eptune (evolutionary parameter tuning) is a python package trying to use evolutionary computation algorithms to do parameter tuning.
pip install eptune
Using following lines can fine tune MNIST dataset with 5-Fold CV performance using the qtuneSimple function.
from eptune.sample_cases import DigitsCV
from eptune.quick import qtuneSimple
from eptune.parameter import *
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Prameter space to search
params = [
LogFloatParameter([0.01, 1e4], 'C'),
CategoricalParameter(['rbf'], 'kernel'),
LogFloatParameter([1e-6, 1e4], 'gamma')
]
# Define objective function
cv_svc_digits = DigitsCV(SVC())
def evaluate(params):
return cv_svc_digits.cv_loss_with_params(cv=5, **params)
# Call `qtuneSimple`
population, logbook, hof = qtuneSimple(params,
evaluate,
n_pop=10,
n_jobs=10,
mutpb=0.6,
cxpb=0.8,
seed=42)
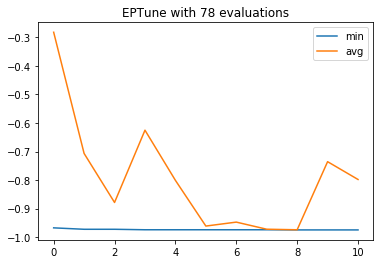
# Plot the logbook if needed
fig = logbook.plot(['min', 'avg'])gen nevals avg std min max
0 10 [-0.28174736] [0.3288165] [-0.96772398] [-0.10072343]
1 7 [-0.70684474] [0.36593114] [-0.97273233] [-0.10072343]
2 4 [-0.8786867] [0.2590384] [-0.97273233] [-0.10183639]
3 8 [-0.62526433] [0.41696083] [-0.97440178] [-0.10072343]
4 8 [-0.80116861] [0.34319099] [-0.97440178] [-0.10072343]
5 6 [-0.96143573] [0.0257779] [-0.97440178] [-0.89816361]
6 7 [-0.9475793] [0.06357501] [-0.97440178] [-0.75959933]
7 6 [-0.97250974] [0.00531551] [-0.97440178] [-0.95659432]
8 7 [-0.97445743] [0.00016694] [-0.97495826] [-0.97440178]
9 8 [-0.73567056] [0.36697176] [-0.97495826] [-0.10072343]
10 7 [-0.79810796] [0.34639554] [-0.97495826] [-0.10072343]
The best parameters are stored in HallofFame object:
hof[({'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.0005362324820364681}, (-0.9749582637729549,)), ({'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}, (-0.9744017807456873,))]
An iterator interface, qtuneIterate, is provided in the quick module, so that one can treat the optimization procedure as a iterative process. When the iterator exhausted, the optimization process is ended. Following is an example:
from eptune.quick import qtuneIterate
from eptune.parameter import *
# Prameter space to search
params = [
LogFloatParameter([0.01, 1e4], 'C'),
CategoricalParameter(['rbf'], 'kernel'),
LogFloatParameter([1e-6, 1e4], 'gamma')
]
qi = qtuneIterate(params, n_pop=10, mutpb=0.6, cxpb=0.8, seed=42)Directly call this class will return an object that can be used as an iterator.
iterator = qi()For each iteration, the iterator will return two elements. The first element is the parameters to be used to in the estimator or function, the other element is the Condition object used in qtuneIterate.set_result function.
p, c = next(iterator)
p{'C': 68.63739474770763, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 26.031847870785032}
One can do what ever you want here, such as query database, download web page, or even ask for user's input. When all the things necessary are done, one need to call qtuneIterate.set_result to return the control to the package and generate next parameters for next iteration.
In this example, the same function in above example is used to get the loss of the estimator with above parameters.
from eptune.sample_cases import DigitsCV
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Define objective function
cv_svc_digits = DigitsCV(SVC())
def evaluate(params):
return cv_svc_digits.cv_loss_with_params(cv=5, **params)
loss = evaluate(p)
loss([-0.10072342793544797], [])
After we get the loss value, we can use qtuneIterate.set_result to return the control to the package as follows:
qi.set_result(loss, c)p, c = next(iterator)
p{'C': 0.2946803132334556, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 23.15859147163727}
Repeat this process until the iterator is exhausted, then the optimization is done. In practice, you can simply use a for loop to do the job.
qi = qtuneIterate(params, n_pop=10, mutpb=0.6, cxpb=0.8, ngen=3, seed=42)
for p, c in qi():
print(f'Calculating loss for {p}')
loss = evaluate(p)
print(f'Loss is {loss[0]}')
qi.set_result(loss, c)Calculating loss for {'C': 68.63739474770763, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 26.031847870785032}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.2946803132334556, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 23.15859147163727}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 114.8674353163588, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.803387600412278}
Loss is [-0.12186978297161936]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.015513010158735236, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00015359594420534672}
Loss is [-0.1580411797440178]
Calculating loss for {'C': 10.767917726598592, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.40968553409851616}
Loss is [-0.1018363939899833]
Calculating loss for {'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00016010548864384288}
Loss is [-0.9677239844184753]
Calculating loss for {'C': 34.3237004592151, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 38.732334272432226}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.09077283474940925, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.002526417757312348}
Loss is [-0.9070673344462994]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.08567951488560228, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 1.0522108244005219e-05}
Loss is [-0.1580411797440178]
Calculating loss for {'C': 1.9035478743608165, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 298.49953812653837}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
gen nevals avg std min max
0 10 [-0.28174736] [0.3288165] [-0.96772398] [-0.10072343]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.09077283474940925, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.002526417757312348}
Loss is [-0.9070673344462994]
Calculating loss for {'C': 1140.5426263798747, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 2.094124216624722e-06}
Loss is [-0.9476905954368392]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.18445781569344738, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 1.0522108244005219e-05}
Loss is [-0.19031719532554256]
Calculating loss for {'C': 2.364783608235729, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}
Loss is [-0.9727323316638843]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.3770940250090288, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 9402.812584317955}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 342.52552858536734, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 3.979422189106964e-05}
Loss is [-0.9538119087367836]
Calculating loss for {'C': 37.612358782164776, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.002526417757312348}
Loss is [-0.9632721202003339]
1 7 [-0.70684474] [0.36593114] [-0.97273233] [-0.10072343]
Calculating loss for {'C': 25.359556967494015, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 1.0522108244005219e-05}
Loss is [-0.9515859766277128]
Calculating loss for {'C': 90.88766299120877, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.18912018070990808}
Loss is [-0.1018363939899833]
Calculating loss for {'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00016010548864384288}
Loss is [-0.9677239844184753]
Calculating loss for {'C': 2.364783608235729, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}
Loss is [-0.9727323316638843]
2 4 [-0.8786867] [0.2590384] [-0.97273233] [-0.10183639]
Calculating loss for {'C': 6.340857718335152, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 6944.6779969379}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 1.085964509751384, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 7.981583922628336e-05}
Loss is [-0.9437952142459655]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.4691058706709815, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 410.66817442961525}
Loss is [-0.10072342793544797]
Calculating loss for {'C': 9901.359072553396, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}
Loss is [-0.9744017807456873]
Calculating loss for {'C': 2.364783608235729, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00016010548864384288}
Loss is [-0.9593767390094602]
Calculating loss for {'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}
Loss is [-0.9744017807456873]
Calculating loss for {'C': 0.191638955526857, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 1.050881589158487e-06}
Loss is [-0.15748469671675014]
Calculating loss for {'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 9.24517286607817}
Loss is [-0.10127991096271564]
3 8 [-0.62526433] [0.41696083] [-0.97440178] [-0.10072343]
After the iteration, the qtuneIterate instance store the results in itself.
qi.population[{'C': 6.340857718335152, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 6944.6779969379},
{'C': 1.085964509751384, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 7.981583922628336e-05},
{'C': 0.4691058706709815, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 410.66817442961525},
{'C': 9901.359072553396, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496},
{'C': 2.364783608235729, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00016010548864384288},
{'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496},
{'C': 0.191638955526857, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 1.050881589158487e-06},
{'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 9.24517286607817},
{'C': 2.364783608235729, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496},
{'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00016010548864384288}]
qi.hof[({'C': 197.75053974020003, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}, (-0.9744017807456873,)), ({'C': 9901.359072553396, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'gamma': 0.00044545277111534496}, (-0.9744017807456873,))]
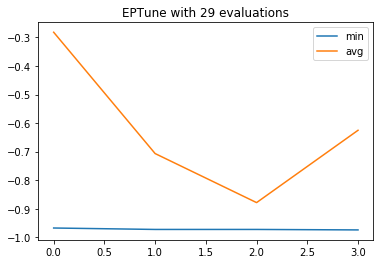
fig = qi.logbook.plot(['min', 'avg'])If you want more control, you can check:
eptune.sklearnmodule providesScikitLearnerorScikitLearnerCVfor fine tune parameter of estimators with scikit learn API. Examples are also provided in the documentation.eptune.algorithmsmodule provides algorithms to access the DEAP framework directly.