This is the online appendix of our paper accepted at the Data Showcase track at MSR 2018. It provides additional information to our dataset, how to build and run our toolchain to collect the data, and a link to our database dump.
- Database Dump
- Entity Relationship Diagram
- Tables
- Example Queries
- Run Instructions
- Build Instructions
A compressed database dump (~1.5 GB) is available here. Use gunzip -c msr18_docker_dataset.sql.gz | psql dbname to decompress and import into a database named dbname.
Note: the database requires ~25 GB of storage.
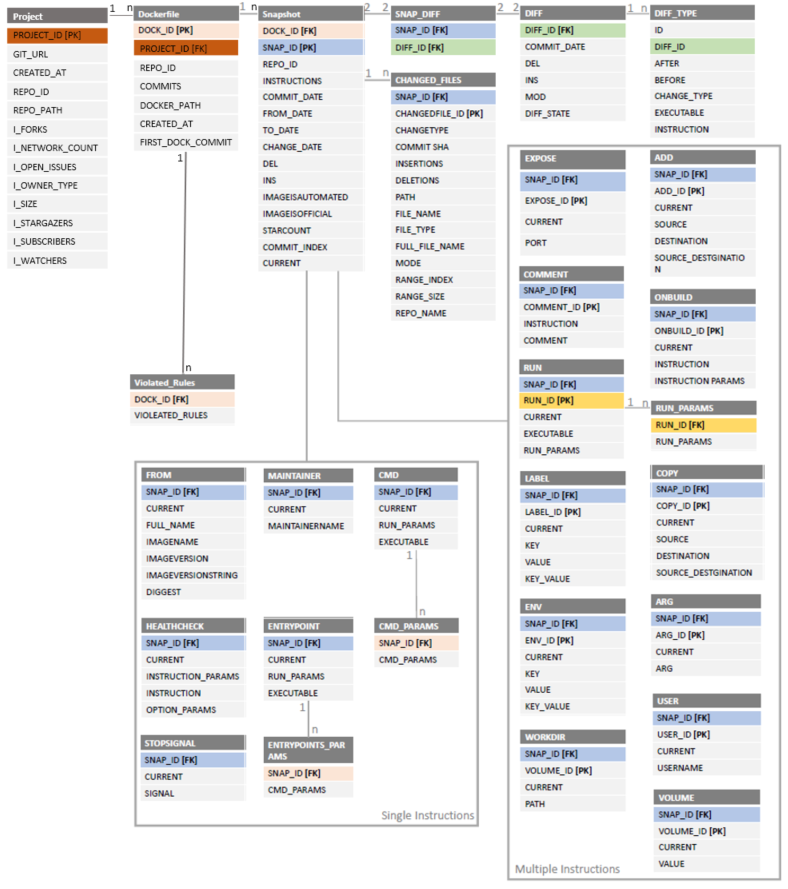
Here you find a simplified entity relationship diagram of our data model. Due to space reasons and to foster readability we omitted some links to single instruction and multiple instructions tables. As the name implies, a single Snapshot can have a single link to a single-instruction table (e.g., Entrypoint, CMD). In addition, all links to a multiple-instruction table are of the form one to many, (i.e., a Snapshot can have multiple RUN instructions).
In the following you will find descriptions of tables, for a comprehensive overview we refer to the attached ERD and a SQL schema (file schema.sql).
Each Git Repository is modelled as a Project and includes meta information about the project (number of followers, forks etc.)
A Project includes one or more Dockerfiles. A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could execute on the command line to assemble an image.
A Snapshot represents a state of a Dockerfile at a certain time, i.e., if a Dockerfile has been changed 8 times, then there will be 8 snapshots. Basically, a Snapshot can be seen as a "Commit".
Each Snapshot has two Diffs. The first Diff connects the old Snapshot with the current one, and the second one connects the current one with the new one. Basically, a Diff is the "Transition" of one Snapshot to a newer one. A Diff contains one or more Diff_Types.
DiffType show what type of change have been done on a Snapshot. It includes the old and new state as a string.
###################################################################################################################################
##1. Dependencies
###################################################################################################################################
##[1] Most frequent used ports
SELECT port, count(port)
FROM df_expose
WHERE current = true
GROUP BY port
ORDER BY count DESC
##[2] How often do dependencies change
SELECT *
FROM diff_type NATURAL JOIN diff NATURAL JOIN snap_diff NATURAL JOIN snap_id
WHERE change_type LIKE '%Updat%' AND instruction = 'RUN'
##[3.1] Which images are preferred
SELECT imagename, count(imagename)
FROM df_from
WHERE current = true
GROUP BY imagename
ORDER BY count DESC
##[3.2] Which image versions are preferred (NUMERIC)
SELECT imageversionnumber, count(imageversionnumber)
FROM df_from
WHERE current = true
GROUP BY imageversionnumber
ORDER BY count DESC
##[3.3] Which image versions are preferred (NOMINAL)
SELECT imageversionstring, count(imageversionstring)
FROM df_from
WHERE current = true
GROUP BY imageversionstring
ORDER BY count DESC
##[4] How many images use the :latest tag?
SELECT imageversionnumber, count(imageversionnumber)
FROM df_from
WHERE current = true
GROUP BY imageversionnumber
ORDER BY count DESC
##[5] Which parameters are most frequently used in RUN instructions?
SELECT run_params, count(run_params)
FROM run_params
GROUP BY run_params
ORDER BY count DESC
##[5] Top RUN instructions
SELECT executable,count(executable), run_params
FROM df_run df NATURAL JOIN run_params rp
WHERE df.current=true
GROUP BY executable, run_params
ORDER BY count(executable) DESC
###################################################################################################################################
##2. Churn and Co-Evolution
###################################################################################################################################
##[1] How often do Dockerfiles change (average)
SELECT avg(count)
FROM (
SELECT dock_id, count(*)
FROM dockerfile NATURAL JOIN snapshot
GROUP BY dock_id) s
##[2] How many times do Dockerfiles change with other files?
SELECT avg(count)
FROM(
SELECT dock_id, count(dock_id)
FROM(SELECT s.snap_id, s.dock_id, count(s.snap_id)
FROM snapshot s NATURAL JOIN changed_files c
WHERE c.range_index = 0
GROUP BY s.snap_id
ORDER BY count ASC) g NATURAL JOIN dockerfile
WHERE g.count = 1
GROUP BY dock_id) f
SELECT avg(count)
FROM(
SELECT dock_id, count(dock_id)
FROM(SELECT s.snap_id, s.dock_id, count(s.snap_id)
FROM snapshot s NATURAL JOIN changed_files c
WHERE c.range_index = 0
GROUP BY s.snap_id
ORDER BY count ASC) g NATURAL JOIN dockerfile
WHERE g.count > 1
GROUP BY dock_id) f
##[2.1] Which changes are made when a Dockerfile changes alone
SELECT change_type, count(change_type)
FROM(
SELECT s.snap_id, s.dock_id, count(s.snap_id)
FROM snapshot s NATURAL JOIN changed_files c
WHERE c.range_index = 0
GROUP BY s.snap_id
ORDER BY count ASC) f NATURAL JOIN snap_diff NATURAL JOIN diff NATURAL JOIN diff_type
WHERE diff_state = 'COMMIT_COMMIT'
GROUP BY change_type
ORDER BY count DESC
##[2.1] Which changes are made when a Dockerfile changes together with other files
SELECT change_type, count(change_type)
FROM(
SELECT s.snap_id, s.dock_id, count(s.snap_id)
FROM snapshot s NATURAL JOIN changed_files c
WHERE c.range_index > 1
GROUP BY s.snap_id
ORDER BY count ASC) f NATURAL JOIN snap_diff NATURAL JOIN diff NATURAL JOIN diff_type
WHERE diff_state = 'COMMIT_COMMIT'
GROUP BY change_type
ORDER BY count DESC
##[3] Which files and file types are changed when a Dockerfile is changed?
SELECT full_file_name, count(full_file_name)
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 0
GROUP BY full_file_name
ORDER BY count DESC
SELECT file_type, count(file_type)
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 0
GROUP BY file_type
ORDER BY count DESC
##[9] Which files are changed within a certain range_index?
SELECT full_file_name
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = -1
INTERSECT
SELECT full_file_name
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 0
INTERSECT
SELECT full_file_name
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 1
INTERSECT
SELECT full_file_name
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 2
##[10] How many files change in average together with a Dockerfile (index= 0)
SELECT avg(snap_id)
FROM (
SELECT snap_id, count(snap_id)
FROM changed_files
WHERE range_index = 0
GROUP BY snap_id
ORDER BY count(snap_id) DESC ) s
##[11] List of most changed instructions
SELECT instruction, count(instruction)
FROM diff_type
WHERE change_type LIKE '%Update%'
GROUP BY instruction
ORDER BY count(instruction) DESC
##[12] How many commits per year and per month
SELECT count(*), date_trunc('year', to_timestamp(commit_date)) s
from snapshot
group by date_trunc( 'year', to_timestamp(commit_date) )
ORDER BY s ASC
SELECT count(*), date_trunc('month', to_timestamp(commit_date)) s
from snapshot
group by date_trunc( 'month', to_timestamp(commit_date) )
ORDER BY s ASC
###################################################################################################################################
## Others
###################################################################################################################################
##[2] Which rules are violated according best practices?
SELECT violated_rules, count(violated_rules)
FROM violated_rules
GROUP BY violated_rules
ORDER BY count DESC
##[3] Docker usage adoption rate according USERS/ORGANIZATIONS ?
SELECT count(*), date_trunc('year', to_timestamp(first_docker_commit)) s, i_owner_type
FROM dockerfile
group by date_trunc( 'year', to_timestamp(first_docker_commit)), i_owner_type
ORDER BY s ASC
##[6] Most used words in comments
SELECT word, count(*)
FROM (
SELECT regexp_split_to_table(comment, '\s') as word
FROM df_comment
) t
GROUP BY word
ORDER BY count DESC
##[7] Which instructions are commented more frequently?
SELECT instruction, count(instruction)
FROM df_comment NATURAL JOIN snapshot
WHERE index = true AND instruction LIKE '%before%'
GROUP by instruction
ORDER BY count DESC
##[8] Preferred source and destination of ADD and COPY instructions
SELECT source, count(source) c
FROM df_add
WHERE current=true
GROUP BY source
ORDER BY c DESC
SELECT source, count(source) c
FROM df_copy
WHERE current=true
GROUP BY source
ORDER BY c DESC
SELECT destination, count(destination) c
FROM df_copy
WHERE current=true
GROUP BY destination
ORDER BY c DESC
SELECT destination, count(destination) c
FROM df_add
WHERE current=true
GROUP BY destination
ORDER BY c DESCThere are different possibilities on how the toolchain can be executed. The tool dfa_tool.jar can be found in the /tool folder):
- Demo purpose, a default GitHub project gets analyzed
- Arguments: No parameter
- Example:
java -jar dfa_tool.jar
- Analyze a specified GitHub project that includes at least one Dockerfile
- Arguments: {Github project url} (i.g. https://github.com/raiden-network/raiden)
- Example:
java -jar dfa_tool.jar https://github.com/raiden-network/raiden
- Analyze a specified GitHub project and save results into a postgres database
- Arguments: {Github project url} -db
- Requirements: Setup a local postgres db with port
5432, usernamepostgres, passwordpostgres, and an empty database with namedfa - Example:
java -jar dfa_tool.jar https://github.com/raiden-network/raiden -db
- Analyze a specified GitHub project and save results into a json file
- Arguments: {Github project url} -json
- Hint: you find the json file in root folder of this project
- Example:
java -jar dfa_tool.jar https://github.com/raiden-network/raiden -json
Build project with mvn install