🔊 A web application to stream audio input to connected clients.
- Watch Netflix on the TV and listen with 2 pairs of wired headphones.
- A TV with an jack audio output.
- A TRRS jack audio cable.
- A smartphone with a jack audio input (e.g. an old iPhone 5).
- At least one other smartphone.
- A local network with WiFi.
- Static web page hosted on Vercel.
- QR code to pair devices.
- Stream with WebRTC (PeerJS).
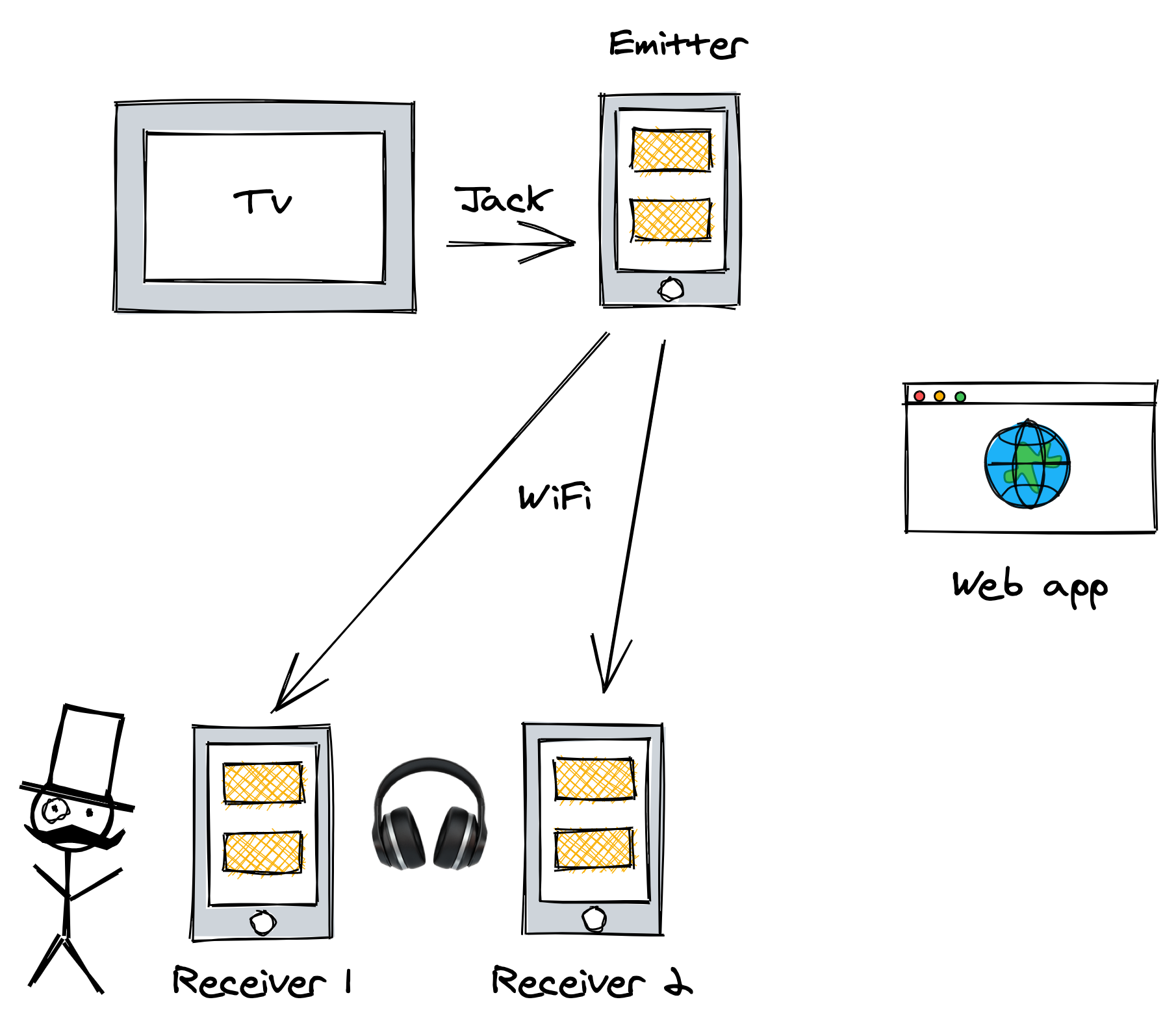
- All phones are connected to the same local network over WiFi.
- The TV outputs audio to the emitter using the TRRS jack audio cable.
- The emitter reaches the web application, opening a WebRTC session.
- The emitter displays a QR code containing a link to the web application with a session link.
- The receivers scan the QR code, reach the web application, and connect to the WebRTC session.
- The emitter listens to audio input from TV and streams it to the receivers.
- The receivers plays the audio through wired headphones.
Bluetooth is a popular protocol to stream audio wirelessly to a headset. While supported on smart TV, most TVs don't support 2 Bluetooth headsets in parallel.
A Bluetooth dongle with signal duplication capabilities along with Bluetooth headsets would replace the whole solution. However, it is never cheap, nor challenging.
The main goal is to watch Netflix on an Android TV, so the emitter could be replaced by an Android TV application, listening to internal audio, and streaming it over WiFi considering the TV is connected to the same network as the receivers. While it is smarter and requires a smaller setup, the hassle of Android development and the risk of permission issues would slow development down. Additionally, the current proposition would also work with any other audio output devices (e.g. non-Android TV), while an Android application would bind the proposition to the Android ecosystem.
Pairing in WebRTC requires a signaling server. For simplicity, PeerJS provides a public signaling server. It is only used for pairing and all the phones are already connected to internet, so the application can use it as is. While depending on a third-party service is suboptimal, it is an acceptable trade-off.