- Requirements: * Other Tools:
- Installation:
- Data preparation
- Training
- Embedding extraction
- Pretrained model
- Results
This repository contains code and models for training an x-vector speaker recognition model using Kaldi for feature preparation and PyTorch for DNN model training. MFCC feature configurations and TDNN model architecture follow the Voxceleb recipe in Kaldi (commit hash 9b4dc93c9). Training procedures including optimizer and step count are similar to, but not exactly the same as Kaldi.
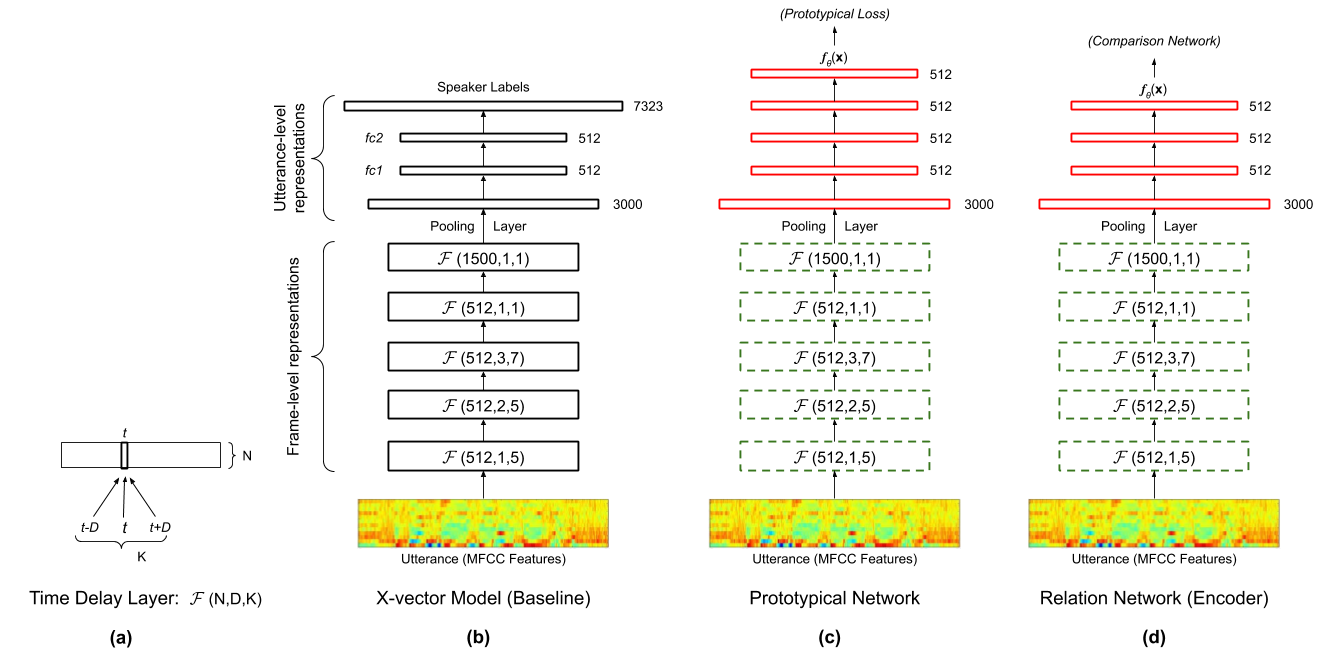
Additionally, code for training meta-learning embeddings are available in train_proto.py and train_relation.py. An overview of these models is available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.16196 and in the below figure:
If you found this toolkit useful in your research, consider citing the following:
@misc{kumar2020designing,
title={Designing Neural Speaker Embeddings with Meta Learning},
author={Manoj Kumar and Tae Jin-Park and Somer Bishop and Catherine Lord and Shrikanth Narayanan},
year={2020},
eprint={2007.16196},
archivePrefix={arXiv}
}
Python Libraries
python==3.6.10
torch==1.4.0
kaldiio==2.15.1
kaldi-python-io==1.0.4
- Spectral Clustering using normalized maximum eigengap GitHub
- Used for speaker clustering during diarization
- Diarization scoring tool GitHub
- Used for computing diarization error rate (DER)
- Install the python libraries listed in Requirements
- Install Kaldi toolkit.
- This repository is tested with commit hash
9b4dc93c9of the above Kaldi repository. - Kaldi is recommended to be installed in
$HOME/kaldi.
- This repository is tested with commit hash
- Download this repository. NOTE: Destination need not be inside Kaldi installation.
- Set the
voxcelebDirvariable inside pytorch_run.sh - (Optional) Install Other Tools listering in Requirements
- Training features are expected in Kaldi nnet3 egs format, and read using the
nnet3EgsDLclass defined in train_utils.py. - The voxceleb recipe is provided in pytorch_run.sh to prepare them.
- Extracted embeddings are written in Kaldi vector format, similar to
xvector.ark.
pytorch_run.sh script augments the training data using the following two datasets.
- Download MUSAN and extract to ./musan.
- Download RIRS_NOISES and extract to ./RIRS_NOISES.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=1 train_xent.py <egsDir>
usage: train_xent.py [-h] [--local_rank LOCAL_RANK] [-modelType MODELTYPE]
[-featDim FEATDIM] [-resumeTraining RESUMETRAINING]
[-resumeModelDir RESUMEMODELDIR]
[-numArchives NUMARCHIVES] [-numSpkrs NUMSPKRS]
[-logStepSize LOGSTEPSIZE] [-batchSize BATCHSIZE]
[-numEgsPerArk NUMEGSPERARK]
[-preFetchRatio PREFETCHRATIO]
[-optimMomentum OPTIMMOMENTUM] [-baseLR BASELR]
[-maxLR MAXLR] [-numEpochs NUMEPOCHS]
[-noiseEps NOISEEPS] [-pDropMax PDROPMAX]
[-stepFrac STEPFRAC]
egsDir
positional arguments:
egsDir Directory with training archives
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--local_rank LOCAL_RANK
-modelType MODELTYPE Refer train_utils.py
-featDim FEATDIM Frame-level feature dimension
-resumeTraining RESUMETRAINING
(1) Resume training, or (0) Train from scratch
-resumeModelDir RESUMEMODELDIR
Path containing training checkpoints
-numArchives NUMARCHIVES
Number of egs.*.ark files
-numSpkrs NUMSPKRS Number of output labels
-logStepSize LOGSTEPSIZE
Iterations per log
-batchSize BATCHSIZE Batch size
-numEgsPerArk NUMEGSPERARK
Number of training examples per egs file
-preFetchRatio PREFETCHRATIO
xbatchSize to fetch from dataloader
-optimMomentum OPTIMMOMENTUM
Optimizer momentum
-baseLR BASELR Initial LR
-maxLR MAXLR Maximum LR
-numEpochs NUMEPOCHS Number of training epochs
-noiseEps NOISEEPS Noise strength before pooling
-pDropMax PDROPMAX Maximum dropout probability
-stepFrac STEPFRAC Training iteration when dropout = pDropMax
egsDir contains the nnet3 egs files.
usage: extract.py [-h] [-modelType MODELTYPE] [-numSpkrs NUMSPKRS]
modelDirectory featDir embeddingDir
positional arguments:
modelDirectory Directory containing the model checkpoints
featDir Directory containing features ready for extraction
embeddingDir Output directory
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-modelType MODELTYPE Refer train_utils.py
-numSpkrs NUMSPKRS Number of output labels for model
The script pytorch_run.sh can be used to train embeddings on the voxceleb recipe on an end-to-end basis.
Two ways to download the pre-trained model:
- Google Drive link (or)
- Command line (reference)
wget --load-cookies /tmp/cookies.txt "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&confirm=$(wget --quiet --save-cookies /tmp/cookies.txt --keep-session-cookies --no-check-certificate 'https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1gbAWDdWN_pkOim4rWVXUlfuYjfyJqUHZ' -O- | sed -rn 's/.*confirm=([0-9A-Za-z_]+).*/\1\n/p')&id=1gbAWDdWN_pkOim4rWVXUlfuYjfyJqUHZ" -O preTrainedModel.zip && rm -rf /tmp/cookies.txt
To reproduce voxceleb EER results with the pretrained model, follow the below steps.
NOTE: The voxceleb features must be prepared using prepare_feats_for_egs.sh prior to evaluation.
- Extract
models/andxvectors/from the pre-trained archive into the installation directory - Set the following variables in pytorch_run.sh:
modelDir=models/xvec_preTrained trainFeatDir=data/train_combined_no_sil trainXvecDir=xvectors/xvec_preTrained/train testFeatDir=data/voxceleb1_test_no_sil testXvecDir=xvectors/xvec_preTrained/test - Extract embeddings and compute EER, minDCF. Set
stage=7in pytorch_run.sh and execute:bash pytorch_run.sh - Alternatively, pretrained PLDA model is available inside
xvectors/traindirectory. Setstage=9in pytorch_run.sh and execute:bash pytorch_run.sh
cd egs/
Place the audio files to diarize and their corresponding RTTM files in demo_wav/ and demo_rttm/ directories. Execute:
bash diarize.sh
| Kaldi | pytorch_xvectors | |
|---|---|---|
| Vox1-test | 3.13 | 2.82 |
| VOICES-dev | 10.30 | 8.59 |
NOTE: Clustering using https://github.com/tango4j/Auto-Tuning-Spectral-Clustering
| Kaldi | pytorch_xvectors | |
|---|---|---|
| DIHARD2 dev (no collar, oracle #spk) | 26.97 | 27.50 |
| DIHARD2 dev (no collar, est #spk) | 24.49 | 24.66 |
| AMI dev+test (26 meetings, collar, oracle #spk) | 6.39 | 6.30 |
| AMI dev+test (26 meetings, collar, est #spk) | 7.29 | 10.14 |