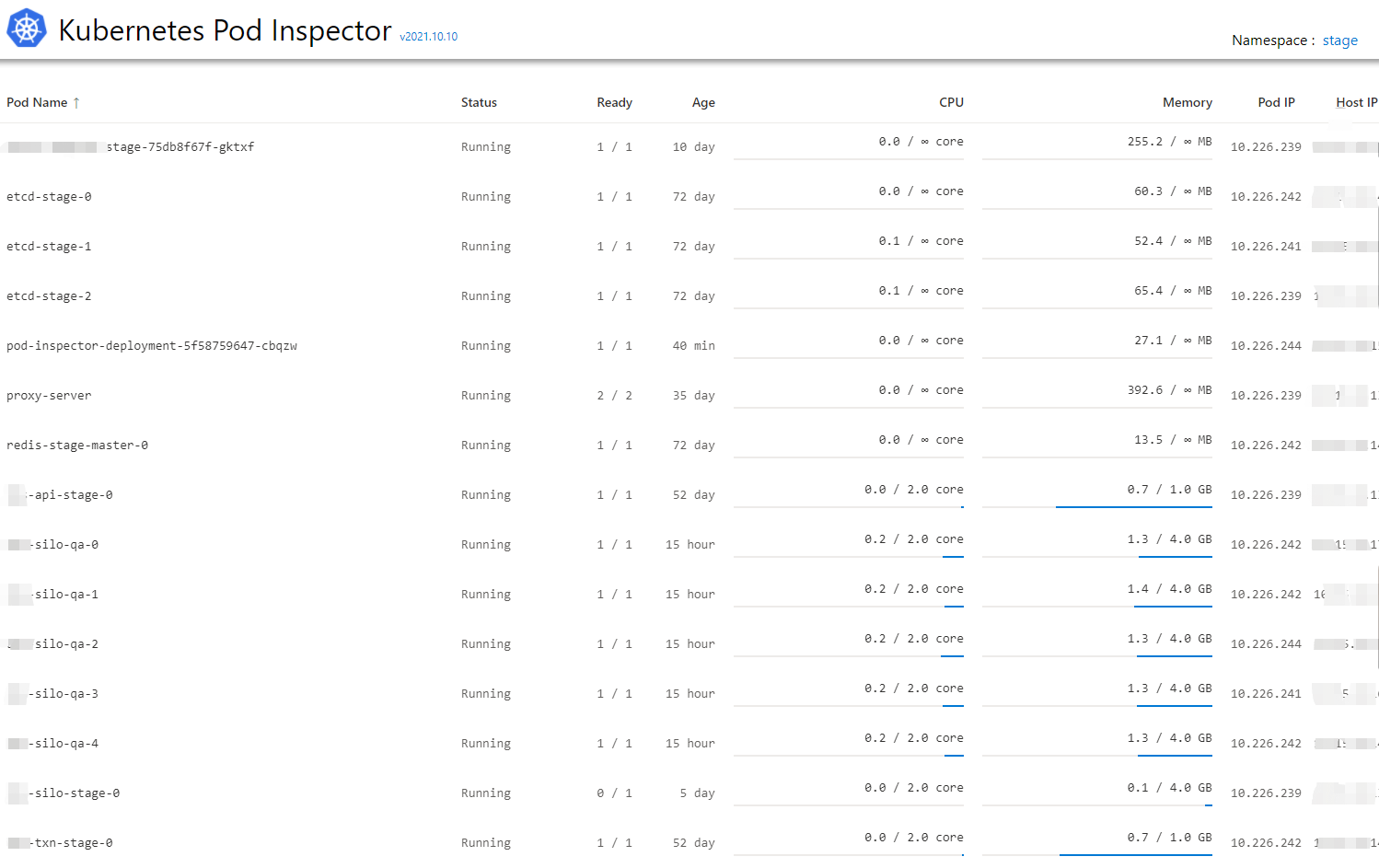
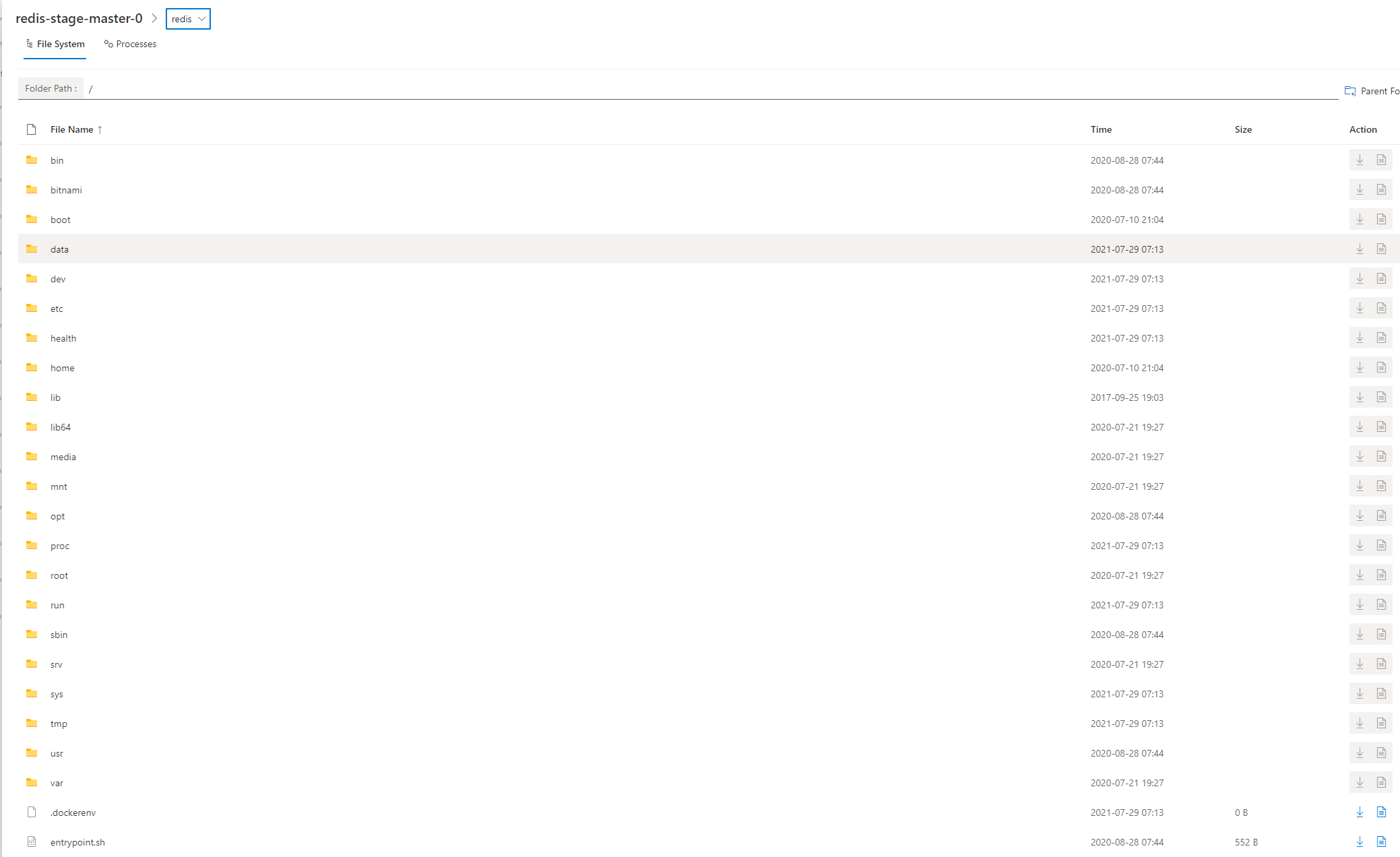
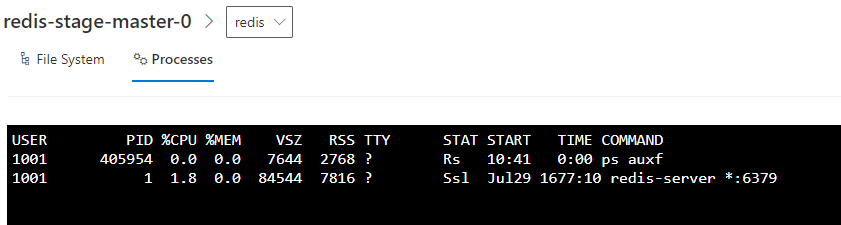
Unlike other dashboardes for Kubernetes(Lens / Rancher / etc), Kubernetes Pod Inspector allows to check the file system and processes within running Linux pods without using kubectl. This is useful when we want to check the files within volumes mounted by pods
The docker image is available at docker.io/wangjia184/pod-inspector. Typically, it can be deployed into K8S cluster with following yaml.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pod-inspector-deployment
labels:
app: pod-inspector
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: pod-inspector
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: pod-inspector
spec:
containers:
- name: pod-inspector
image: docker.io/wangjia184/pod-inspector:latest
args: ["-port", "8080", "-user", "", "-password", ""]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: K8S_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: NODE_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name']
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
imagePullPolicy: AlwaysIt listens on port 8080 for HTTP service. You can specify user and password in arguments to enable http authentication.
Next, expose port 8080 so that you can access it. Here is an example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: pod-inspector
spec:
selector:
app: pod-inspector
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: pod-inspector
spec:
rules:
- host: your.kubernetes.cluster.domain-name.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: pod-inspector
port:
number: 80
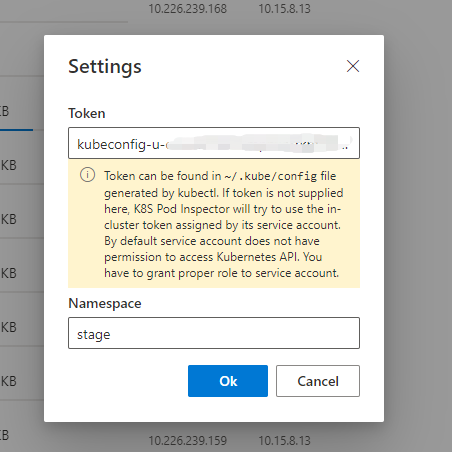
Finally you should be able to access the web site. By filling the token and namespace of K8S cluster, it will connect to the same cluster the pod is running. Token can be retrieved in ~/.kube/config file.
If your cluster uses RBAC, you can also run the inspector with a dedicated service account and grant proper roles in order to use in-cluster token assigned from the service account. Here is an example to create the service account and its role.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: pod-inspector
automountServiceAccountToken: true
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: pod-inspector
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: ["metrics.k8s.io"]
resources: ["pods", "nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: inspect-pods
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: pod-inspector # service account name
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-inspector # role name
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioThen specifiy the service account in your pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: pod-inspector-deployment
labels:
app: pod-inspector
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: pod-inspector
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: pod-inspector
spec:
serviceAccountName: pod-inspector # service account
containers:
- name: pod-inspector
image: docker.io/wangjia184/pod-inspector:latest
args: ["-port", "8080", "-user", "admin", "-password", "654321"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: K8S_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: NODE_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name']
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
imagePullPolicy: Always