Install Miniconda
*Note for Windows: If you have previous versions of Python on your system, it may make it difficult for Anaconda/Miniconda to use the command conda. If this is the case, you have two options:
- You can choose to uninstall previous versions of Python using IObit Uninstaller
- If uninstalling previous version of Python is not an option, you can do a full Anaconda install and then use the Anaconda Prompt that gets installed with it to execute the following commands.
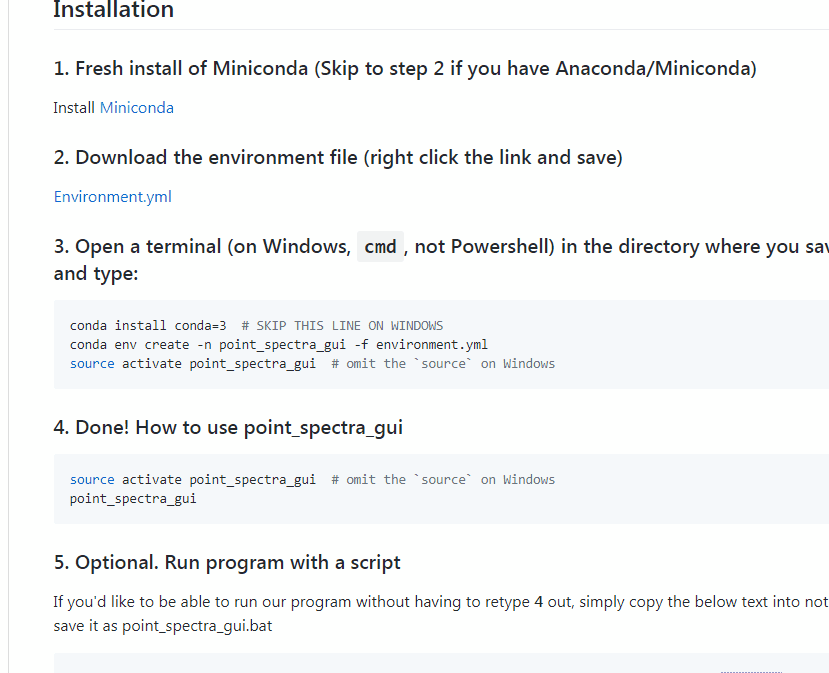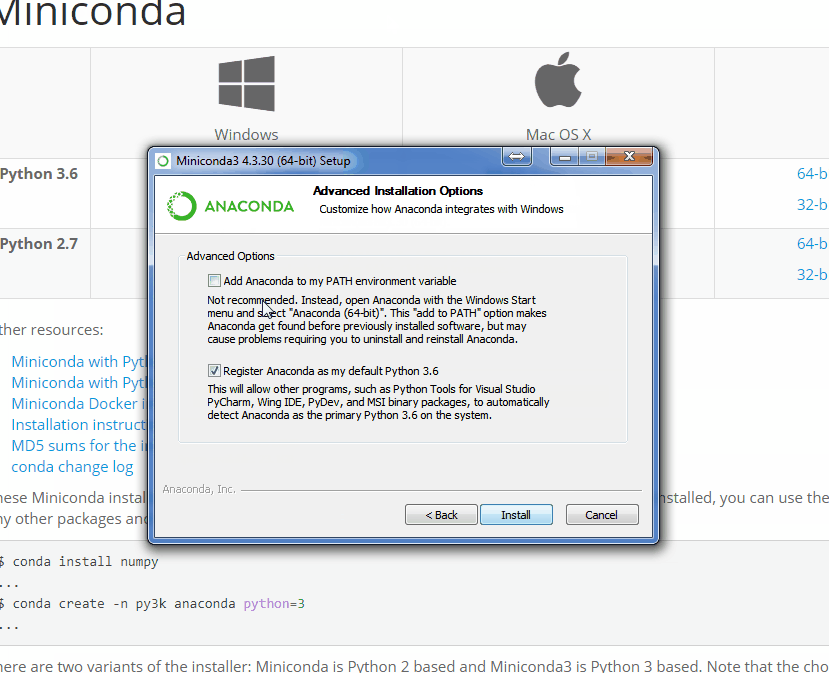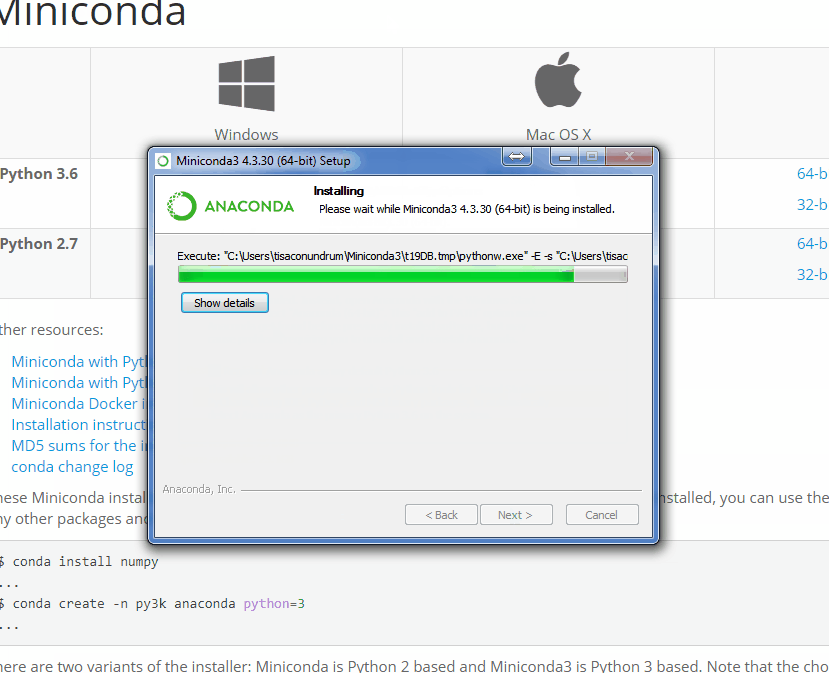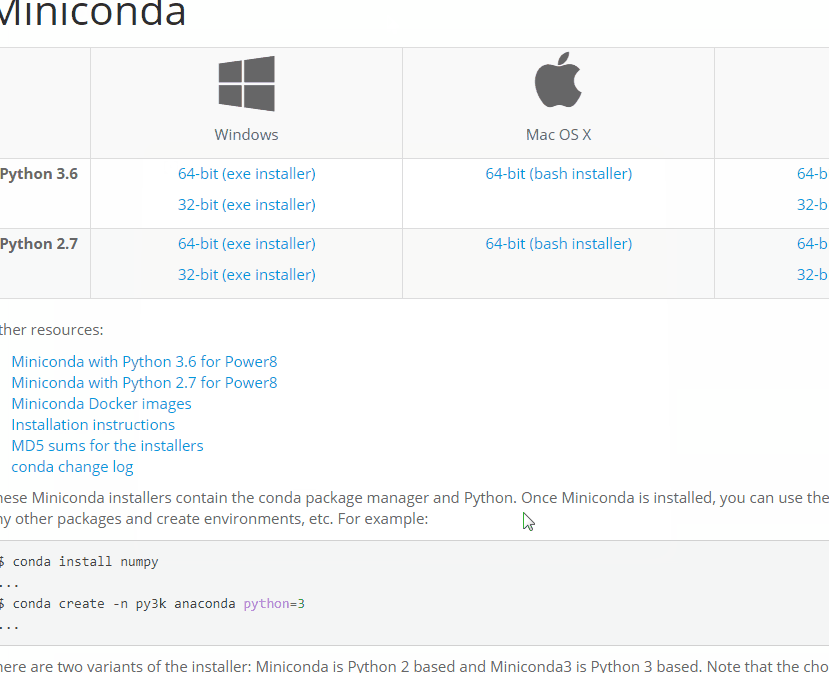
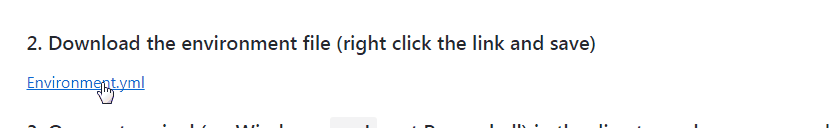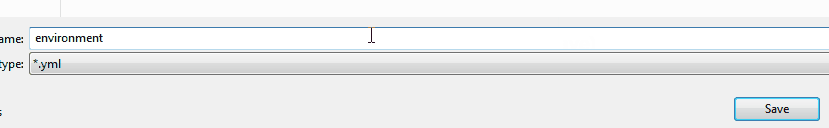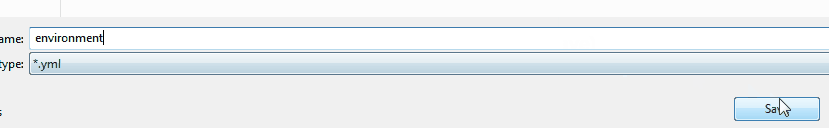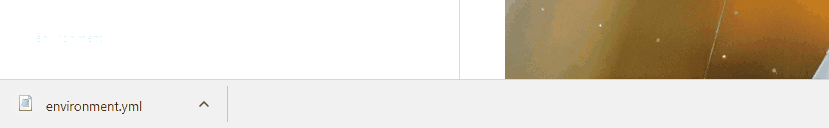
3. Open a terminal (on Windows, use the Anaconda prompt or cmd, not Powershell) in the directory where you saved the file and type:
conda --v # this will give you your version, make sure it is 4 or greater, if not use the below command
conda install conda=4 # SKIP THIS LINE ON WINDOWS
conda env create -n point_spectra_gui -f environment.yml
source activate point_spectra_gui # omit the `source` on Windowssource activate point_spectra_gui # omit the `source` on Windows
point_spectra_guiIf you'd like to be able to run our program without having to retype 4 out, simply copy the below text into notepad, and then save it as point_spectra_gui.bat
call activate point_spectra_gui
point_spectra_gui
If you already have an earlier version of the PySAT Point Spectra GUI installed as described above and you want to wipe it and update to the latest version, just do:
conda env remove -n point_spectra_guiAnd then follow the instructions above to install a fresh version.
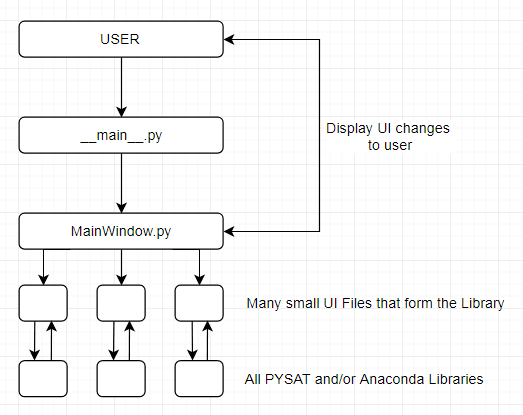
- The UI's backend is designed and created in Python with the QT framework
- The user begins by starting __main__.py.
- __main__.py will load MainWindow.py which in turn will load the splash screen and all necessary UI pieces
- MainWindow.py displays the mainframe in which the UI's submodules will be loaded into
- MainWindow.py will then foward control to each submodule of focus
- Each of the submodules build the collective UI library
- Each submodule also contains all the necessary functions that will interact with Anaconda and PYSAT
- The PYSAT and Anaconda libraries will then do the necessary data manipulations
- The values are then returned back up to the Submodule which in turn is returned back to MainWindow which will then deal with changed data