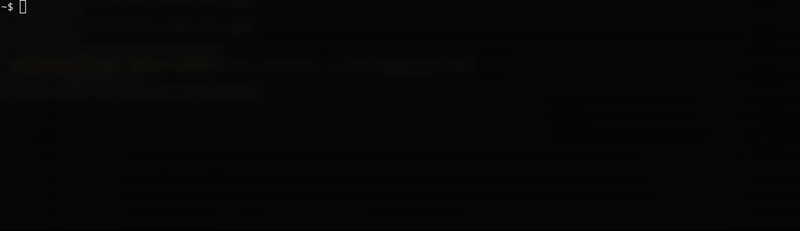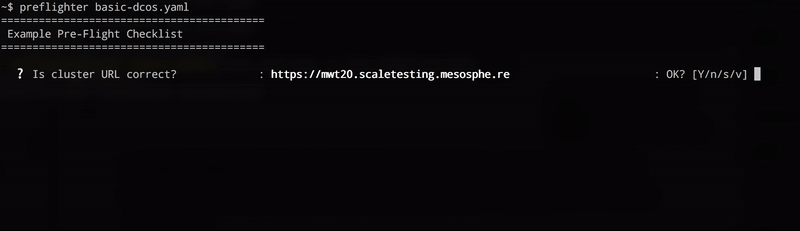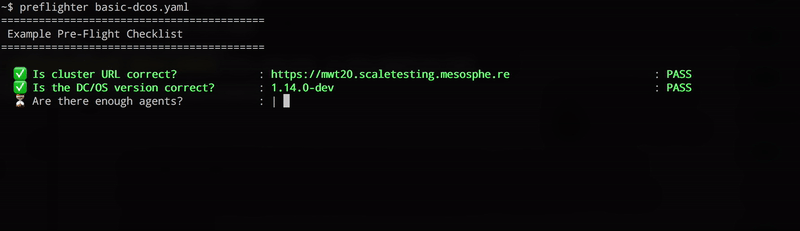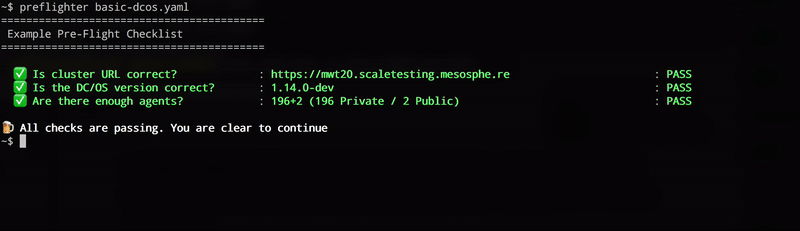preflighter
Runs interactive pre-flight checklists
Preflighter is a command-line utility that makes it simple to run small probe scripts in order to visually confirm if a list of pre-flight checks are met.
Installation
You can use go get to install the preflighter executable.
go get github.com/mesosphere-incubator/preflighterUsage
Invoke preflighter pointing to one or more checklist YAML files:
preflighter path/to/checklist.yamlThe preflighter will invoke the probe scripts for each test case and prompt the operator to visually confirm the outcome.
- Pressing
yconfirms that the value is correct - Pressing
nrejects the value and stops the test - Pressing
sskips (ignores) the value and continues with the next test - Pressing
vshows thestderroutput (useful for debugging)
If a test has failed, the operator has the chance to re-start it.
Tutorial
This short guide will help you getting started with writing your own custom checklist files.
In all of the examples we are assuming that you are saving it's contents to a checklist.yaml file in your current working directory.
1. Simple Checklist
The following checklist demonstrates a very simple checklist:
title: My Checklist
checklist:
- title: "Does the date look correct?"
script: |
dateWe are giving a title to our checklist, and we are adding a single item to the checklist array.
Each checklist script is assumed to be any valid bash script. It can be as complex as you like but it must return a single line on stdout. In our example, we are invoking the date command and we are asking the user to confirm.
You can run the checklist with preflighter checklist.yaml. This will display the following prompt:
==========================================
My Checklist Pre-Flight Checklist
==========================================
❔ Does the date look correct? : Tue Mar 31 18:38:35 CEST 2020 : OK? [Y/n/s/v]
2. Items that take long to complete
Syntax
The checklist is a YAML file with an array of checks to perform. Each check is executed under bash and it's expected to echo it's output on stdout.
The stderr output can be used for debugging or progress messages. Feel free to dump a verbose stream of messages on stderr if your probe takes a lot of time. The operator can choose to see the message when needed.
For example:
title: "Awesome Checklist"
checklist:
- title: "Is cluster URL correct?"
script: |
dcos config show core.dcos_urlReference
Each probe script is executed in a bash environment,
Functions
The following accelerator functions available in the bash environment:
-
cluster_curl[<args>] <path>: Calls-out tocurl, with the DC/OS cluster URL and authentication headers pre-populated. For example:script: | cluster_curl dcos-metadata/dcos-version.json | jq -r .version
-
cached_cluster_curl[<args>] <path>: The same ascluster_curl, but caches the output for this session. -
node_ssh<arg> <command> [<args>]: Calls-out todcos node ssh, with the correct arguments in order to avoid error messages to pollute the standard output stream:script: | local FOUND=$(node_ssh --leader ping mesosphere.io -c1 -t1 | grep -c 'not known') [ $FOUND -ne 0 ] && echo "Cannot resolve mesosphere.io" && return 1 echo "Yes (resolved mesosphere.io)"
-
cached_node_ssh[<args>] <path>: The same asnode_ssh, but caches the output for this session.
Variables
The following accelerator variables available in the bash environment:
${DCOS_URL}- The URL to the DC/OS Cluster${DCOS_ACS_TOKEN}- The Authentication token to use for logging-in to DC/OS cluster
Additional variables can be defined using the vars object in the YAML object:
vars:
TARGET_NODE: "--leader"
checklist:
- title: "Test"
script: |
node_ssh ${TARGET_NODE} ping mesosphere.io -c1 -t1