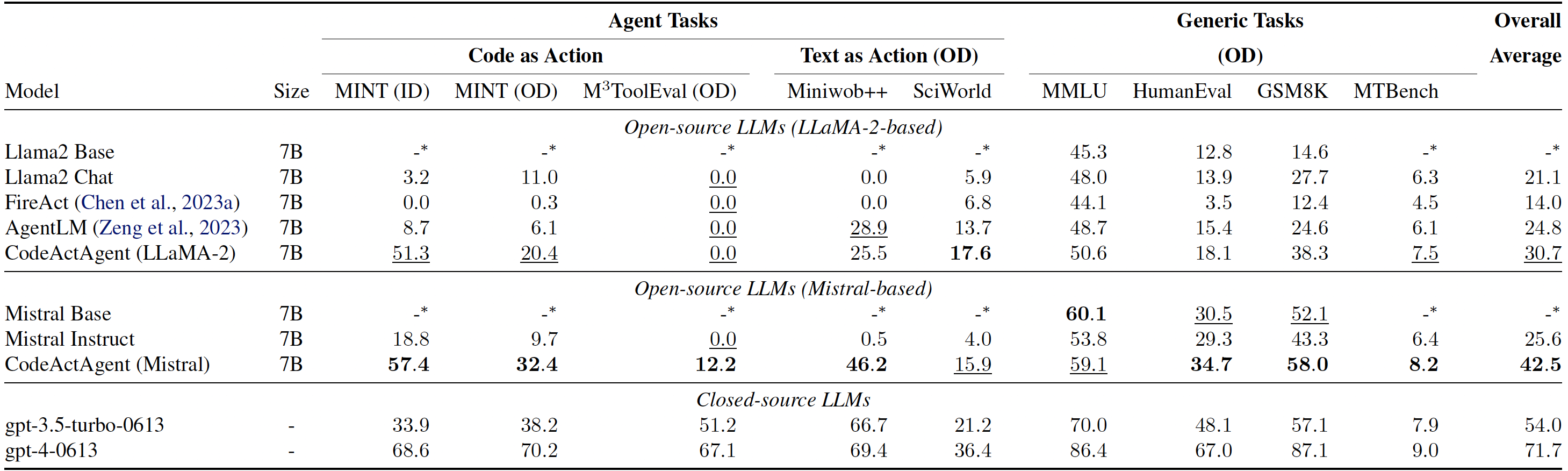 Evaluation results for CodeActAgent. ID and OD correspondingly stand for in-domain and out-of-domain evaluation. Overall averaged performance normalizes the MT-Bench score to be consistent with other tasks and excludes in-domain tasks for fair comparison.
Evaluation results for CodeActAgent. ID and OD correspondingly stand for in-domain and out-of-domain evaluation. Overall averaged performance normalizes the MT-Bench score to be consistent with other tasks and excludes in-domain tasks for fair comparison.
Please check out 📃 our paper for more details about data collection, model training, evaluation, and more!
codeact-demo.mp4
A CodeActAgent system contains the following components:
- LLM Serving: We use vLLM as an example, but any serving software that can serve the model into an OpenAI compatile API should be fine.
- Interaction Interface:
- Code Execution Engine: This service will start an API that accepts code execution requests from Chat-UI or the Python script, then starts an individual docker container to execute code for each chat session.
🌟 If you have access to a Kubernetes cluster: You can follow our Kubernetes setup guide that allows you to spin up all of these components using one command!
Follow the guide below to set up with Docker.
Using VLLM via Docker (requires nvidia-docker)
# You should download the model first, here is an example for CodeActAgent-Mistral
cd $YOUR_DIR_TO_DOWNLOADED_MISTRAL_MODEL
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/xingyaoww/CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1
./scripts/chat/start_vllm.sh $YOUR_DIR_TO_DOWNLOADED_MISTRAL_MODEL/CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1
# OR
# ./scripts/chat_ui/start_vllm.sh $YOUR_DIR_TO_DOWNLOADED_LLAMA_MODEL/CodeActAgent-Llama-7bThis script (docker-required) will start hosting the model based on CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES to port 8080 and you may access the model via OPENAI_API_BASE of http://localhost:8080/v1 (by default). You may check the OpenAI API's official documentation for detailed instruction. You may also check vLLM's official instruction for more information.
This is tested on MacOS (M2 Max, Ventura 13.6).
Install LLama.cpp
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp.git
# optionally create a conda environment for installation
conda create -n llamacpp python=3.10
# Install dependencies for llama cpp
cd llama.cpp
conda activate llamacpp
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Build (refer to https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp?tab=readme-ov-file#build for more details)
make(Optional) Convert Model into gguf Format
OR you can skip the following commands by downloading the pre-converted quantized version (q8_0) here.
# Download the model if you haven't
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/xingyaoww/CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1
# Assume you are in the directory of llama.cpp
python convert.py ./CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1 --outtype f16 --outfile CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.f16.gguf
# (optional) Quantize for faster inference
./quantize CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.f16.gguf CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf Q8_0Serve into OpenAI compatible API
See this for a detailed description of the arguments.
./server -m CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf -c 8192 --port 8080Now you can access the OpenAI compatible server on http://localhost:8080/v1 with model name being CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf. You need to change model name from CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1 to CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf for the interaction interface in the following section (in chat-ui configuration file or in the Python script)!
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions' -d '{
"model": "CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "How to build a website?"}
]
}'We implemented a containerized code execution engine based on JupyterKernelGateway. The idea is to start a Jupyter server inside a docker container per chat session to support code execution request from the model (the session will timeout in a fixed period of time). It requires docker to be installed locally.
# Start a code execution server at 8081
./scripts/chat/code_execution/start_jupyter_server.sh 8081If you don't want to spin up a fancy interface and just want to play with it from the command line, we got you covered!
# Make sure you started model server (vLLM or llama.cpp) and code execution engine before running this!
python3 scripts/chat/demo.py --model_name xingyaoww/CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1 --openai_api_base http://$YOUR_API_HOST:$YOUR_API_PORT/v1 --jupyter_kernel_url http://$YOUR_CODE_EXEC_ENGINE_HOST:$YOUR_CODE_EXEC_ENGINE_PORT/executeIf you've served the model and the code execution engine, you can run your own chat interface just like this!
If you want user management, you may need to start your own mongoDB instance:
./scripts/chat/start_mongodb.sh $YOUR_MONGO_DB_PASSWORD
# The database will be created at `pwd`/data/mongodb and available at localhost:27017Then, you can configure your chat-ui interface.
cp chat-ui/.env.template chat-ui/.env.local
# Make sure you modify .env.local to your configuration by correctly fill-in
# 1. JUPYTER_API_URL
# 2. model endpoint (search for 'TODO_OPENAI_BASE_URL');
# You also need to change the model name to CodeActAgent-Mistral-7b-v0.1.q8_0.gguf if you are using llama.cpp to infer the model
# 3. MONGODB_URL - You may leave this empty, the chat-ui will automatically start a database (but it will be deleted once the container is stopped)Now you can build and start your own web application (docker-required)!
./scripts/chat/run_chat_ui.sh
# It will starts the interface on localhost:5173 by default
# Run this script for debug mode
# ./scripts/chat/run_chat_ui_debug.shFor more information (e.g., if you don't want to use docker), please check-out chat-ui's documentation!
git clone https://github.com/xingyaoww/code-act
# To clone all submodules
git submodule update --init --recursiveRecommended: You may download the processed CodeActInstruct from huggingface dataset 🤗.
For reproducibility: You can optionally generate data follow instructions in docs/DATA_GENERATION.md to generate interaction data.
We use a fork of Megatron-LLM for training. You can follow docs/MODEL_TRAINING.md for detailed instructions.
Please refer to docs/EVALUATION.md for detailed instruction.
@inproceedings{wang2024executable,
title={Executable Code Actions Elicit Better LLM Agents},
author={Xingyao Wang and Yangyi Chen and Lifan Yuan and Yizhe Zhang and Yunzhu Li and Hao Peng and Heng Ji},
year={2024},
eprint={2402.01030},
booktitle={ICML}
}