It is the official repository of LogicMP where MP stands for message passing. LogicMP aims to combine neural networks (semantic representations) with first-order logic (symbolic knowledge).
Note: The code for the relational graphs is included. Due to the privacy issues in Ant Group, the code for document images cannot be fully provided. Even though, I will show it is easy to reimplement.
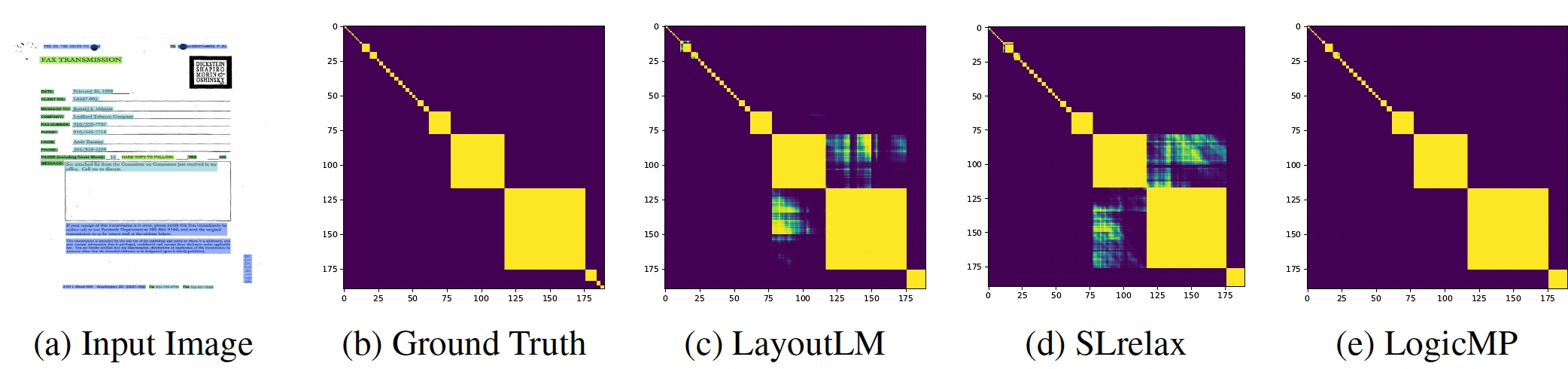
Task: Given the input image and input tokens, the task is to develop a function to predict whether two tokens coexist in a block.
Rule: If tokens
The transitivity rule is
-
$\forall i, j, k: \mathtt{C}(i, j) \wedge \mathtt{C}(j, k) \implies \mathtt{C}(i, k)$ . It means that when (i, j) coexist and (j, k) coexist, then (i, k) coexist. -
$\forall i, j, k: \neg \mathtt{C}(i, k) \wedge \mathtt{C}(j, k) \implies \neg \mathtt{C}(i, j)$ . It means that when (i, k) coexist and (j, k) don't exist, then (i, j) don't coexist. -
$\forall I, j, k: \neg \mathtt{C}(i, k) \wedge \mathtt{C}(i, j) \implies \neg \mathtt{C}(j, k)$ . It means that when (i, k) coexist and (i, j) don't exist, then (j, k) don't coexist.
The above three rules are equivalent. They are the same rule in three different statements.
Each implication corresponds to a message passing:
- msg_to_ik = einsum('bij,bjk->bik', Q[...,1], Q[...,1])
- msg_to_ij = - einsum('bjk,bik->bij', Q[...,1], Q[...,0])
- msg_to_jk = - einsum('bij,bik->bjk', Q[...,1], Q[...,0])
where b stands for dimension batchsize, Q is the marginal of size [BatchSize, #Entities, #Entities, 2] (2 for binary classification).
# logits: torch.Tensor, size=[batchsize, nentities, nentities, 2]
# niterations: int, number of iterations
cur_logits = logits.clone()
for i in range(niterations):
Q = softmax(cur_logits, dim=-1)
cur_logits = logits.clone()
# Message Aggregation for Implication ∀i, j, k : C(i, j) ∧ C(j, k) => C(i, k)
msg_to_ik = einsum(’bij,bjk->bik’, Q[...,1], Q[...,1])
# Message Aggregation for Implication ∀i, j, k : C(i, j) ∧ ¬C(i, k) => ¬C(j, k)
msg_to_jk = - einsum(’bij,bik->bjk’, Q[...,1], Q[...,0])
# Message Aggregation for Implication ∀i, j, k : C(j, k) ∧ ¬C(i, k) => ¬C(i, j)
msg_to_ij = - einsum(’bjk,bik->bij’, Q[...,1], Q[...,0])
msg = msg_to_ij + msg_to_jk + msg_to_ik
cur_logits[..., 1] += msg * weight
# Returns cur_logit
As shown in this code, any first-order logic with universal quantifier can be converted into Einsum operations, turning previous MLN inference problem into forward tensor computations in milliseconds.
Here we provide a package to parse the first-order logic and automatically convert it into the LogicMP layer.
from logicmp import *
# step 1: define the fields
token = Field('token', list(range(512)))
# step 2: define the predicates
coexist = Predicate('coexist', [token, token])
name2predicate = {'coexist': coexist}
# step 3: define the LogicMP
# rules in str
fstr = 'forall i: forall j: forall k: coexist(i, j) & coexist(i, k) -> coexist(j, k)'
# parse the rules
ftree = pyparsing_parse(fstr)
print(ftree)
# using predefined classes
formula = construct(ftree, name2predicate)
print(formula)
res = is_conjunctive_normal_form(formula)
print(res)
# to CNF
formula = formula.apply()
print(formula)
res = is_conjunctive_normal_form(formula)
print(res)
logicmp = LogicMP(formula.clauses(), 5)
logits = LayoutLM(tokens) # logits: [batchsize, entities, entities, 2]
logits = LogicMP({'token': logits})
prob = torch.nn.softmax(logits, dim=-1)